Scalar field Hadamard renormalisation in AdS n Carl Kent University - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Scalar field Hadamard renormalisation in AdS n Carl Kent University of Sheffield (Supervisor: Elizabeth Winstanley) Outline 1. Scalar field theory in AdS n 2. Overview of research 3. Calculation of the vacuum polarisation 2 ren
Scalar field Hadamard renormalisation in AdS n Carl Kent University of Sheffield (Supervisor: Elizabeth Winstanley)
Outline 1. Scalar field theory in AdS n 2. Overview of research 3. Calculation of the ‘vacuum polarisation’ � Φ 2 � ren
Scalar field theory in AdS n Geometry Anti-de Sitter space AdS n is the maximally symmetric vacuum solution to Einstein’s classical field equations with constant negative curvature. Hyperspherical coordinates Timelike Radial Polar Azimuthal 0 ≤ ρ < π − π ≤ τ ≤ π 0 ≤ θ j < π 0 ≤ θ n − 2 < 2 π 2 ( j = 1 , 2 , . . . n − 3) Metric n − 2 i − 1 ds 2 = − a 2 sec 2 ρ dτ 2 − dρ 2 − sin 2 ρ sin 2 θ j dθ 2 dθ 2 � � . 1 + i i =2 j =1
Scalar field theory in AdS n Propagation Homogenous scalar field wave equation ✷ − m 2 − ξ R � � φ ( x ) = 0 Inhomogenous scalar field wave equation ✷ x − m 2 − ξ R G F ( x, x ′ ) = g − 1 � � 2 δ ( x, x ′ ) , g := | det g µν | Short-distance behaviour of G F ( x, x ′ ) as x ′ → x − iG F ( x, x ′ ) → ‘ � Φ 2 ( x ) � ’
Scalar field theory in AdS n Maximal Symmetry General effect of maximal symmetry G F ( x, x ′ ) �→ G F ( s ) , s := s ( x, x ′ ) . Synge’s ‘world function’ σ := 1 2 s 2 Inhomogenous scalar field wave equation ✷ − m 2 − ξ R � � G F ( σ ) = δ ( σ ) ∀ σ < 0 Short-distance behaviour of G F ( σ ) − iG F ( σ ) → ‘ � Φ 2 � ’ as σ → 0
Overview of research ✽ ✽ Φ (+) � Φ 2 � ren n , l ( x ) − → G F ( σ ) − → − → � T µν � ren Field Feynman Renormalised Renormalised modes propagator v.e.v. of the v.e.v. of the quadratic field stress-energy fluctuations tensor Analytic � � ✽ ✽ � Φ 2 ( x ) � β � T µν ( x ) � β ren ren Renormalised Renormalised t.e.v. of the t.e.v. of the quadratic field stress-energy fluctuations tensor Numeric
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Hadamard theorem Hadamard form of the Feynman Green’s function � � U ( σ ) σ 1 − n G H 2 + V ( σ ) ln ¯ F ( σ ) = iν ( n ) σ + W ( σ ) ∀ n > 2 (where ν ( n ) is a constant). Hadamard functions • U ( σ ), V ( σ ) and W ( σ ) are regular as σ → 0. • Expansion coefficients are obtained from recursion relations [1]. • U ( σ ), V ( σ ) are uniquely defined but W ( σ ) is not . Singularity structure � � G H U ( σ ) σ 1 − n 2 + V ( σ ) ln ¯ F , sing ( σ ) = iν ( n ) purely geometric σ , G H F , reg ( σ ) = iν ( n ) W ( σ ) , state-dependent
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Hadamard renormalisation Given G F ( σ ) = G H F , reg ( σ ) + G H G F ( σ ) → ‘ i � Φ 2 � ’ as σ → 0 , F , sing ( σ ) and ‘ � Φ 2 � ’ = � Φ 2 � phys + ‘ � Φ 2 � unphys ’ when σ = 0 , where � Φ 2 � phys = − i lim σ → 0 G H F , reg ( σ ) = ν ( n ) lim σ → 0 W ( σ ) . Therefore � Φ 2 � phys = � Φ 2 � ren because � � � Φ 2 � ren = − i lim G F ( σ ) − G H F , sing ( σ ) σ → 0 � � �� U ( σ ) σ 1 − n 2 + V ( σ ) ln ¯ = − i lim G F ( σ ) − iν ( n ) σ σ → 0
