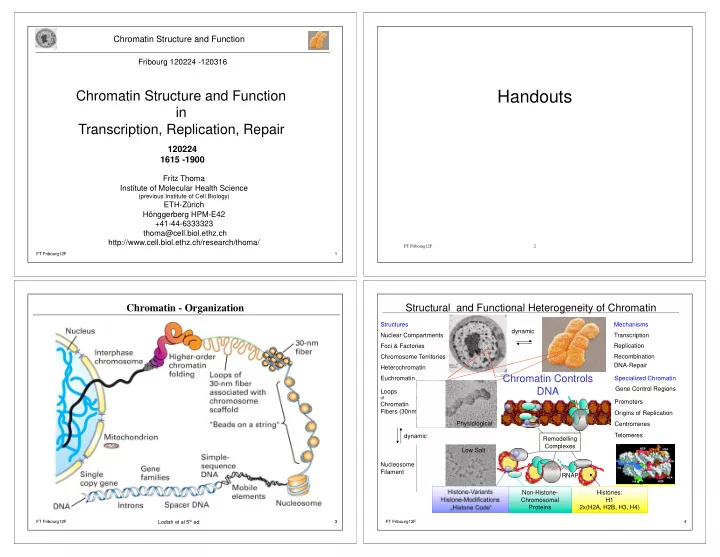

Chromatin Structure and Function Fribourg 120224 -120316 Handouts Chromatin Structure and Function in Transcription, Replication, Repair 120224 1615 -1900 Fritz Thoma Institute of Molecular Health Science (previous Institute of Cell Biology) ETH-Zürich Hönggerberg HPM-E42 +41-44-6333323 thoma@cell.biol.ethz.ch http://www.cell.biol.ethz.ch/research/thoma/ FT Fribourg12F � 2 � FT Fribourg12F � 1 � Chromatin - Organization � Structural and Functional Heterogeneity of Chromatin Structures Mechanisms dynamic Transcription Nuclear Compartments Foci & Factories Replication Chromosome Territories Recombination DNA-Repair Heterochromatin Chromatin Controls Euchromatin Specialized Chromatin Gene Control Regions DNA Loops of Promoters Chromatin Fibers (30nm) Origins of Replication Physiological Centromeres Telomeres dynamic Remodelling Complexes H2B Low Salt H2A H2B Nucleosome H3 Filament RNAP H2A H2B H4 Histone-Variants Non-Histone- Histones: Histone-Modifications Chromosomal H1 „Histone Code“ Proteins 2x(H2A, H2B, H3, H4) FT Fribourg12F � Lodish et al 5 th ed 3 � FT Fribourg12F � 4 �
Chromatin Structures Locus Specific Heterogeneity in Structure and Function Genome-wide patterns of histone modifications in yeast. Millar, C.B., and Grunstein, M. (2006). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7 , 657-666. � FT Fribourg12F � 5 � FT Fribourg12F � 6 � Chromatin Structure and Function Chromatin Structure and Function Focus Chromatin ? � Chromatin Structure s Transcription Replication Repair Recombination Aims Concepts - Facts – Fiction Terms, Keywords Key Experiments Approaches Methods "Feeling for Chromatin" Motivation to Read Chromatin Papers www.tropechopf.ch � www.tropechopf.ch � FT Fribourg12F � 7 � FT Fribourg12F � 8 �
Chromatin Structure and Function Chromatin Definition and Composition Definition When and where is chromatin made? � • Ready stainable material in nuclei, substance of chromosomes (W. Flemming, 1880) • The packaged state of eukaryotic genomes (in nuclei and chromosomes) • (Not correct: chromatin = nucleosomes) Composition • DNA • Histone Proteins • "linker histones" H1 • "core histones" H2A H2B H3 H4 • "histone variants" with specific functions • Non-Histone-Chromosomal Proteins (NHCPs) • with various structural and functional roles • RNA • nascent RNAs during transcription • structural RNAs (involved in silencing) Stoichiometry • DNA : histones = 1 : 1 (w/w); NHCP, RNA variable • H1 : H2A : H2B : H3: H4 = 1 : 2 : 2 : 2 : 2 Heterogeneity in structure and composition • Locus dependent • Time dependent (µs – minutes – hours – years – generations) FT Fribourg12F � 9 � FT Fribourg12F � 10 � Replication of Chromatin Genome – Organization � CdkC = Cyclin dependent kinase- Complex = heterodimer Cdk+cyclin APC = Anaphase Promoting Complex chromatin Lodish 13-02 Lodish et al 5 th ed FT Fribourg12F � 11 � FT Fribourg12F � 12 �
Genome - Organization � Chromatin How are genomes packaged in nuclei & metaphase is chromosomes � to allow precise and accurate � Complex expression of genes � Fascinating douplication and segregation of genomes � Multidisciplinary repair of DNA damage � ? � Lodish et al 5 th ed FT Fribourg12F � 14 � FT Fribourg12F � 13 � Chromatin Structure and Function Chromatin Structure and Function cell biology Molecular Life Science lampbrush chromosome � disease � Immunofluorescence � FISH � polytene chromosomes � in vivo � in vitro � cancer � metaphase EM � interphase chromosomes � silencing chromosomes � phenotype genomics FISH � biochemistry (reverse-) genetics biophysics molecular biology epi-genomics Immuno repair foci replication foci fluorescence � DAPI � systems biology Immuno fluorescence � Immuno fluorescence � repair foci Immuno transcription foci fluorescence � "factories" � Lodish 5e-1-12 Lodish 5e-1-12 FT Fribourg12F � 15 � FT Fribourg12F � 16 �
Basic Chromatin Concepts Chromatin � Precisely Coordinated in Time and Space Protection Assembly - Disassembly Enzymes Accessibility Interactions Multi- Protein Felsenfeld, G. and Groudine, M. (2003) Nature 421, 448-453. � Turnover Proteins Complexes T Synthesis - Degradation B TFI P IB Protein Modifications RNA Protein – DNA Polymerase II DNA Structures Interactions RNA – Protein Interactions Structures Protein – Protein DNA Modifications Interactions RNA – DNA Interactions FT Fribourg12F � 17 � FT Fribourg12F � 18 � DNA Nature 421, 421-422. � FT Fribourg12F � 19 � FT Fribourg12F � 20 �
