Switch-mode converters as feedback systems A B m e v o v - PDF document
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-1] Control of switch-mode converters [8-2] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Control objectives Produce control command to Regulate the output voltage Obtain zero or small
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-1] Control of switch-mode converters [8-2] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Control objectives Produce control command to • Regulate the output voltage • Obtain zero or small steady-state (DC) error • Quick response to reference changes • Fast recovery • Immunity to input and load changes • Reasonable overshoot 1
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-3] Switch-mode converters as feedback systems A B m e v o v d e f f f Power stage Compensator Modulator d v V o e • Power stage is a Switching System (non-linear) • Compensator is an analog or digital controller • Linear control theory based design small signal response [8-4] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Control of PWM converters disturbances in voltage mode 2
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-5] Voltage regulation V in ( power ) V O Duty cycle ( power ) Power stage C O R O Feedback k V O V e PWM Driver modulator error amp V ref [8-6] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies PWM modulator comp V e V V t + p v V V t v T - s V p V V t p v on V V V V e t e v T s V v Oscillator t V V on e v D on T V V D s p v 1 Practical D on max 0.8 0.9 0 V e V v V p 3
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-7] Sawtooth generator [8-8] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Transfer functions V e t D Zoom m e t d D t 4
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-9] Control of PWM converters disturbances in voltage mode v out A d v 0 d in i 0 out v out A vin v d 0 in i 0 out v out Z out v 0 i in out d 0 v dA v A i Z out d in vin out out LG 1 LG A Z K K BA t M d vin out v v v i out ref in out K 1 LG 1 LG 1 LG t [8-10] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Dynamics of feedback systems Block diagram division B S S A S + in out H P 1 - S f K LG ( f ) A B A – known (power stage + divider) B – unknown (have to be designed) 5
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-11] LoopGain test Nyquist Criterion A ( s ) A CL 1 LG ( s ) • The system is unstable if {1+LG(s)} has roots in the right half of the complex plane. • Nyquist criterion is a test for location of {1+LG(s)} roots. • Nyquist criterion is normally translated into the Bode plane (frequency domain) [8-12] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies LoopGain test db |LG| f A f f +180 In negative feedback f 0 o o systems 180 ( 180 ) At f 0 6
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-13] Bode plot db A A 1 f 180 o already substracted f 0 m -180 o o ( 180 ) 180 m | A | 1 | A | 1 [8-14] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Graphical representation of BA conventional method A [ dB ] A AB [ dB ] f [ Hz ] AB B [ dB ] B f [ Hz ] f f f 1 2 3 f [ Hz ] f f f 1 2 3 Tedious – need to re-plot BA Analysis (not design) oriented Requires iterations 7
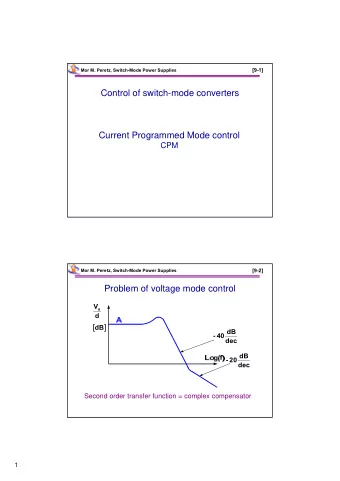
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-15] Graphical Representation of BA 1 20log A 20log 20log(BA) B 1 20logA 20log B A 1 A [ dB ] B A BA 1 LG ( f ) BA 1 B B A 1 BA 1 f o [ Hz ] [8-16] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Possible compensations V o d A dB dB 1/B - 40 dec dB Log(f) - 20 dec 1/B 1/B 8