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Scalar field propagator on AdS n The ISFWE is a hypergeometric differential equation [2] in z ( σ ) with solution � n − 1 � � n − 1 � + µ, n − 1 − µ ; n + µ, n − 1 − µ ; n G F ( σ ) = CF 2 ; z + DF 2 ; 1 − z 2 2 2 2 where � �� 2 ( n − 1) 2 � � 1 � σ + m 2 a 2 + ξ R a 2 , z ( σ ) := − µ := • sinh , a 2 4 • C, D are constants, • F is the hypergeometric function, and G F ( σ ) = G F, reg ( σ ) + G F, sing ( σ )
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Code structure Code was first written in Maple to generate expressions for 1. G F , sing ( σ ) as σ → 0 2. G H F , sing ( σ ) as σ → 0 Example: n = 5 as σ → 0 √ � 1 � 1 2 � − m 2 − 4 a 2 + 20 ξ 1 � G F , sing ( σ ) = i + , 32 π 2 3 a 2 1 σ σ 2 2 √ � 1 � 1 2 � − m 2 − 4 a 2 + 20 ξ 1 � F , sing ( σ ) = i G H + . 32 π 2 3 a 2 1 σ σ 2 2
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Code structure Example: n = 6 as σ → 0 G F , sing ( σ ) � 1 � 1 i � − 1 2 m 2 − 10 a 2 + 15 ξ 1 1 = σ 2 + 16 π 3 3 a 2 σ � 1 � m 2 � − 1 � − 5 4 + 15 � − 3 + 75 2 ξ − 225 � 8 m 4 + 2 ξ 2 + 2 ξ a 2 + ln ¯ σ a 4 � 1 m 2 � 101 � + 1 720 − 5 a 2 + 8 ξ , 48 a 4 G H F , sing ( σ ) � 1 � 1 � − 1 2 m 2 − 10 a 2 + 15 ξ 1 1 i = σ 2 + 16 π 3 3 a 2 σ � 1 � m 2 � − 1 � − 5 4 + 15 � − 3 + 75 2 ξ − 225 � 8 m 4 + 2 ξ 2 + 2 ξ a 2 + ln ¯ σ a 4 � 1 m 2 + 5 � 173 288 − 25 � a 2 + 8 ξ . 48 a 4
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Code structure 3. Subtraction of singular parts as σ → 0 Defining � � f 0 G F , sing ( σ ) − G H n := lim F , sing ( σ ) , σ → 0 � = 0 n odd, f 0 n � = 0 n even. 4. Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Recalling � � � Φ 2 � ren = − i lim G F ( σ ) − G H F , sing ( σ ) σ → 0 and G F ( σ ) = G F , reg ( σ ) + G F , sing ( σ ) , then � Φ 2 � ren = − i lim G F , reg ( σ ) + f 0 � � . n σ → 0
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Results Example: n = 10 1 � Φ 2 � ren = − 12288 π 5 a 8 �� � � � 1 � � µ 8 − 21 µ 6 + 987 8 µ 4 − 3229 16 µ 2 + 11025 × 2 + µ + γ − ln ¯ ψ a 256 − 25 24 µ 8 + 461 24 µ 6 − 87983 960 µ 4 + 3854941 40320 µ 2 + 288563 � ; 30720 Example: n = 11 1 µ 9 − 30 µ 7 + 273 µ 5 − 820 µ 3 + 576 µ � Φ 2 � ren = − � � ; 60480 π 5 a 9 where � ( n − 1) 2 + m 2 a 2 + ξ R a 2 . µ := 4
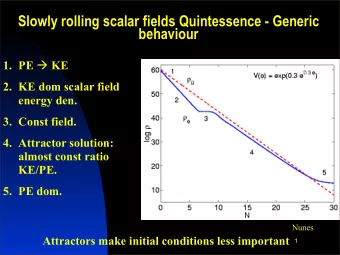
Calculation of � Φ 2 � ren Results (for ¯ a = 1 ) 0.3 n = 2 n = 3 n = 4 0.2 n = 5 n = 6 n = 7 0.1 n = 8 � Φ 2 � ren n = 9 n = 10 0.0 n = 11 -0.1 -0.2 0.00 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50 µ
Scalar field Hadamard renormalisation in AdS n Conclusions • Using the Hadamard theorem, we have obtained expressions of � Φ 2 � ren analytically. • Expressions have been obtained for a massive neutral scalar field in n = 2 to n = 11 inclusive involving an arbitrary coupling ξ . • The method used is easily extended to higher n with sufficient processing power. Key references 1. D´ ecanini, Y., Folacci, A., Phys. Rev. D. 78 , 044025 (2008). 2. Allen, B., Jacobson, T., Commun. Math. Phys. 103 , 669 (1986).
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.