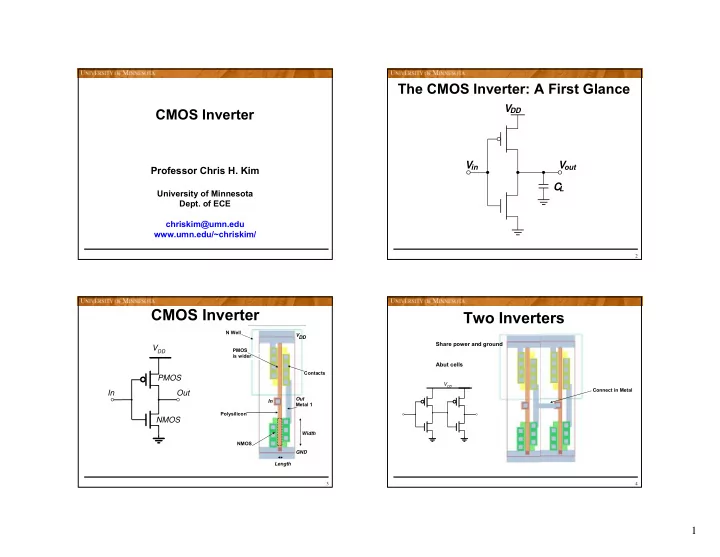

The CMOS Inverter: A First Glance V CMOS Inverter DD V in V out Professor Chris H. Kim C L University of Minnesota Dept. of ECE chriskim@umn.edu www.umn.edu/~chriskim/ 2 CMOS Inverter Two Inverters N Well VDD Share power and ground V DD PMOS is wider Abut cells Contacts PMOS V DD Connect in Metal In Out Out In Metal 1 Polysilicon NMOS Width NMOS GND Length 3 4 1
CMOS Inverter First-Order DC Analysis V DD V DD Voltage Transfer R p V OL = 0 Characteristics V OH = V DD V M = f(R n , R p ) V out V out R n V in = V DD V in = 0 6 CMOS Inverter VTC CMOS Inverter Load Characteristics NMOS off PMOS lin 2.5 I Dn NMOS sat V in = 0 V in = 2.5 PMOS lin 2 PMOS in = 0.5 V in = 2 NMOS V V out NMOS sat 1.5 PMOS sat in = 1 in = 1.5 V V 1 NMOS lin in = 1.5 V in = 1 V PMOS sat 0.5 NMOS lin in = 1.5 V in = 1 V V in = 2 PMOS off in = 0.5 V in = 2.5 V in = 0 V 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 V in V out 7 8 2
Simulated Inverter VTC (hspice) Switching Threshold as a Function of Transistor Ratio 2.5 1.8 2 1.7 1.6 1.5 V out (V) 1.5 V (V) 1.4 M 1.3 1 1.2 1.1 0.5 1 0.9 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 0.8 10 0 10 1 V in (V) W p /W n 9 10 VTC as a function of VDD Impact of Sizing 2.5 2.5 0.2 2 Wider 2 PMOS 0.15 1.5 out (V) 1.5 out (V) Symmetrical out (V) 0.1 Wider V V V 1 1 NMOS 0.05 0.5 0.5 Gain=-1 0 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 V in (V) 0 V in (V) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 V in (V) 11 12 3
Impact of Process Variations DC Operation Voltage Transfer Characteristic 2.5 V(y) VOH = f (VOL) 2 Fast PMOS VOH f VOL = f (VOH) Slow NMOS V(y)=V(x) VM = f (VM) out (V) 1.5 Nominal Switching Threshold Fast NMOS V V M 1 Slow PMOS VOL 0.5 VOL VOH V(x) 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 V in (V) Nominal Voltage Levels 13 14 Mapping between analog and digital Definition of Noise Margins signals Vout "1" VOH “ 1” Slope = -1 V OH VOH VIH NM H Noise margin high VIH Undefined Undefined Region Region VIL NM L Noise margin low VOL Slope = -1 VIL "0" V OL Gate Input “ 0” VOL Gate Output VIL VIH Vin 15 16 4
Regenerative Property Example: CMOS Inverter DC Properties out out v 3 v 3 • V OH = V DD = 2.5V f (v) fin v(v) • V OL = 0V v 1 v 1 • V IL = 1.05V v 3 fin v(v) f (v) • V IH = 1.45V • N MH =1.05V • N ML = 1.05V v 2 v 0 in v 0 v 2 in • V M = 1.2V Regenerative Non-Regenerative 17 18 Regenerative Property v0 v1 v2 v v v v 3 4 5 6 A chain of inverters Propagation Delay 5 v 0 V (Volt) 3 v 1 1 v 2 2 1 0 2 4 6 8 10 Simulated response t (nsec) 19 5
Computing the Capacitances CMOS Inverter: Transient Response V DD V DD V DD V DD t pHL = f(R on .C L ) M 2 R p M 4 C g 4 C db 2 = 0.69 R on C L C gd 12 V out V out 2 V in V out C db 1 C w C g 3 V out M 3 M 1 C L Interconnect C L R n Fanout V in V out Simplified C L Model V in = 0 V in = V DD (a) Low-to-high (b) High-to-low 21 22 Delay Definitions CMOS Inverter Propagation Delay V in V DD 50% t pHL = C L V dd /2 I av t t pHL t pLH V out V out 90% I av C L 50% t 10% t f t r V in = V DD 23 24 6
Design for Performance Transient Response • Keep capacitances small 3 • Increase transistor sizes 2.5 2 – watch out for self-loading! t p = 0.69 C L (R eqn +R eqp )/2 • Increase V DD 1.5 out (V) t pHL t pLH V 1 0.5 0 -0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 t (sec) -10 x 10 25 26 Device Sizing Delay as a function of V DD -11 3.8 x 10 5.5 (for fixed load) 5 3.6 t p (normalized) 4.5 3.4 4 3.2 t p (sec) 3.5 3 3 2.8 Self-loading effect: Intrinsic capacitances 2.5 2.6 dominate 2 2.4 1.5 2.2 1 2 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Size Vdd (V) 27 28 7
NMOS/PMOS ratio Impact of Rise Time on Delay -11 5x 10 0.35 tpHL tpLH 4.5 0.3 t pHL (nsec) tp t p (sec) 0.25 β = W p /W n 4 0.2 3.5 0.15 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 t rise (nsec) 3 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 β t p = t step ( i ) + ht step ( i -1) 29 30 Ring Oscillator Fan-in and Fan-out v 0 v 1 v 2 v 3 v 4 v 5 M N v 0 v 1 v 5 Fan-out N Fan-in M T = 2 × t p × N 31 32 8
CMOS Properties • Full rail-to-rail swing • Symmetrical VTC • Propagation delay function of load capacitance and resistance of transistors • No static power dissipation (ignoring leakage current) • Direct path current during switching 33 9
Recommend
More recommend