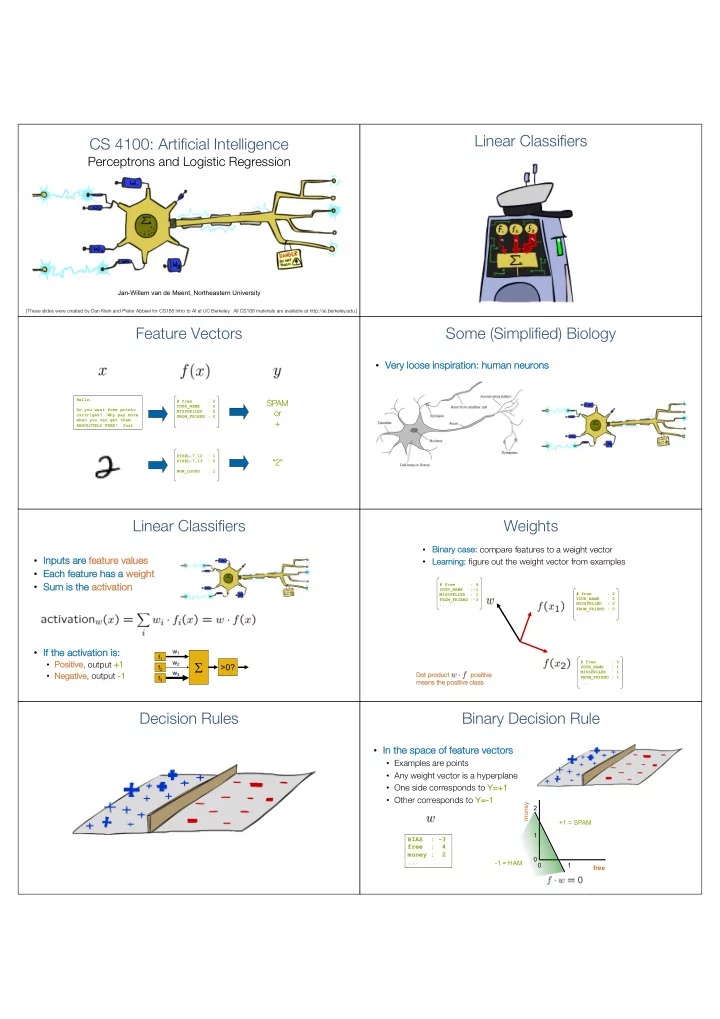

Linear Classifiers CS 4100: Artificial Intelligence Perceptrons and Logistic Regression Jan-Willem van de Meent, Northeastern University [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] Feature Vectors Some (Simplified) Biology • Ve Very loose se insp spiration: human neurons Hello, # free : 2 SPAM SP YOUR_NAME : 0 Do you want free printr or or MISSPELLED : 2 cartriges? Why pay more FROM_FRIEND : 0 when you can get them + ... ABSOLUTELY FREE! Just PIXEL-7,12 : 1 “2 “2” PIXEL-7,13 : 0 ... NUM_LOOPS : 1 ... Linear Classifiers Weights • Bi Bina nary case: compare features to a weight vector • In Inputs s are fe feature values ng: figure out the weight vector from examples • Le Learni ning • Ea Each feature has s a we weight • Su Sum is the act activat ation # free : 4 YOUR_NAME :-1 # free : 2 MISSPELLED : 1 FROM_FRIEND :-3 YOUR_NAME : 0 MISSPELLED : 2 ... FROM_FRIEND : 0 ... • If If the activa vation is: s: w 1 f 1 ve , output +1 w 2 S • Po Positive +1 # free : 0 >0? f 2 YOUR_NAME : 1 w 3 MISSPELLED : 1 • Ne Negative , output -1 Do Dot t pr produ duct t po positive itive f 3 FROM_FRIEND : 1 me means the positive class ... Decision Rules Binary Decision Rule • In In the sp space of feature ve vectors • Examples are points • Any weight vector is a hyperplane • One side corresponds to Y= Y=+1 • Other corresponds to Y= Y=-1 money 2 +1 = SPAM 1 BIAS : -3 free : 4 money : 2 0 ... -1 = HAM 0 1 free
Weight Updates Learning: Binary Perceptron Start with we • St weights = = 0 • Fo For each training instance: • Cl Classify with current weights • If If co correct ect: (i.e., y=y*), no change! • If If wrong: adjust the weight vector Learning: Binary Perceptron Examples: Perceptron • St Start with we weights = = 0 • Separable Case • Fo For each training instance: • Cl Classify with current weights • If If co correct ect: (i.e., y= y=y* y* ), no change! • If If wrong: adjust the weight vector by adding or subtracting the feature vector. Subtract if y* y* is -1 . Multiclass Decision Rule Learning: Multiclass Perceptron • St Start with all we weights = = 0 • If If we e hav ave e multiple e cl clas asses es: • Pi Pick training examples one by one • A we weig ight vector for each class: • Pr Predi dict with current weights • Sc Score (activation) of a class y: • If If c correct: no change! • If If wr wrong: lower score of wrong answer, raise score of right answer • Prediction with hi highe ghest st sc scor ore wins Binary = multiclass where the negative class has weight