Linking Fiscal and Debt Management Policies The Role of Debt - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Linking Fiscal and Debt Management Policies The Role of Debt Sustainability Analysis Sen Nolan International Monetary Fund December 3, 2014 Deb Sustainability Analyses The Tool Box Handling Debt Portfolio Risks Handling
Linking Fiscal and Debt Management Policies – The Role of Debt Sustainability Analysis Seán Nolan International Monetary Fund December 3, 2014
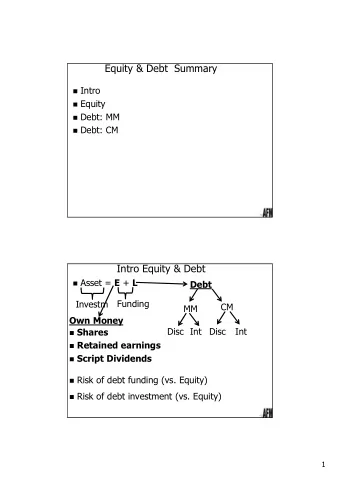
Deb Sustainability Analyses The Tool Box Handling Debt Portfolio Risks Handling Macro-Fiscal Shocks Handling Contingent Liabilities Role in Fund –Supported programs
I. Debt Sustainability Analysis The Tool Box
DSAs: Origins and Lessons LIC DSF was introduced in 2005: most recent review in 2012, joint Bank-Fund product MAC DSA was introduced in 2002, major refinements in 2011 MAC DSA 2011 review identified several areas for improvement, including: Realism of baseline assumptions Risks associated with the debt profile Analysis of macro-fiscal risks (including contingent liabilities)
Previously, for MACs the focus was mainly on debt trajectories What’s missing • Debt profile risks • Contingent liability risks • ……
Public DSAs and Debt Profile Revised DSA for MACs Public debt vulnerabilities are associated not only with the level of debt, but with its profile Debt portfolio characteristics—maturity, currency composition, and the creditor base—have received much attention in the analysis of public debt distress The Fund’s MAC DSA brings these (and other) elements together in its new risk-based approach to public debt sustainability The DSA assesses risks from the debt profile by comparing a set of indicators to early warning benchmarks
Revised DSA for MACs MAC DSA: Debt Profile Benchmarks Debt Profile Vulnerabilities (Indicators vis-à-vis risk assessment benchmarks, in 2013) example Lower early warning Upper early warning 51% 273 29% 600 15 1 45 60 bp 13% 0.5 15 20 200 5 - 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1.3% Annual Change in External Financing Public Debt Held Public Debt in Bond spread Short-Term Public Requirement by Non-Residents Foreign Currency Debt (in percent of total) (in percent of total) (in basis points) 4/ (in percent of total) (in percent of GDP) 5/
MAC DSA: Key Outputs Revised DSA for MACs Example Public DSA Risk Assessment Heat Map Real GDP Primary Real Interest Exchange Rate Contingent Debt level 1/ Growth Shock Balance Shock Rate Shock Shock Liability shock Real GDP Primary Real Interest Exchange Rate Contingent Gross financing needs 2/ Growth Shock Balance Shock Rate Shock Shock Liability Shock External Change in the Public Debt Foreign Market Debt profile 3/ Financing Share of Short- Held by Non- Currency Perception Requirements Term Debt Residents Debt Evolution of Predictive Densities of Gross Nominal Public Debt (in percent of GDP) 10th-25th 25th-75th 75th-90th Baseline Percentiles: Symmetric Distribution Restricted (Asymmetric) Distribution 160 160 140 140 120 120 100 100 80 80 60 60 Restrictions on upside shocks: 40 40 no restriction on the growth rate shock no restriction on the interest rate shock 20 20 0 is the max positive pb shock (percent GDP) no restriction on the exchange rate shock 0 0 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019
LIC External DSA Revised DSA for MACs a. Debt Accumulation b.PV of debt-to GDP ratio 70 7 45 6 35 60 5 4 50 25 3 40 2 15 1 30 5 0 -1 2013 2018 2023 2028 2033 20 -5 -2 10 -3 -15 0 Rate of Debt Accumulation 2013 2018 2023 2028 2033 Grant-equivalent financing (% of GDP) Grant element of new borrowing (% right scale) d.PV of debt-to-revenue ratio c.PV of debt-to-exports ratio 300 250 250 200 200 150 150 100 100 50 50 0 0 2013 2018 2023 2028 2033 2013 2018 2023 2028 2033 e.Debt service-to-exports ratio f.Debt service-to-revenue ratio 40 40 35 35 30 30 25 25 20 20 15 15 10 10 5 5 0 0 2013 2018 2023 2028 2033 2013 2018 2023 2028 2033 Baseline Most extreme shock 1/ Threshold Historical scenario Sources: Country authorities; and staff estimates and projections. 1/ The most extreme stress test is the test that yields the highest ratio in 2023. In figure b. it corresponds to a One-time depreciation shock; in c. to a Exports shock; in d. to a One-time depreciation shock; in e. to a Exports shock and in figure f. to a Exports shock
Revised DSA for MACs DSA for LICs: Times are a changing for some For most LICs, debt portfolio management is “passive” as debt managers have less influence over the design of the debt portfolio composition than in MACs But changing financing landscape and more market access is highlighting the relevance of debt portfolio risks Improving public debt management capacity in LICs remains a priority The Joint IMF/WB Debt Management Facility (DMF II) will make important contributions in this regard
II. Contingent Liability Risks
Revised DSA for MACs Contingent Liability (CL) Risks in DSAs Risks from contingent liabilities should inform both fiscal and debt management policies and strategies Analysis of the risks posed by CLs has become important for the assessment of public debt sustainability Assessment of banking sector CL is now an integral part of the MAC DSA But depending on country circumstances, other types of contingent liability risks may be also relevant
Revised DSA for MACs Contingent Liability (CL) Risks in MAC DSAs
Revised DSA for MACs Contingent Liability (CL) Risks in LICs In LICs large public investments needs cannot all be financed by public debt without jeopardizing debt sustainability Public private partnership (PPP) arrangements offer burden sharing with the private sector, but also exposes public sector to fiscal risks
III. DSAs in Fund-Supported Programs
Revised DSA for MACs DSAs in Fund-Supported Programs In Fund programs debt conditionality is generally expected when a country has significant debt vulnerabilities For countries using the LIC DSF, debt vulnerabilities is informed by the assessed risk of external debt distress or, where relevant, by the assessed overall risk of debt distress For countries using the MAC DSA debt vulnerabilities is assessed by the set of standard indicators in the MAC DSA
Useful Links on IMF’s Website Guidance Note on DSA for Market-Access Countries: http://www.imf.org/external/np/pp/eng/2013/050913.pdf Guidance Note on the Joint Bank-Fund Debt Sustainability Framework for Low-Income Countries: http://www.imf.org/external/np/pp/eng/2013/110513.pdf IMF’s online DSAx course: http://www.imf.org/external/mmedia/view.aspx?vid=333511 5563001 https://www.edx.org/course/debt-sustainability-analysis- imfx-dsax#.VH3WC4UhAyp
Thank you
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.