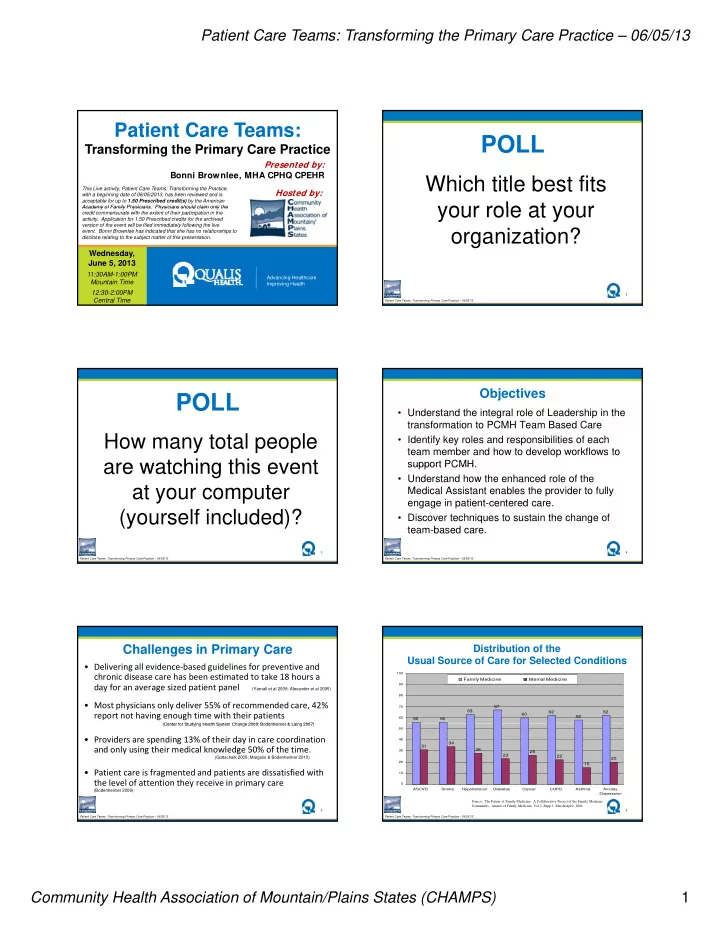

Patient Care Teams: Transforming the Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: POLL Transforming the Primary Care Practice Presented by: Bonni Brownlee, MHA CPHQ CPEHR Which title best fits This Live activity, Patient Care Teams: Transforming the Practice, Hosted by: with a beginning date of 06/05/2013, has been reviewed and is acceptable for up to 1.50 Prescribed credit(s) by the American your role at your your role at your Academy of Family Physicians. Physicians should claim only the Academy of Family Physicians Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity. Application for 1.50 Prescribed credits for the archived version of the event will be filed immediately following the live organization? event. Bonni Brownlee has indicated that she has no relationships to disclose relating to the subject matter of this presentation. Wednesday, June 5, 2013 11:30AM-1:00PM Advancing Healthcare Mountain Time Improving Health 12:30-2:00PM 2 Central Time Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Objectives POLL • Understand the integral role of Leadership in the transformation to PCMH Team Based Care How many total people • Identify key roles and responsibilities of each team member and how to develop workflows to are watching this event are watching this event support PCMH support PCMH. • Understand how the enhanced role of the at your computer Medical Assistant enables the provider to fully engage in patient-centered care. (yourself included)? • Discover techniques to sustain the change of team-based care. 3 4 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Challenges in Primary Care Distribution of the Usual Source of Care for Selected Conditions • Delivering all evidence ‐ based guidelines for preventive and chronic disease care has been estimated to take 18 hours a 100 Family Medicine Internal Medicine day for an average sized patient panel 90 (Yarnall et al 2009; Alexander et al 2005) 80 • Most physicians only deliver 55% of recommended care, 42% 70 67 63 62 62 report not having enough time with their patients 60 58 60 56 56 (Center for Studying Health System Change 2008; Bodenheimer & Laing 2007) (Center for Studying Health System Change 2008; Bodenheimer & Laing 2007) 50 • Providers are spending 13% of their day in care coordination 40 34 31 and only using their medical knowledge 50% of the time. 28 30 26 23 22 (Gottschalk 2005; Margolis & Bodenheimer 2010) 20 20 15 • Patient care is fragmented and patients are dissatisfied with 10 the level of attention they receive in primary care 0 ASCVD Stroke Hypertension Diabetes Cancer COPD Asthma Anxiety (Bodenheimer 2008) /Depression Source: The Future of Family Medicine: A Collaborative Project of the Family Medicine Community. Annals of Family Medicine, Vol 2, Supp 1, March/April 2004 5 6 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Community Health Association of Mountain/Plains States (CHAMPS) 1
Patient Care Teams: Transforming the Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: The New Way What does a Patient Care Team look like? • Teams place the patient at the center of staff attention– • Defined -- a group of people working together ---the provider is no longer the center toward a common goal. • Teams know their panel of patients and take ownership of their care • High functioning teams demonstrate the following characteristics: • The work of care delivery is distributed to team members – Flattened hierarchy according to level of training, competence and legal scope of practice – Shared mental model – Clear roles and responsibilities • The team works together to improve efficiency, clinical – Effective communications quality outcomes, and patient experience of care – Conflict resolution skills 7 8 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Imagine a High Functioning NCQA PCMH 1G: The Practice Team Clinical Team The practice uses a team to provide a range of patient care services by: • Providers assess, diagnose and treat, always 1. Defining roles for clinical and nonclinical team members doing something that requires their clinical 2. Having regular meetings or a structured communication process knowledge. 