
The Play Cycle – Understanding and Application Dr Pete King Swansea University Somerset Play Conference – June 19 th 2019
A Quick Snapshot: Pete 1. Senior Lecturer at Swansea University in the College for Human and Health Science 2. Programme Manager for the MA Childhood Studies and MA Developmental and Therapeutic Play Courses 3. Teach research methods across both undergraduate and postgraduate courses 4. Researcher in play and playwork p.f.king@swansea.ac.uk https://www.facebook.com/MastersVivianTower https://twitter.com/Dr_Pete_King
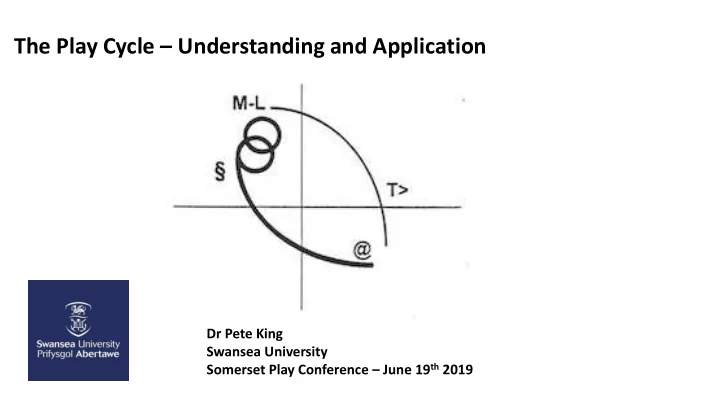
The Play Cycle (Sturrock & Else, 1998) L (ludic or play cycle) = (M-L.T>.@. §): • M-L: The metalude, where the play cue is issued • T>: termination or decay • @: the active development where there is a response to the play cue termed the play return • § : the loop or flow: This is where both the original play cue and the responding play return goes back to the metalude • Play frame, the boundary where the Play Cycle ‘sits’ • Annihilation , the end of the Play Cycle
What is the adult role in the Play Cycle Adult Description Intervention Play The Play is self-contained – no intervention is necessary; the worker observes the activity Maintenance Simple The adult acts as a resource for the play – this may be subtle, as in making a tool available for use, Involvement or more overt responding to a request from children Medial At the request of the child, the adult becomes involved in the play – such as by offering Intervention alternatives from which the child chooses, or by initiating a game then withdrawing Complex There is a direct and extended overlap between playing children and the adult – the adult may Intervention need to take on a role in the play, or act as a partner to the playing child Source: Sturrock and Else, 1998; Sturrock, Russell and Else, 2004
Enter code BSE19 for 20% off
Recommend
More recommend