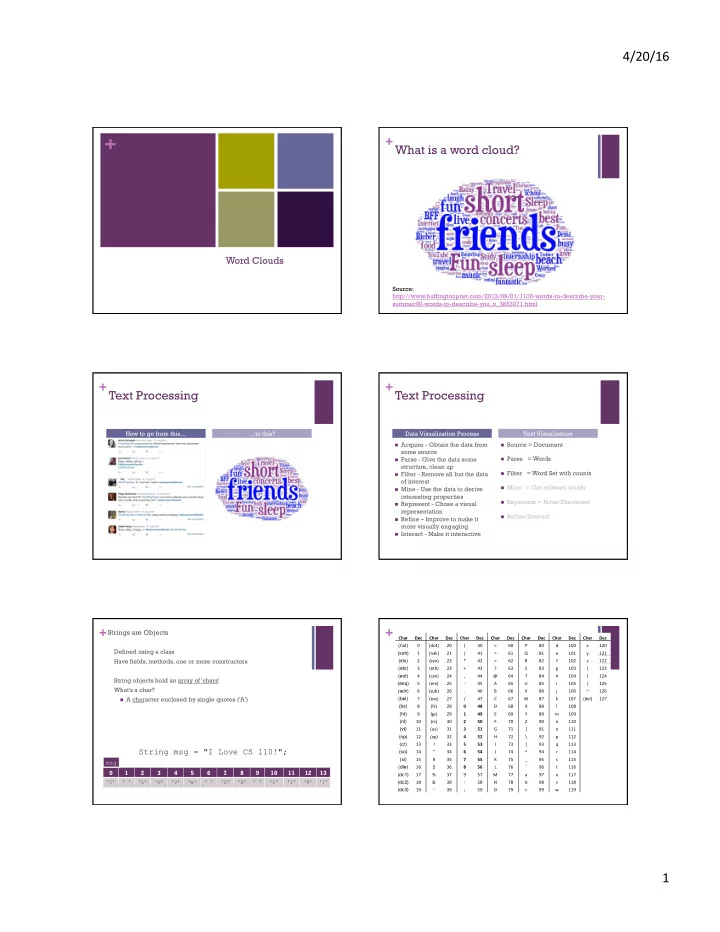

4/20/16 ¡ + + What is a word cloud? Word Clouds Source: http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2013/09/01/1100-words-to-describe-your- summer00-words-to-describe-you_n_3853071.html + Text Processing + Text Processing How to go from this… …to this? Data Visualization Process Text Visualization n Acquire - Obtain the data from n Source = Document some source n Parse = Words n Parse - Give the data some structure, clean up n Filter - Remove all but the data n Filter = Word Set with counts of interest n Mine = Get relevant words n Mine - Use the data to derive interesting properties n Represent = Fonts/Placement n Represent - Chose a visual representation n Refine/Interact n Refine – Improve to make it more visually engaging n Interact - Make it interactive + Strings are Objects + Char ¡ Dec ¡ Char ¡ Dec ¡ Char ¡ Dec ¡ Char ¡ Dec ¡ Char ¡ Dec ¡ Char ¡ Dec ¡ Char ¡ Dec ¡ (nul) 0 ¡ (dc4) ¡ 20 ¡ ( ¡ 40 ¡ < ¡ 60 ¡ P ¡ 80 ¡ d ¡ 100 ¡ x ¡ 120 ¡ Defined using a class (soh) 1 ¡ (nak) ¡ 21 ¡ ) ¡ 41 ¡ = ¡ 61 ¡ Q ¡ 81 ¡ e ¡ 101 ¡ y ¡ 121 ¡ Have fields, methods, one or more constructors (stx) 2 ¡ (syn) ¡ 22 ¡ * ¡ 42 ¡ > ¡ 62 ¡ R ¡ 82 ¡ f ¡ 102 ¡ z ¡ 122 ¡ (etx) 3 ¡ (etb) ¡ 23 ¡ + ¡ 43 ¡ ? ¡ 63 ¡ S ¡ 83 ¡ g ¡ 103 ¡ { ¡ 123 ¡ (eot) 4 ¡ (can) ¡ 24 ¡ , ¡ 44 ¡ @ ¡ 64 ¡ T ¡ 84 ¡ h ¡ 104 ¡ | ¡ 124 ¡ String objects hold an array of 'chars' (enq) 5 ¡ (em) ¡ 25 ¡ -‑ ¡ 45 ¡ A ¡ 65 ¡ U ¡ 85 ¡ i ¡ 105 ¡ } ¡ 125 ¡ What's a char? (ack) 6 ¡ (sub) ¡ 26 ¡ . ¡ 46 ¡ B ¡ 66 ¡ V ¡ 86 ¡ j ¡ 106 ¡ ~ ¡ 126 ¡ (bel) n A character enclosed by single quotes ('A') 7 ¡ (esc) ¡ 27 ¡ / ¡ 47 ¡ C ¡ 67 ¡ W ¡ 87 ¡ k ¡ 107 ¡ (del) ¡ 127 ¡ (bs) 8 ¡ (fs) ¡ 28 ¡ 0 ¡ 48 ¡ D ¡ 68 ¡ X ¡ 88 ¡ l ¡ 108 ¡ ¡ ¡ (ht) 9 ¡ (gs) ¡ 29 ¡ 1 ¡ 49 ¡ E ¡ 69 ¡ Y ¡ 89 ¡ m ¡ 109 ¡ ¡ ¡ (nl) 10 ¡ (rs) ¡ 30 ¡ 2 ¡ 50 ¡ F ¡ 70 ¡ Z ¡ 90 ¡ n ¡ 110 ¡ ¡ ¡ (vt) 11 ¡ (us) ¡ 31 ¡ 3 ¡ 51 ¡ G ¡ 71 ¡ [ ¡ 91 ¡ o ¡ 111 ¡ ¡ ¡ (np) 12 ¡ (sp) ¡ 32 ¡ 4 ¡ 52 ¡ H ¡ 72 ¡ \ ¡ 92 ¡ p ¡ 112 ¡ ¡ ¡ (cr) 13 ¡ ! ¡ 33 ¡ 5 ¡ 53 ¡ I ¡ 73 ¡ ] ¡ 93 ¡ q ¡ 113 ¡ ¡ ¡ String msg = "I Love CS 110!"; (so) 14 ¡ " ¡ 34 ¡ 6 ¡ 54 ¡ J ¡ 74 ¡ ^ ¡ 94 ¡ r ¡ 114 ¡ ¡ ¡ (si) 15 ¡ # ¡ 35 ¡ 7 ¡ 55 ¡ K ¡ 75 ¡ _ ¡ 95 ¡ s ¡ 115 ¡ ¡ ¡ msg (dle) 16 ¡ $ ¡ 36 ¡ 8 ¡ 56 ¡ L ¡ 76 ¡ ` ¡ 96 ¡ t ¡ 116 ¡ ¡ ¡ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 (dc1) 17 ¡ % ¡ 37 ¡ 9 ¡ 57 ¡ M ¡ 77 ¡ a ¡ 97 ¡ u ¡ 117 ¡ ¡ ¡ (dc2) 'I' ' ' 'L' 'o' 'v' 'e' ' ' 'C' 'S' ' ' '1' '1' '0' '!' 18 ¡ & ¡ 38 ¡ : ¡ 58 ¡ N ¡ 78 ¡ b ¡ 98 ¡ v ¡ 118 ¡ ¡ ¡ (dc3) 19 ¡ ' ¡ 39 ¡ ; ¡ 59 ¡ O ¡ 79 ¡ c ¡ 99 ¡ w ¡ 119 ¡ ¡ ¡ 1 ¡
� 4/20/16 ¡ + + Split a String based on a single or multiple Join a String Array with a join char separator chars String s1 = "12, 34, 56"; [0] "12" String[] as; [1] " 34" [2] " 56" String[] as = new String[] {"one", "two", "buckle my shoe"}; void setup() { as = split (s1, ","); void setup() { //as = trim(as); String s1 = join( as, " | " ); println( as ); println( s1 ); } } String s1 = "Data: 12, 34, 56"; [0] "Data" String[] as; [1] " 12" one | two | buckle my shoe [2] " 34" void setup() { [3] " 56" as = splitTokens (s1, ":,"); //as = trim(as); println( as ); } + + Acquire data: Source = Document Numbers can be formatted as Strings String s1 = "She is the"; n // Sketch 7-1: Parsing an input text file � String s2 = "programmer."; String inputTextFile = "NewYorkPrimaries.txt"; � String [] fileContents; � fileContents = loadStrings(inputTextFile); � phrase = s1 + nf(7, 3) + " " + s2; // nf( integer , number of digits ) n fileContents has the source! � // "She is the 007 programmer." n What next? � phrase = s1 + nf(3.14159,3, 2) + " " + s2; // nf( float , digits before decimal , digits after decimal ) // "She is the 003.14 programmer." + Parsing ¡ + Parse n CSV ¡files ¡ n How do we turn fileContents into words? n always ¡split ¡on ¡ "," ¡first ¡ n join array into one long string String rawText; � n Special ¡characters ¡ rawText = join(fileContents, " "); � n \", \', \\ n make all same case n Removing ¡" ¡(or ¡anything ¡else) ¡ rawText = rawText.toLowerCase(); � n int i = str.indexOf("\""); n String front = str.substring(0, i); n remove symbols and split string into words String delimiters = " ,./?<>;:'\"[{]}\\|=+-_()*&^%$#@!~"; � n String back = str.substring(i+1); tokens = splitTokens(rawText, delimiters); � n str = front+back; 2 ¡