3. Using standing orders for services • Nursing role is re-established 4. Training and assigning care teams to coordinate care for individual patients patients – Clinical expertise, leadership and educating – Clinical expertise leadership and educating becomes their focus, extending their reach 5. Training and assigning care teams to support patients and families in self-management, self-efficacy and behavior change • The MA/LPN role is enhanced 6. Training and assigning care teams for patient population – Using standards and training provided by providers management and RN’s, they function more independently and 7. Training and designating care team members in communication enhance team delivery skills • Upward mobility strategy 8. Involving care team staff in the practice’s performance evaluation – Opportunities for stars to shine! and quality improvement activities 9 10 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 A Culture of Learning and Growth • Acknowledge that it is common to feel uncomfortable with new tasks • Make it “safe” to ask questions to encourage a What does it take to get to culture of shared responsibility for continuous quality improvement. Team-Based care? • Measure and reward accomplishments – publicly and privately to encourage growth • Encourage everyone to recognize and acknowledge small and great successes! 11 12 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Community Health Association of Mountain/Plains States (CHAMPS) 2
Patient Care Teams: Transforming the Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 A Culture of Open Communication A Culture of Support Executive and clinic leadership should: Leaders should be prepared to: • Create opportunities for shared information – • Guide the team through the journey meetings, 1:1, emails, posters…. • Provide reassurance • Communicate early and often • Be the cheerleader when needed • Be visible at the clinics. Do “rounds”. Use staff names Be visible at the clinics Do “rounds” Use staff names • Drive (or nudge) the change forward and talk to them about PCMH and teamwork. • Stay involved so you will see when potential and real • Ask for their ideas and opinions. barriers arise. • Acknowledge and respect each person’s contribution • Recognize when something isn’t working and • Find out who is engaged, not engaged and actively discuss alternative options with the team. disengaged and follow up to improve. 13 14 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Benefits of Employee Engagement Engagement is the Key • Staff – Are loyal – lower turnover • Engaged team members work with passion. – Excited about work, high morale, better teamwork.. with a desire to create a positive experience for patients • Not-Engaged team members do the work • Patients expected of them, but do not put in extra – Perceive that they are receiving higher quality care Perceive that they are receiving higher quality care effort. – Increased satisfaction leading to customer loyalty – More likely to be active partners in their care • Actively Disengaged team members aren’t • Clinic just unhappy, but are spreading their – Return patients and referral of new patients unhappiness to other staff. – Improved patient outcomes – Improved productivity with increased cost savings – Financially secure and successful 15 16 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 What’s in it for staff? What makes a team successful? • Fewer unplanned events • Care organized through daily huddles • Evenly distributed workload • Brief, frequent meetings to review and plan • Organized and orderly workflow PDSA cycles • Being recognized for contributions – • Continuous attention to improvement • Continuous attention to improvement acknowledgement by leadership and peers. eventually becomes part of the care team’s • The opportunity to learn new skills thought process, culture and daily work • Having the skills and resources to do the job • Regular communication with leadership to • Higher patient satisfaction; fewer patient discuss successes and barriers complaints 17 18 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Patient Care Teams: Transforming Primary Care Practice – 06/05/13 Community Health Association of Mountain/Plains States (CHAMPS) 3
Recommend
More recommend