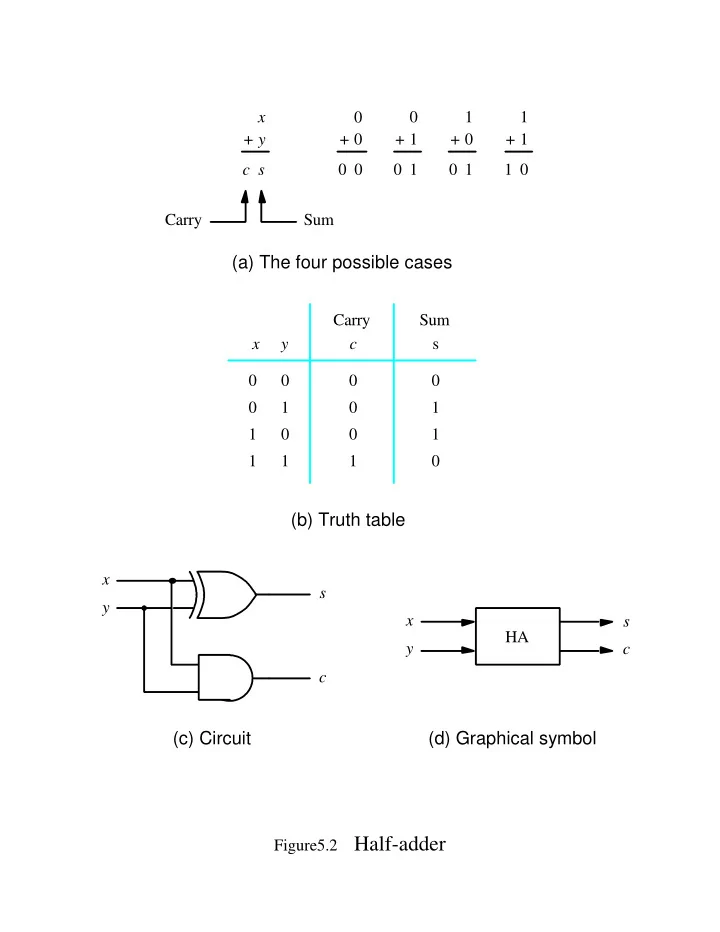

x 0 0 1 1 + y + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 c s 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 Carry Sum (a) The four possible cases Carry Sum x y c s 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 (b) Truth table x s y x s HA y c c (c) Circuit (d) Graphical symbol Figure5.2 Half-adder
x i y i c 00 01 11 10 i 1 1 0 c i x i y c s i i + 1 i 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 s = x y c ⊕ ⊕ i i i i 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 x i y i 1 0 0 0 1 c 00 01 11 10 i 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (a) Truth table c = x i y + x i c + y i c i + 1 i i i (b) Karnaugh maps x i y s i i c i c i + 1 (c) Circuit Figure5.4 Full-adder
A : a a 7 0 x x y y 7 0 7 0 c 7 s s 7 0 0 x x x y y y 8 7 0 8 7 0 c 8 s s 8 0 = 3 : P A P P P 9 8 0 (a) Naive approach A : a a 7 0 0 0 x x 1 x y y y 8 0 8 7 0 c 8 s s 8 0 : P = 3 A P P P 9 8 0 (b) Efficient design Figure5.7 Circuit that multiplies an 8-bit unsigned number by 3
Multiplicand M (14) 1 1 1 0 Multiplier Q (11) 1 0 1 1 × 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 Product P (154) 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 (a) Multiplication by hand Multiplicand M (11) 1 1 1 0 Multiplier Q (14) × 1 0 1 1 Partial product 0 1 1 1 0 + 1 1 1 0 Partial product 1 1 0 1 0 1 + 0 0 0 0 Partial product 2 0 1 0 1 0 + 1 1 1 0 Product P (154) 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 (b) Multiplication for implementation in hardware Figure5.32 Multiplication of unsigned numbers
0 m m m m 3 2 1 0 q 0 0 PP1 q 1 q 2 0 PP2 q 3 0 p p p p p p p p 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 (a) Structure of the circuit m m k + 1 k Bit of PPi m k q 0 q q j 1 c c c c FA FA out out in in (b) A block in the top row (c) A block in the bottom two rows Figure5.33 A 4 x 4 multiplier circuit
Multiplicand M (+14) 0 1 1 1 0 x Multiplier Q (+11) 0 1 0 1 1 Partial product 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 + 0 0 1 1 1 0 Partial product 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 + 0 0 0 0 0 0 Partial product 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 + 0 0 1 1 1 0 Partial product 3 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 + 0 0 0 0 0 0 Product P (+154) 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 (a) Positive multiplicand Multiplicand M ( 14) – 1 0 0 1 0 Multiplier Q (+11) 0 1 0 1 1 × Partial product 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 + 1 1 0 0 1 0 Partial product 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 + Partial product 2 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 + 1 1 0 0 1 0 Partial product 3 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 + 0 0 0 0 0 0 – Product P ( 154) 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 (b) Negative multiplicand Figure5.34 Multiplication of signed numbers
Table 5.4 The seven-bit ASCII code
Recommend
More recommend