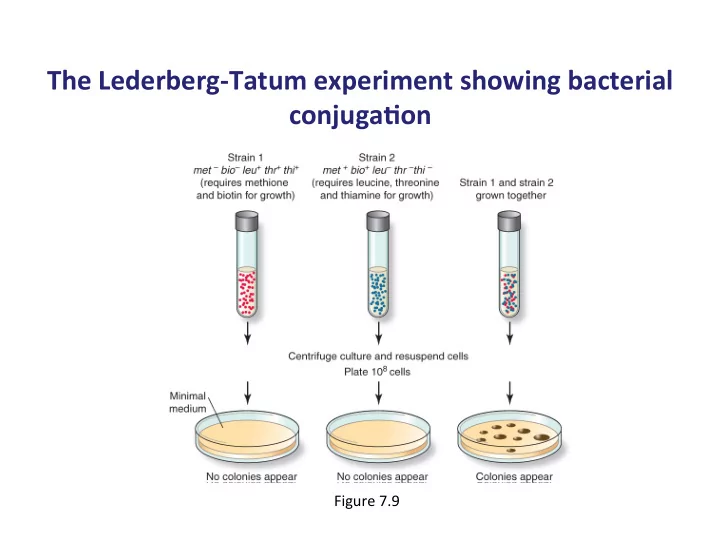

The ¡Lederberg-‑Tatum ¡experiment ¡showing ¡bacterial ¡ conjuga9on ¡ ¡ Figure ¡7.9 ¡
Table 6.2
Figure 10.16 IS 3 ¡ Tn 1000 ¡ 99.2kbp/0 ¡ tra ¡ region ¡ IS 3 ¡ IS 2 ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡ 75 ¡kbp ¡ 25 ¡kbp ¡ oriT ¡ 50 ¡kbp ¡ oriV ¡
Figure 10.17 Pilus ¡with ¡ aFached ¡ phage ¡virions ¡
Figure ¡11: ¡F ¡pili ¡connec2ng ¡ma2ng ¡ E. ¡coli ¡ cell. ¡ Photo ¡courtesy ¡of ¡Professor ¡Ron ¡Skurray, ¡School ¡of ¡Biological ¡Sciences, ¡ University ¡of ¡Sydney ¡
Figure 10.15 Host ¡ ¡ chromosome ¡ Lysogenized ¡ cell ¡ Galactose ¡ genes ¡of ¡ Phage ¡DNA ¡ host ¡DNA ¡ Induc9on ¡ Rare ¡event: ¡ Normal ¡event: ¡ A ¡por9on ¡of ¡ Phage ¡DNA ¡ host ¡DNA ¡is ¡ circularizes ¡ exchanged ¡for ¡ and ¡detaches ¡ phage ¡DNA ¡ from ¡host ¡DNA ¡ Detached ¡ DNA ¡ replicates ¡ Phage ¡replica9on ¡ is ¡completed. ¡ Cell ¡lyses ¡ Normal ¡ Defec9ve ¡phage ¡ phage ¡ that ¡can ¡transduce ¡ galactose ¡genes ¡
Protein ¡complexes ¡encoded ¡ by ¡ ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡genes ¡ Figure ¡7.12 ¡ Adapted ¡from ¡L. ¡S. ¡Frost, ¡et ¡al., ¡ Nat. ¡Rev. ¡Microbiol . ¡3 ¡(2005): ¡722-‑732. ¡
The ¡relaxosome ¡ Figure ¡7.13 ¡
Figure ¡10: ¡Conjugal ¡transfer ¡of ¡DNA ¡mediated ¡by ¡bacterial ¡sex ¡plasmids. ¡
Figure 10.18 Bacterial ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡ chromosome ¡ Pilus ¡ F + ¡cell ¡ F -‑ ¡cell ¡ Pilus ¡retracts ¡ (donor) ¡ (recipient) ¡ Donor ¡ Retained ¡strand ¡ Cell ¡pairs ¡stabilized. ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡nicked ¡in ¡one ¡strand ¡ DNA ¡polymerase ¡ Unwinding ¡protein ¡ (Tral) ¡ Transfer ¡of ¡one ¡strand ¡from ¡F + ¡cell ¡to ¡F -‑ ¡cell. ¡ Primer ¡ Plasmid-‑encoded ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡simultaneously ¡replicated ¡in ¡F + ¡cell ¡ membrane ¡proteins ¡ Cell ¡walls ¡ Specific ¡outer ¡ membrane ¡protein ¡ of ¡recipient ¡ Synthesis ¡of ¡complementary ¡strand ¡ begins ¡in ¡recipient ¡cell ¡ Donated ¡strand ¡ DNA ¡polymerase ¡ Primer ¡ Recipient ¡ Comple9on ¡of ¡DNA ¡transfer ¡ and ¡synthesis. ¡Cells ¡separate ¡ F + ¡cell ¡ F + ¡cell ¡
Figure 10.19 oriT ¡ rep ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡ tra ¡ IS 3 ¡ Recombina9on ¡ pro ¡ lac ¡ Chromosome ¡ IS 3 ¡ oriT ¡ IS 3 ¡ rep ¡ tra ¡ IS 3 ¡ lac ¡ pro ¡
Figure 10.20 Transfer ¡to ¡F -‑ ¡recipient ¡ oriT ¡ rep ¡ IS 3 ¡ pro ¡ tra ¡ leu ¡ thr ¡ IS 3 ¡ Inserted ¡ F ¡plasmid ¡ lac ¡ Chromosome ¡ gal ¡ arg ¡ trp ¡ his ¡
In ¡an ¡ ¡ Hfr ¡X ¡F -‑ ¡ma9ng, ¡ ¡ part ¡of ¡the ¡chromosome ¡is ¡ transferred ¡ ¡ Hfr ¡cells ¡have ¡the ¡F ¡plasmid ¡ integrated ¡into ¡the ¡chromosome ¡ and ¡are ¡males. ¡Recipient ¡cells ¡ usually ¡remain ¡female. ¡ ¡
Time-‑of-‑entry ¡curves ¡ can ¡be ¡used ¡to ¡derive ¡ a ¡linear ¡map ¡of ¡gene ¡ order ¡ ¡
Hfr ¡mapping ¡was ¡used ¡ to ¡generate ¡an ¡ extensive ¡gene9c ¡map ¡ of ¡ E. ¡coli ¡ Figure ¡7.16 ¡
Recommend
More recommend