zero Example: Multiclass Perceptron Example: Multiclass Perceptron Question: What will the weights w be for each class after 3 updates? Qu Qu Question: What will the weights w be for each class after 3 updates? w sp sports f( x 1 ) = 1 y 1 = “p “politics” , x 1 = “wi “win the vote” y 1 = “p “politics” , x 1 = “wi “win the vote” Pr Prediction: y 2 = “p “politics” , x 2 = “wi “win the election” y 2 = “p “politics” , x 2 = “wi “win the election” w po politics f( x 1 ) = 0 “s “sports” (wr (wrong) y 3 = “s “sports” , x 3 = “wi “win the game” ” y 3 = “s “sports” , x 3 = “wi “win the game” ” w te tech f( x 1 ) = 0 BIAS : 1 BIAS : 0 BIAS : 0 1 BIAS : 1 - 1 BIAS : 0 + 1 BIAS : 0 win : 0 win : 0 win : 0 1 win : 0 - 1 win : 0 + 1 win : 0 game : 0 game : 0 game : 0 f( x 1 ) = 0 game : 0 - 0 game : 0 + 0 game : 0 vote : 0 vote : 0 vote : 0 1 vote : 0 - 1 vote : 0 + 1 vote : 0 the : 0 the : 0 the : 0 1 the : 0 - 1 the : 0 + 1 the : 0 ... ... ... ... ... ...
Example: Multiclass Perceptron Example: Multiclass Perceptron Qu Question: What will the weights w be for each class after 3 updates? Qu Question: What will the weights w be for each class after 3 updates? y 1 = “p “politics” , x 1 = “wi “win the vote” w sp sports f( x 1 ) = -2 y 1 = “p “politics” , x 1 = “wi “win the vote” w sp sports f( x 1 ) = -2 Pr Prediction: Prediction: Pr w po politics f( x 1 ) = 3 w po politics f( x 1 ) = 3 y 2 = “p “politics” , x 2 = “wi “win the election” “politics” “p y 2 = “p “politics” , x 2 = “wi “win the election” “p “politics” (c (correct) (wrong) (wr y 3 = “s “sports” , x 3 = “wi tech f( x 1 ) = -3 y 3 = “s “sports” , x 3 = “wi tech f( x 1 ) = -3 “win the game” ” w te “win the game” ” w te 1 BIAS : 0 BIAS : 1 BIAS : 0 1 BIAS : 0 + 1 BIAS : 1 - 1 BIAS : 0 1 win : -1 win : 1 1 win : -1 + 1 win : 1 win : 0 - 1 win : 0 f( x 2 ) = 0 f( x 3 ) = 1 game : 0 game : 0 game : 0 game : 0 + 1 game : 0 - 1 game : 0 0 vote : -1 vote : 1 vote : 0 0 vote : -1 + 0 vote : 1 - 0 vote : 0 1 the : -1 the : 1 1 the : -1 the : 1 the : 0 + 1 - 1 the : 0 ... ... ... ... ... ... Example: Multiclass Perceptron Properties of Perceptrons Qu Question: What will the weights w be for each class after 3 updates? Separable • Se Separability: y: tr true if there exists weights w w that get the training set perfectly correct y 1 = “p “politics” , x 1 = “wi “win the vote” y 2 = “p “politics” , x 2 = “wi “win the election” • Co Conv nvergenc nce: if the training data are se separable , a perceptron will eventually converge (binary case) y 3 = “s “sports” , x 