
Brownian motion (on a phylogeny) ‘borrowed’ ¡from ¡Liam ¡Revell ¡lecture ¡notes ¡
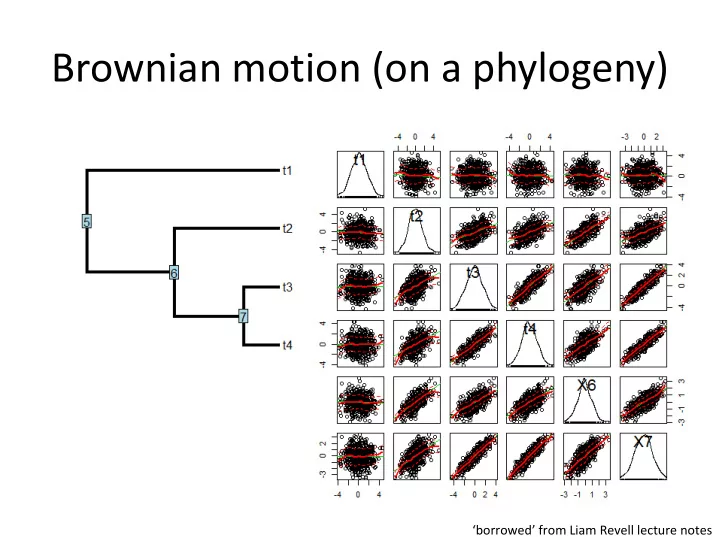
Brownian motion (on a phylogeny) The expected distribution of the tips & nodes of the tree under Brownian motion is multivariate normal with variance- covariance matrix in which each i , j th term is proportional to the height above the roots for the common ancestor of i and j . ‘borrowed’ ¡from ¡Liam ¡Revell ¡lecture ¡notes ¡
Blomberg ’ s K – measure of phylogenetic signal phylogenetic signal low brownian high K = 0.18 K ~ 1 K = 1.62 Blomberg et al. 2003 Evolution Data diagnostics examples from Ackerly 2009 PNAS
K ¡> ¡1 ¡
Brownian motion – assumptions and interpretations Evolutionary models
Brownian motion – assumptions and interpretations ∞ -∞ Evolutionary models
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model (OU-1) the math: brownian motion + ‘ rubber band e ff ect ’ change is unbounded (in theory), but as rubber band gets stronger, bounds are established in practice repeated movement back towards center erases phylogenetic signal, leading to K << 1 15 10 5 trait value 0 -5 -15 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 time see Hansen 1997 Evolution Evolutionary models Butler and King 2004 Amer. Naturalist
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck model (OU-1) the math: brownian motion + ‘ rubber band e ff ect ’ change is unbounded (in theory), but as rubber band gets stronger, bounds are established in practice repeated movement back towards center erases phylogenetic signal, leading to K << 1 15 10 5 trait value 0 -5 -15 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 time see Hansen 1997 Evolution Evolutionary models Butler and King 2004 Amer. Naturalist
Rates of phenotypic diversification under Brownian motion 1 Var(log e (trait)) 1 felsen = million yrs time var(x)
Rates of phenotypic diversification under Brownian motion higher rate lower rate time var(x)
Diversification of height in maples, Ceanothus and silverswords rate = 0.015 felsens 0.10 felsens 0.83 felsens ~5.2 Ma ~30 Ma ~45 Ma Evolutionary rates Ackerly 2009 PNAS
Rates of phenotypic diversification (estimated for Brownian motion model) North temperate California Hawai ’ i Height Leaf size Rate (felsens) ±1 s.e. Ackerly, PNAS in review
Recommend
More recommend