4/20/16 ¡ + Display the words + Parse ¡and ¡Filter ¡ String raw; String delimiters = " ,.?!;:-\'\"()*![]{}|\\~`@#$%^&"; n Let's start by displaying all of the words: String[] fileText, words; int[] freqs; for (String t : tokens) { � void setup() { //textSize(15); � fileText = loadStrings("EliotLoveSong.txt"); if(random(100) < 40) { // more blue than red � println("Read " + fileText.length + " lines."); fill(random(150,250),0, 0,190); // make red � } else { � raw = join(fileText, " "); fill(0, 0, random(150,250),190); // make blue � raw = raw.toLowerCase(); } � text(t, random(0,width-50), random(20,height)); � words = splitTokens(raw, delimiters); } // for � println("Found " + words.length + " words."); } + Filter ¡ + Filtering: Word Frequency List String raw; String delimiters = " ,.?!;:-\'\"()*![]{}|\\~`@#$%^&"; String[] fileText, words, uniqueWords; n Create a set of word frequency pairs. int[] freqs; n Algorithm: void setup() { fileText = loadStrings("EliotLoveSong.txt"); n create empty set pairs println("Read " + fileText.length + " lines."); n for each token n if pairs has (token,count) raw = join(fileText, " "); n increment count raw = raw.toLowerCase(); n otherwise n add (token, 1) words = splitTokens(raw, delimiters); println("Found " + words.length + " words."); freqs = makeUnique(words); println("Found "+uniqueWords.length+" unique words."); } + The word class + Data Structures n Ways of storing and organizing data n Arrays n Must know the size ahead of time n Can not grow and shrink at will n except: n append(array, value) ¡-‑ ¡Expands ¡an ¡array ¡by ¡one ¡element ¡and ¡ adds ¡value ¡to ¡the ¡new ¡posi•on. ¡Type ¡of ¡value ¡must ¡match ¡type ¡of ¡array. ¡ Creates ¡a ¡new ¡array. ¡ ¡ 3 ¡
Recommend
More recommend