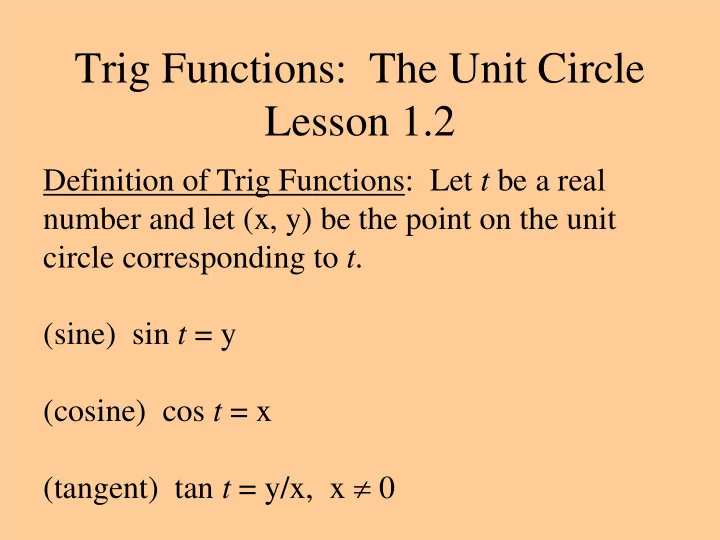

Trig Functions: The Unit Circle Lesson 1.2 Definition of Trig Functions: Let t be a real number and let (x, y) be the point on the unit circle corresponding to t . (sine) sin t = y (cosine) cos t = x (tangent) tan t = y/x, x 0
Ex 1: Find the point (x, y) on the unit circle that corresponds to the real number t . A. t = /4 B. t = 7 /6 C. t = 4 /3 2 , − 1 3 2 2 − 1 3 2 , − 2 , − 2 2 2 Ex 2: Evaluate (if possible) the sine, cosine, and tangent of the real number. A. t = /4 2 2 2 sin ( /4) = cos ( /4) = tan ( /4) = 1 2 2 2 2 2
Ex 2 (cont’d) : Evaluate (if possible) the sine, cosine, and tangent of the real number. −1,0 B. t = 0 sin ( ) = 1 cos ( ) = 0 0 tan ( ) = 1
Ex 2 (cont’d) : Evaluate (if possible) the sine, cosine, and tangent of the real number. − 1 3 2 , C. t = - 4 /3 2 3 2 tan (-4 /3) = 1 3 sin (-4 /3) = 2 2 3 2 1 2 1 cos (-4 /3) = 2 3 3 1
Definition of Reciprocal Trig Functions: Let t be a real number and let (x, y) be the point on the unit circle corresponding to t . (cosecant) csc t = 1/sin t = 1/y, y 0 (secant) sec t = 1/cos t = 1/x, x 0 (cotangent) cot t = 1/tan t = x/y, y 0
Ex 3: Evaluate (if possible) the six trig functions of the real number. 2 2 − 2 , A. t = 3 /4 2 2 2 2 2 sin (3 /4) = csc (3 /4) = 2 2 2 cos (3 /4) = sec (3 /4) = 2 2 2 1 1 tan (3 /4) = cot (3 /4) = 1 1
Ex 3 (cont’d) : Evaluate (if possible) the six trig functions of the real number. 0, −1 B. t = - /2 1 1 csc (- /2) = sin (- /2) = 1 1 1 Undefined sec (- /2) = cos (- /2) = 0 0 1 0 0 cot (- /2) = tan (- /2) = 1 0 Undefined Homework: p.147 #6-28 even
Recommend
More recommend