Remember DNA ? Different Forms of Double Stranded DNA � „Normal“- B-Form DNA In vitro: In vivo: 3' � 5' � 3' � 5' � • PCR • Helicases • Hybridizations • Transcription • Identification of DNA • Replication sequences with probes • Recombination 5' � 3' � • FISH (fluoresence in situ (homologous) hybridization) • DNA Repair 5' � 3' � negatively charged � Denaturation ("melting") Renaturation, Hybridization Formamide Temp Urea < Tm http://www.fli-leibniz.de/IMAGE_DNA_MODELS.html FT Fribourg12F � 21 � FT Fribourg12F � 22 � Chromatin Structure and Function DNA-Flexibility and DNA-Bending � Loops of Double DNA structure containing a Stranded DNA � junction between left-handed Z-DNA and right-handed Chromatin Structures B-DNA. Ha et al. Nature 437, 1183-6 (2005). Packaging Genomes The solution structure and dynamics of the complex of a dimeric lac repressor DNA binding domain with nonspecific DNA . The same set of residues can switch roles from a purely electrostatic interaction with the How much DNA? DNA backbone in the nonspecific complex to a highly specific binding mode with the base pairs of the cognate operator sequence. The protein-DNA interface of the nonspecific complex is flexible on biologically relevant time scales that may assist in the rapid and efficient finding of the target site. � Kalodimos et al.(2004). Science 305 , 386-389. FT Fribourg12F � 23 � FT Fribourg12F � 24 �
Packaging Genomes Packaging Genomes Space Questions � Volume of the DNA? Volume of the chromatin? Alberts A8-6 � Volume between chromatin ("interchromatin" space")? (Ball 2003, Nature) � 1 bp =1.077*10 -9 pg � 10 -3 pg � 10 -2 pg � 0.1 pg � 1pg � 10pg � 100pg � FT Fribourg12F � 25 � FT Fribourg12F � 26 � How many chromosomes per cell? � How many chromosomes per cell? Genetic Approach � Genetic Map - „Linkage“ Map“ Isolation of Metaphase Chromosomes Meiotic recombination Interphase between decondensed homologous chromosomes chromosomes Replication The closer two loci, the lower the frequency of recombination Metaphase Colchicine Map Unit (m.u.): The distance condensed Karyotype: (colcemid) chromosomes Number, sizes, and shapes of the entire set of between two linked gene pairs binds metaphase chromosomes of a eukaryotic cell tubulin and where 1 percent of the Segregation prevents products of meiosis are their recombinant = a unit of polymeri- distance in a linking map. zation (also known as centi-Morgan, Lodish 5e-9-45 cM). Lodish 5e-1-12 Method: Chromosome painting by FISH FT Fribourg12F � 27 � FT Fribourg12F � 28 �
How Many DNA Molecules per Eukaryotic Chromosome? � Baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae 1. Cells were imbedded in Nuclei agarose 2. Digested with Zymolyase, 16 linkage groups protease, RNAse Small genome 3.Pulsed-Field-Agarose- Small chromosomes Electrophoresis 4. Gel stained with Ethidium Karyotyping is not possible Bromide The DNA of yeast chromosomes can be physically separated by electrophoresis 16 bands correspond to 16 linkage groups Yeast chromosomes contain one linear ds DNA FT Fribourg12F � 29 � FT Fribourg12F � 30 � Chromosome Territories Localization of genes (DNA sequences) on chromosomes of higher eukaryotes � Metaphase Metaphase Metaphase Chromosome Interphase Nucleus (not shown) � A7-18/19FISH FISH (Fluorescence-In-Situ-Hybridisierung) 1. Immoblize and fix on cover slip DAPI-Staining FISH FISH Color Set 2. Denature DNA (high pH) Interphase Chromosome Territories 3. Hybridize with fluorescently labeled probes or detect probes with fluorescent antibodies against probes 4. Stain DNA unspecifically with DAPI Multicolor FISH 5. Detect probes by fluoresence microscopie Chicken Chromosomes and Nuclei Chromosome-Painting by Multicolor FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) FT Fribourg12F � Cremer, T. and Cremer, C. (2001) Nat Rev Genet , 2, 292-301. FT Fribourg12F � 31 � 32 �
Recommend
More recommend