The Roaring 20s An era of prosperity, Republican power, Republican - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
The Roaring 20s An era of prosperity, Republican power, Republican Power President Harding Elected 1920 Legacy of corruption like the Teapot Dome bribery scandal and reduced taxes on businesses Died in office, 1923
The Roaring 20’s An era of prosperity, Republican power,
Republican Power President Harding Elected 1920 Legacy of corruption like the “Teapot Dome” bribery scandal and reduced taxes on businesses Died in office, 1923
By the 1920s, the U.S. had become the leading industrial power in the world. This boom was due to several factors: A. a wealth of natural resources B. government support for business C . a growing urban population for cheap labor and markets for new products .
16 th Amendment passes in 1913: begins Individual and Corporate Income Taxes Today we pay our taxes to the Federal and State governments no later than April 15 th Taxes are reduced under Presidents Harding and Coolidge
World War I left much of the American public divided. The end of the war hurt the economy. Returning soldiers took jobs away from many women and minorities, or faced unemployment themselves. Many Americans wanted to reduce the number of immigrants arriving in the US.
The 19 The 1921 21 Quota Act Quota Act and and the 1 the 192 924 4 Im Immigr migration ation Act Act ref reflec lecte ted d US nati US nativi vism. sm. The They g y greatl reatly y redu reduce ced the n d the numbers of ne umbers of new Ame w Americans as icans as peop people b le became ecame su susp spiciou icious s of of foreig foreigner ners s an and d wanted to pull anted to pull away y from from worl orld d aff affair airs.
President Coolidge “The business of America is business. The man who builds a factory builds a temple. The man who works in it worships there.” 1923-29 The political genius of President Coolidge, Walter Lippmann pointed out in 1926, was his talent for effectively doing nothing: "This active inactivity suits the mood and certain of the needs of the country admirably. It suits all the business interests which want to be let alone....
Presidents Harding and Coolidge reduce the Progressives’ regulations of businesses. America switches from war goods to consumer goods and advertising to sell products. Instalment Buying: Get it now and pay later Credit: pay a small amount each month until an item is paid for Interest: financial charge for borrowing $ Demand for US goods greatly increases but so does American debt. “I f we want anything, all we have to do is go and buy it on credit. So that leaves us without any economic problems whatever, except some day to have to pay for it. But we are certainly not thinking about it this early” Comedian Will Rogers, 1928
1920s Soaring Stock Market Companies sell stocks to gain the money they need to expand their business. Investors buy the stocks and hope the value of them will increase The 1920s were a Bull Market where stock prices rose rapidly. Often the price rose not because the company was improving but simply because investors expected the price to rise. Investors became rich overnight, buying stocks and selling them for more not long afterwards. As long as prices continued to rise all was well.
The 1920s is a period of great change in American Society - modern America is born at this time, with many people enjoying a much higher standard of living. For first time the census (population count every 10 years) reflected an urban society – over 50% of the US population lived in cities.
1920's Great Changes for Women... 1920 - 19th Amendment gave them the federal vote The League of Women Voters worked to educate women on voting and to ensure women could serve on juries During WWI many women worked in factories After the war, many women kept working outside the home More women went to college and wanted to join the professions
Women didn't want to sacrifice their wartime gains in income and life outside of the home - amounted to a social revolt the FLAPPER became the name for "new woman” who wore skirts that only went to the knee, smoke cigarettes and drank alcohol in public, drove cars fast, and cut their hair short With income from working, women bought appliances like vacuum cleaners, refrigerators, and radios Some women had to work and also run their homes. It was hard for them to combine these roles. While many women worked, most remained homemakers.
