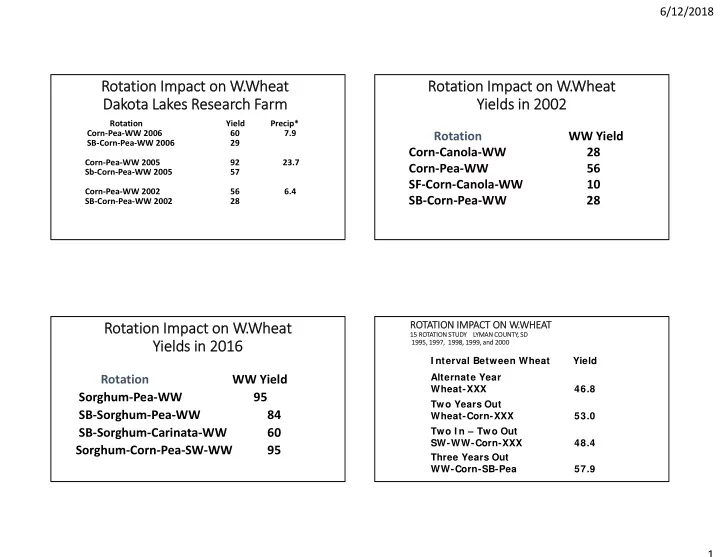

6/12/2018 Ro Rotation Im Impact on on W. W.Wheat Ro Rotation Im Impact on on W. W.Wheat Dak Dakota Lak Lakes Re Research Fa Farm Yields in Yi in 2002 2002 Rotation Yield Precip* Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 2006 60 7.9 Rotation WW Yield SB ‐ Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 2006 29 Corn ‐ Canola ‐ WW 28 Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 2005 92 23.7 Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 56 Sb ‐ Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 2005 57 SF ‐ Corn ‐ Canola ‐ WW 10 Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 2002 56 6.4 SB ‐ Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 28 SB ‐ Corn ‐ Pea ‐ WW 2002 28 ROTATI RO TION IM IMPACT ON ON W. W.WHEAT Rotation Im Ro Impact on on W. W.Wheat 15 RO 15 ROTATIO TION ST STUDY LY LYMAN COU COUNTY TY, SD SD Yields in Yi in 2016 2016 1995, 95, 1997 1997, 1998, 998, 1999, 99, and and 2000 2000 I nterval Between Wheat Yield Rotation WW Yield Alternate Year Wheat-XXX 46.8 Sorghum ‐ Pea ‐ WW 95 Two Years Out SB ‐ Sorghum ‐ Pea ‐ WW 84 Wheat-Corn-XXX 53.0 SB ‐ Sorghum ‐ Carinata ‐ WW 60 Two I n – Two Out SW-WW-Corn-XXX 48.4 Sorghum ‐ Corn ‐ Pea ‐ SW ‐ WW 95 Three Years Out WW-Corn-SB-Pea 57.9 1
6/12/2018 Rotation Impact on Spring Wheat W. W.Wheat Cost/Unit of of Produc oduction tion 199 1994 ‐ 19 1995 95 & 199 1997 ‐ 199 1999 Ly Lyman Coun County ty WCS 2002 • Rotation SW Yield Rotation Cost in $/bu. • Wheat-Canola 15.4 WW ‐ Fallow $4.60 • Wheat-Fallow 20.7 WW ‐ Corn ‐ Fallow $3.79 • Wheat-Corn-Fallow 23.7 WW ‐ Corn ‐ Pea $2.45 • Wheat-Corn-Pea 25.8 SW ‐ WW ‐ Corn ‐ SB $2.64 • Wheat-Corn-Soybean 8.9 27,0 27,000 gallo allons of of wa water pr provid ides es 1 Commonality Com onality Among Among Ti Tillag llage To Tools inch of in of wa water on on 1 acr acre. • All Tillage Tools Destroy Soil Structure. Ther There ar are 1,800,000 1,800,000 lb lbs of soil soil in in 1 • All tillage tools decrease water infiltration acr acre 6 in inches deep deep. • All tillage tools reduce organic matter • All tillage tools increase weeds . If 1% If 1% OM OM ther there is is 18,0 18,000 lb lbs. s. If 4% If 4% OM OM ther there is is 72,0 72,000 lb lbs. s. 2
6/12/2018 OM OM hold holds 5 to to 10 10 tim times its its we weight ht OM OM hold holds 5 to to 10 10 tim times its its we weight ht in in wa water in wa in water In top In top 6 in inches tot total wa water held held on on In In top top 12 12 in inches tot total wa water held held the the OM OM alo alone wi with th on the on the OM OM alo alone wi with th 1% 1% OM OM is is 0.39 0.39 to to 0.78 0.78 in inches 1% OM 1% OM is is 0.78 0.78 to to 1.56 1.56 in inches 4% 4% OM OM is is 1.5 1.5 to to 3.1 3.1 inc inches 4% 4% OM OM is is 3.0 3.0 to to 6.2 6.2 inc inches When soil water storage capacity is “ Within all textural groups, as low, much of the rain that falls during organic matter increased from 1 to extended periods of precipitation is 3%, the available water capacity lost. In contrast, a high water storage approximately doubled. When capacity, combined with the effective organic matter content increased to capture of rain and snowmelt over the 4%, it then accounted for more fall, winter and spring can support a than 60% of total AWC “. 8 crop through an extended dry period. 3