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-17] Possible compensations o 90 o m 45 m o 90 m o 45 m o 90 1 m o 45 m 0 db dec 20 db dec A s u db db 40 s dec db 20 u 0 db dec dec s db db 20 60 dec dec f s 40 db 1 dec B db [8-18] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Overshoot and Q in Closed Loop in Response to step in S in Excitation Overshoot t ACL cos Q o m Q for 50 m sin m f Overshoot o Design target 45 m m o 50 9
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-19] Extracting the power stage control-to-output transfer function L S V o D R V C o in o E V D L in in on V o G G I D C b b on I L o V R L in o E V V E in o L in [8-20] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Linearization out V(in) I(3) V out ( ) V in ( ) I (3) R ( ( V out )) ( ( V out )) d V out ( ( )) v in ( ) i (3) ( ( )) V in ( (3)) I V out ( ) V out ( ) V out ( ) v in ( ) i (3) V in ( ) I (3) 10
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-21] SPICE Linearization (AC Analysis) out out F V(in) I(3) i ( 3 ) I ( 3 ) R o R F V ( in ) V ( in ) o F F I (3) V in ( ) 0 0 V in ( ) I (3) [8-22] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Buck linearization L in out in E V D in C b I R G I D V o in E L o L G in b E in I D L L in o out 0 V ( in ) v ( d ) d 0 V in R o V ( d ) i ( L ) C o VAC 0 R 0 V ( d ) v ( in ) I ( L ) v ( d ) V D G G b E b I in D L o V o in o 11
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-23] Possible phase compensation schemes Lag network R A f o R in 1 f p 2 C R f f [8-24] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Design example 12
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-25] Lag network 40 R2 0 out1 0V C1 100k 0V -40 10n R1 E1 db(V(out1)) 0d IN+ OUT+ V1 0V 1k IN- OUT- 1Vac EVALUE 0Vdc V(%IN+, %IN-)*1E6 -50d SEL>> -100d 10Hz 100Hz 10KHz 1.0MHz p(-V(out1)) Frequency [8-26] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Lag – Lead network 1 f 20 db dec A A ( ampl .) o OL A 0 f 2 1 f f L 2 C R f 1 A 2 f f R f A 2 R in 13
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-27] Lag-Lead network 100 R9 0V 0V 1g 50 R3 C2 out2 10k 10n 0 db(V(out2)) R4 E3 0d IN+ OUT+ V2 0V 1k IN- OUT- 1Vac EVALUE 0Vdc -50d V(%IN+, %IN-)*1E6 SEL>> -100d 10Hz 100Hz 10KHz 1.0MHz p(-V(out2)) Frequency [8-28] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Double zero compensation scheme R A 3 OL R 1 R C C 3 2 3 β 1 R R R 2 1 2 π 2 f R 2 C 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 π π π π R C R C R C R C 3 2 2 1 1 1 3 3 1 1 π 2 f R 2 C 3 β dB 20 dec 14
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-29] Double Zero 40 R8 1g C4 0V 100p 20 R7 C3 100k 10n out3 C5 R5 0 E2 db(V(out3)) 0V IN+ OUT+ 0V V3 100d 10n 1k IN- OUT- 1Vac R6 EVALUE 0Vdc V(%IN+, %IN-)*1E6 100k 0d SEL>> -100d 0 10Hz 100Hz 10KHz 1.0MHz p(-V(out3)) Frequency [8-30] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies The relationship to PID compensators v K K s ω s ω c I d z1 z2 K s K p d v s K s e I V c V e B dB V f f c Log(f) 1 2 V e Log(f) dB f f 1 2 1 / B 15
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-31] The relationship to PID compensators V o d A dB dB 1/B - 40 dec dB Log(f) - 20 dec 1/B 1/B [8-32] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies 16
Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-33] [5-34] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies 17
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.
![1 [9-4] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Current feedback loop I o L i o V o v o S V](https://c.sambuz.com/1071065/1-s.webp)

![1 Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies [8-4] Control of PWM converters disturbances in](https://c.sambuz.com/1062650/1-s.webp)



![1 [2-4] Mor M. Peretz, Switch-Mode Power Supplies Capacitor types Polarized (electrolytic) Non](https://c.sambuz.com/1065911/1-s.webp)