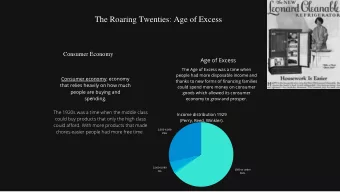
Consumer Economy
Age of Prosperity Employment and wages/salaries are strong in the 1920s as the economy expands Henry Ford introduces the assembly line to factories – reduces costs and increases supply so the price goes down and more Americans can afford a car Assembly lines and mass production spread throughout the US economy In 1919 there are 7 million cars in the US but by 1929 there are 23 million on the road; creating an estimated 4 million new jobs
Age of Prosperity The car transforms the US economy Competition increases as General Motors manufactures cars and Ford does not have a monopoly New jobs are needed to keep up with the demand for refining oil into gasoline, gas stations, building roads, restaurants, and shopping centers. People move from the crowded cities to the suburbs further away from work because they can drive there
Culture of the Roaring 20’s <<< Radio: GE, Westinghouse,& RCA form NBC Silent nt Movi vies es >>>> >>>> Charl rlie e Chapl plin in “Talkies” The e Jaz azz z Singer ger Starrin rring g Al Jolson lson Mary Pickford “America’s Sweetheart”
The 20’s is The Jazz Age The Flappers make up cigarettes short skirts Writers Musicians F. Scott Fitzgerald Louis Armstrong Ernest Hemingway Duke Ellington
Th The J e Jazz azz Ag Age Jazz b azz began egan in Ne in New Or w Orleans leans, based based on on West est Afr African ican rh rhythms ythms, Black Black spi spirituals ituals and and work songs ork songs, and and Eu Euro ropean pean ha harmoni monies es. Greats Greats inclu included L ded Loui ouis Ar s Armst mstron rong and g and Duk Duke Elling e Ellington. ton. Ev Eventuall entually, rock rock and and rol roll l plu plus s hi hip p hop hop wil will l de develop elop from it. from it. Ame Americans bou icans bough ght t rad radios ios and and went t ent to o the m the movi vies es. P Popu opular lar fads ads grabbed the nation’s attention, lik like f e fla lag-pol pole sit e sitting ting (2 (21 1 da days ys was as the rec the record ord) ) and and then di then disa sapp ppeared eared . The Ch The Charl arlest eston dance bec on dance became ame an another other f fad ad.
Celebrities Babe Ruth & Ty Cobb Charles Lindbergh The Spirit of St. Louis Jack Dempsey
America was becoming more prosperous. Business and industry required a more educated work force. These two factors caused a huge increase in the number of students going to high school. The nation’s schools were successful in teaching large numbers of Americans and immigrants to read. As a result of increased literacy, more people read newspapers than before.
Charles A. Lindbergh thrilled the nation by becoming the first person to fly solo across the Atlantic Ocean. Lindbergh took off from New York City in his plane, The Spirit of St. Louis. On May 20-21, 1927 he flew for 33 hours and landed outside of Paris, France. On his return to the United States, Lindbergh became the idol of America. In an age of sensationalism and excess, Lindbergh stood for the honesty and bravery the nation seemed to have lost.
Charles Lindbergh
The “Roaring Twenties” "Old" Culture "New" Culture Emphasized Production Emphasized Consumption Character Personality Scarcity Abundunce Religion Science Idealized the Past Looked to the Future Local Culture Mass Culture Substance Image The above graph indicates in a general sense what historians mean when they refer to the "old" and the "new" cultures of the 1920s. This list is not meant to be definitive. Source: Culture as History: The Transformation of American Society in the Twentieth Century (New York: Pantheon Books, 1984).
The Ku Klux Klan: Great increase Anti-black In power across the US, not just the South Anti-immigrant Anti-Semitic Anti-Catholic Anti- women’s suffrage Anti-bootleggers
Scopes “Monkey” Trial Evolution vs. Creationism Science vs. Religion Dayton, Tennessee Famous Lawyers John Scopes High School Biology teacher
During the 1920s, the nation saw the rise of Christian fundamentalism. This religious movement was based on the belief that everything written in the Bible was literally true. Fundamentalists were concerned with the growing trust in science that most Americans had. These beliefs led fundamentalists to reject Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution (natural selection)
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.