6/12/2018 2013 2013 Yi Yield Da Data 2013 Yi 2013 Yield Da Data Dakota Lak Dak Lakes Re Research Fa Farm Dakota Lak Dak Lakes Re Research Fa Farm • C – SB rotation (Cover Crops historically • C – C – SB – Wheat ‐ SB rotation increases soybean yield 7.3 bu/a on • 1 st year SB yield ‐ NO cover crop = 76.3 average vs no CC in this rotation). bu/ac • Yield 2013: Soybean with WW CC 62.9 • 2 nd SB yield – Cover Crop = 81.2 bu/ac bu/a. We would have expected around 55.6 bu/a without CC. 2013 2013 Yi Yield Da Data DIVER DI VERSITY ITY IM IMPACT IF IF 5,000 5,000 ACRE ACRES Dak Dakota Lak Lakes Re Research Fa Farm • CONTINUOUS CORN • Cover crop increased SB yield (7.3 bu/ac), • 203 bu/a but more importantly crop diversity • CORN ‐ SOYBEAN increased SB yield by 15.9 bu/ac. • 217 bu/a C – SB rotation = 62.9 • C ‐ C ‐ SB ‐ W ‐ SB • 235 Corn C – C – SB – Wheat – SB = 78.8 bu/ac 4
6/12/2018 Pio 33P67 C ‐ SB 2005. DI DIVER VERSITY ITY IM IMPACT IF IF 5,000 5,000 ACRE ACRES Nitrogen Starter Pop-up Yield Moisture • CONTINUOUS CORN 28% TOP Surface Yes 194 23.2 • 1,015,000 corn, 0 soybean, 0 wheat • CORN ‐ SOYBEAN Urea Side Yes Yes 207 21.7 • 542,500 Corn, 157,250, 0 Wheat • C ‐ C ‐ SB ‐ W ‐ SB Urea Side Yes Surface 202 23.3 • 470,000 Corn, 157 ,600, 120,000 Wheat Urea Side Surface Yes 197 23.6 Pio 33P67 W/cc 2005. Pioneer 33W44 Diverse Pinto 2005 Nitrogen Starter Pop-up Yield Moisture Nitrogen Starter Pop-up Yield Moisture Urea Side Surface Yes 207 23.7 28% Yes Yes 220 18.5 Surface Urea Side Yes Yes 212 24.4 28% Surface Yes 223 19.3 Urea Side Yes Surface 215 23.1 Surface Urea Side Yes Yes 223 18.6 28% TOP Surface Yes 200 23.7 5
6/12/2018 Pio 0448 AM1 Corn II Diverse 2013 Starter Response by Corn in Different Tillage Systems in Indiana Olsen P less than 5 ppm Nitrogen Starter P Pop-up Yield Number of Average Type of responses response tillage out of 11 (all sites) 60 N side Yes Yes 217 bu/A 60 N side Yes No 214 Conv. 1 0.9 60 N Over row Over row Yes 198 No ‐ till 8 7.8 60 N Middle Middle Yes 197 Fertility Management Mycogen 2T498 Corn II Diverse 2013 • Some starter P with the seed . Olsen P less than 5 ppm • Other nutrients placed near row at Nitrogen Starter P Pop-up Yield seeding or on soil surface after crop 60 N side Yes Yes 206 canopy. • broadcast fertilizer before or at 60 N side None Yes 212 seeding encourages weeds. 60 N side Yes None 206 • Three key factors – 1 Available Nutrient 60 N side None None 204 – 2 Moisture – 3 Roots 6
Recommend
More recommend