3 = “wi “win the game” ” δ • Mistake ke Bound: the maximum number of mistakes (updates) Non-Separable (binary case) is related to the num number of featur ures k BIAS : 1 BIAS : 0 BIAS : 0 and the ma margin δ or degree of separability win : 0 win : 0 win : 0 game : 1 game : -1 game : 0 vote : -1 vote : 1 vote : 0 the : 0 the : 0 the : 0 ... ... ... Problems with the Perceptron Improving the Perceptron • No Noise: if the data isn’t separable, weights might thrash • Av Averaging weight vectors over time can help (averaged perceptron) • Med Mediocr cre e gen ener eral alizat ation: finds a “barely” separating solution • Ov Overtraining: te test t / held-ou out t accuracy usually rises, then falls • Overtraining is a kind of overfitting Non-Separable Case: Deterministic Decision Non-Separable Case: Probabilistic Decision Even the best linear boundary makes at least one mistake 0.9 | 0.1 0.7 | 0.3 0.5 | 0.5 0.3 | 0.7 0.1 | 0.9
How to get probabilistic decisions? Best w? • Pe Perceptron on scor orin ing: g: • Maximum like kelihood estimation: z = w · f ( x ) • If If very po positive à want probability going to 1 z = w · f ( x ) X log P ( y ( i ) | x ( i ) ; w ) max ll ( w ) = max • If If very ne negative ive à want probability going to 0 z = w · f ( x ) w w i • Sigmoid Sigmoid fu function ion 1 P ( y ( i ) = +1 | x ( i ) ; w ) = with wi th: 1 + e − w · f ( x ( i ) ) 1 φ ( z ) = 1 P ( y ( i ) = − 1 | x ( i ) ; w ) = 1 − 1 + e − z 1 + e − w · f ( x ( i ) ) Th This is is is calle lled Lo Logis istic ic Regressio ion Separable Case: Deterministic Decision – Many Options Separable Case: Probabilistic Decision – Clear Preference 0.7 | 0.3 0.5 | 0.5 0.7 | 0.3 0.3 | 0.7 0.5 | 0.5 0.3 | 0.7 Multiclass Logistic Regression Best w? • Re Recall Perceptron: n: • Maximum like kelihood estimation: • A we weig ight vector for each class: X log P ( y ( i ) | x ( i ) ; w ) Score (activation) of a class y: max ll ( w ) = max • Sc w w • Prediction with hi highe ghest st sc scor ore wins ns i e w y ( i ) · f ( x ( i ) ) • Ho How w to tur urn n sc scores s in into pr proba babi bilities? ? P ( y ( i ) | x ( i ) ; w ) = wi with th: y e w y · f ( x ( i ) ) P e z 1 e z 2 e z 3 z 1 , z 2 , z 3 → e z 1 + e z 2 + e z 3 , e z 1 + e z 2 + e z 3 , e z 1 + e z 2 + e z 3 Th This is is is calle lled Mu Multi-Cl Class L ss Logist stic R Regressi ssion original activations softmax activations Next Lecture • Op Opti timizati tion • i.e., how do we solve: X log P ( y ( i ) | x ( i ) ; w ) max ll ( w ) = max w w i
Recommend
More recommend