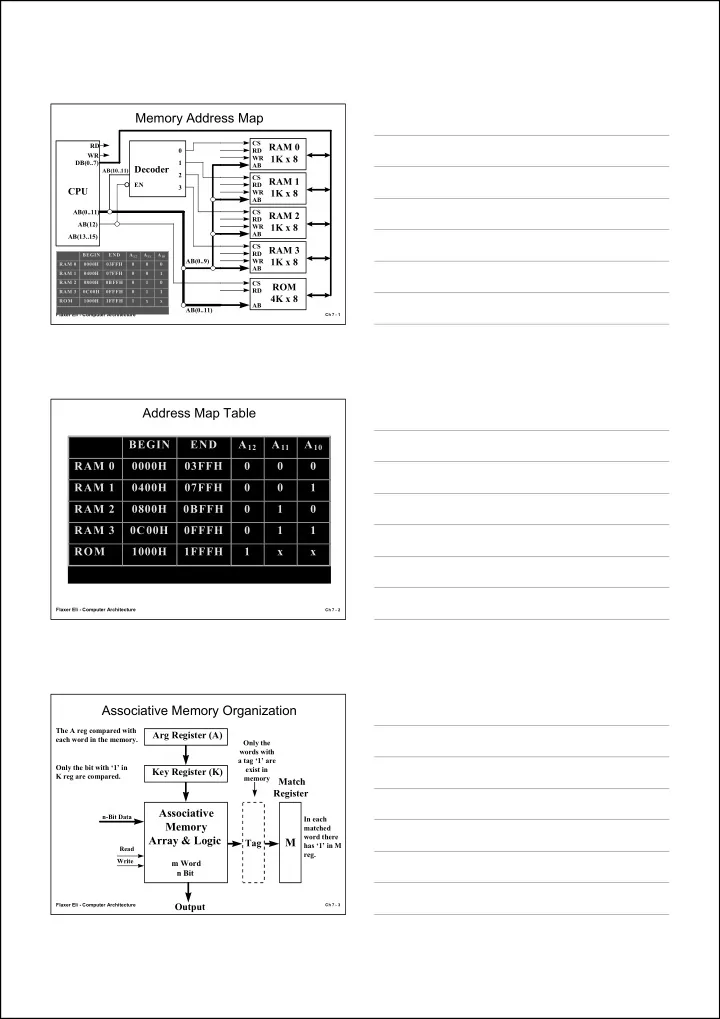

Memory Address Map CS RD RAM 0 0 RD WR 1K x 8 WR DB(0..7) 1 AB Decoder AB(10..11) 2 CS RAM 1 EN RD 3 CPU WR 1K x 8 AB AB(0..11) CS RAM 2 RD AB(12) 1K x 8 WR AB AB(13..15) CS RAM 3 RD BEGIN END A 12 A 11 A 10 AB(0..9) WR 1K x 8 RAM 0 0000H 03FFH 0 0 0 AB RAM 1 0400H 07FFH 0 0 1 RAM 2 0800H 0BFFH 0 1 0 CS ROM RD RAM 3 0C00H 0FFFH 0 1 1 4K x 8 ROM 1000H 1FFFH 1 x x AB AB(0..11) Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 1 Address Map Table BEGIN END A 12 A 11 A 10 RAM 0 0000H 03FFH 0 0 0 RAM 1 0400H 07FFH 0 0 1 RAM 2 0800H 0BFFH 0 1 0 RAM 3 0C00H 0FFFH 0 1 1 ROM 1000H 1FFFH 1 x x Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 2 Associative Memory Organization The A reg compared with Arg Register (A) each word in the memory. Only the words with a tag ‘1’ are Only the bit with ‘1’ in exist in Key Register (K) K reg are compared. memory Match Register Associative n-Bit Data In each Memory matched word there Array & Logic M Tag has ‘1’ in M Read reg. Write m Word n Bit Output Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 3
Example 16-Bit Address CPU Main Memory 64K x 12 Cache Memory 256 x 12 8-Bit Address Mapping Controller Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 4 Direct Mapping No choice is possible for 8 bits 8 bits replacing Tag Index 00H 00 00H Cache Memory 256 x 12 Main Memory FFH 64K x 12 ● If the cache size is 2 K FF FFH and the main memory size is 2 N then: It impossible to map ● Index length = K addresses with the same ● Tag length = N - K index and difference tag. Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 5 Direct Mapping Main Memory Main Memory Cache Cache Cache Address Memory Memory Address (16 Bit) Data 12 Bit Tag Data 0000H 123H 00 00 123H FF 00 234H 00FFH 234H 0100H 345H 00 01 345H 01FFH 456H FF 01 456H 0200H 567H 00 02 567H 02FFH 678H FF 02 678H Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 6
Address Space & Memory Space Auxiliary Memory 00000H Main Memory Program 1 0000H Data 1, 1 Virtual Program 1 Data 1, 2 Address Mapper Program 2 Data 1, 1 Data 2, 1 7FFFH Memory Space M=32K=2 15 FFFFFH Address Space N=1024K=2 20 The address field of the instruction code has a sufficient number of bits to specify all virtual addresses. Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 7 Memory Page Table Page no Line Number 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 Virtual Address Table Main Memory Presence Address Bit 000 0 Block 0 001 11 1 Block 1 010 Block 2 00 1 01 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 011 Block 3 0 Main Memory 100 0 Address Reg 101 01 1 MBR 110 10 1 Main Memory Main Memory = 4K 111 0 Buffer Reg Virtual Memory = 8K Page = 1K 01 1 Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 8 Associative Page Table Page no Line Number 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 Virtual Address Main Memory Arg Reg Block 0 101 00 Block 1 Key Reg Block 2 111 00 01 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 Block 3 Main Memory 001 11 Address Reg 010 00 MBR Associative 101 01 Memory 110 10 Main Memory = 4K Virtual Memory = 8K 101 01 Page = 1K Flaxer Eli - Computer Architecture Ch 7 - 9
Recommend
More recommend