
EE-452 13 - 1
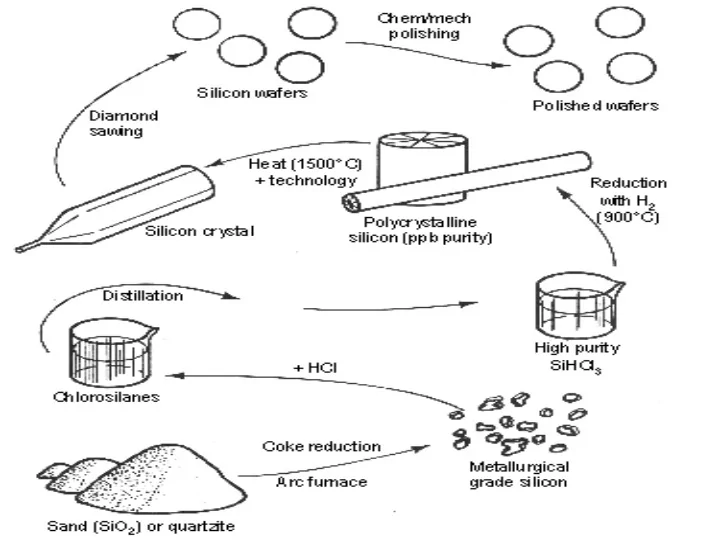
Czochralski (CZ) crystal growing • Si is purified from SiO2 (sand) by refining, distillation and CVD. • It contains < 1 ppb impurities. Pulled crystals contain O ( ~ 1018 EE-452 13 - 2 Plummer cm-3) and C ( ~ 1016 cm-3), plus dopants placed in the melt.
CZ Crystal Puller Crystal puller and rotation Crystal seed mechanism Molten Single polysilicon crystal silicon Quartz Heat shield crucible Carbon heating Water jacket element Plummer Figure 4.10 EE-452 13 - 3
• All Si wafers come from “Czochralski” grown crystals. • Polysilicon is melted, then held just below 1417 °C, and a single crystal seed starts the growth. • Pull rate, melt temperature and rotation rate control the growth lummer EE-452 13 - 4
lummer EE-452 13 - 5
Silicon Ingot Grown by CZ Method Photograph courtesy of Kayex Corp., 300 mm Si ingot Photo 4.1 lummer EE-452 13 - 6
EE-452 13 - 7
An alternative process is the “Float Zone” process which can be used for refining or single crystal growth. Plummer EE-452 13 - 8
Float Zone Crystal Growth Gas inlet (inert) Chuck Polycrystalline Molten zone rod (silicon) Traveling RF RF coil Seed crystal Chuck Inert gas out lummer Figure 4.11 EE-452 13 - 9
• In the float zone process, dopants and other impurities are rejected by the regrowing silicon crystal. Impurities tend to stay in the liquid and refining can be accomplished, especially with multiple passes. (See the Plummer for models of this process) EE-452 13 - 10
Ingot Diameter Grind Preparing crystal ingot for grinding Diameter grind Flat grind Plummer Figure 4.20 EE-452 13 - 11
Internal Diameter Saw Internal diameter wafer saw Figure 4.23 Plummer EE-452 13 - 12
After crystal pulling, the boule is shaped and cut into wafers which are then polished on one side. Plummer EE-452 13 - 13
Wafer Notch and Laser Scribe 1234567890 Notch Scribed identification number Plummer Figure 4.22 EE-452 13 - 14
Polished Wafer Edge Plummer Figure 4.24 EE-452 13 - 15
Chemical Etch of Wafer Surface to Remove Sawing Damage Figure 4.25 EE-452 13 - 16
Wafer Dimensions & Attributes Thickness Diameter Area Weight Weight/25 (cm 2 ) ( µ m) (mm) (grams/lbs) Wafers (lbs) 150 1.5 675 ± 20 176.71 28 / 0.06 200 3 725 ± 20 314.16 53.08 / 0.12 300 7 775 ± 20 706.86 127.64 / 0.28 400 13 825 ± 20 1256.64 241.56 / 0.53 Plummer Table 4.3 EE-452 13 - 17
Increase in Number of Chips on Larger Wafer Diameters (Assume large 1.5 x 1.5 cm microprocessors) 88 die 200-mm wafer 232 die 300-mm wafer Plummer Figure 4.13 EE-452 13 - 18
Wafer Polishing EE-452 13 - 19
Recommend
More recommend