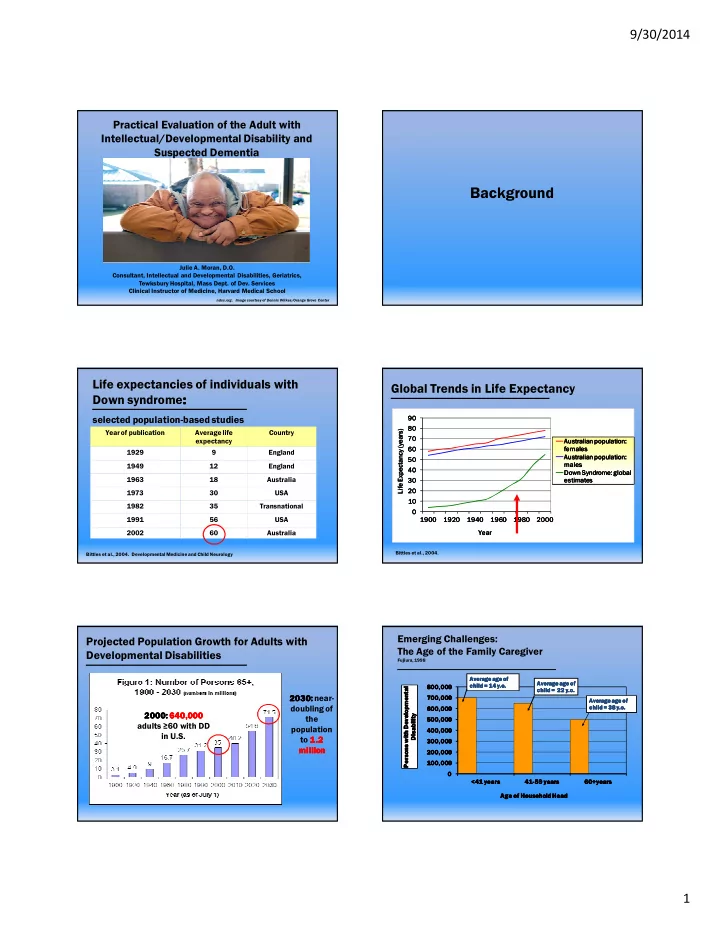

9/30/2014 Practical Evaluation of the Adult with Intellectual/Developmental Disability and Suspected Dementia Background Julie A. Moran, D.O. Consultant, Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, Geriatrics, Tewksbury Hospital, Mass Dept. of Dev. Services Clinical Instructor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School ���������������������������������������������������������������� Life expectancies of individuals with Global Trends in Life Expectancy Down syndrome: : : : selected population8based studies �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� Year of publication Average life Country ����������������������� ����������������������� ����������������������� ����������������������� �� �� �� �� expectancy ������������ ������ �!� ������������ ������ �!� ������������ ������ �!� ������������ ������ �!� �� �� �� �� ��"���� ��"���� ��"���� ��"���� 1929 9 England ������������ ������ �!� ������������ ������ �!� ������������ ������ �!� ������������ ������ �!� �� �� �� �� "���� "���� "���� "���� 1949 12 England �� �� �� �� # $��%��&� "�!�'� (��� # $��%��&� "�!�'� (��� # $��%��&� "�!�'� (��� # $��%��&� "�!�'� (��� 1963 18 Australia �� �� ����"���� ����"���� ����"���� ����"���� �� �� �� �� �� �� 1973 30 USA �� �� �� �� 1982 35 Transnational � � � � 1991 56 USA ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� ���� 2002 60 Australia ���� ���� ���� ���� Bittles et al., 2004 � Bittles et al., 2004. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology Emerging Challenges: Projected Population Growth for Adults with The Age of the Family Caregiver Developmental Disabilities Fujiura, 1998 Average age of Average age of Average age of Average age of Average age of Average age of Average age of Average age of child = 14 y.o child = 14 y.o. . Disability Disability Disability Disability 800,000 800,000 800,000 800,000 child = 14 child = 14 y.o y.o . . Persons with Developmental Persons with Developmental Persons with Developmental Persons with Developmental child = 22 y.o child = 22 child = 22 child = 22 y.o. y.o y.o . . . 2030 2030: 2030 2030 : : near8 : 700,000 700,000 700,000 700,000 Average age of Average age of Average age of Average age of doubling of child = 38 child = 38 y.o child = 38 child = 38 y.o. y.o y.o . . . 600,000 600,000 600,000 600,000 2000 2000 2000: 2000 : : : 640,000 640,000 640,000 640,000 the 500,000 500,000 500,000 500,000 adults ≥60 with DD population 400,000 400,000 400,000 400,000 in U.S. to 1.2 1.2 1.2 1.2 300,000 300,000 300,000 300,000 million million million million 200,000 200,000 200,000 200,000 100,000 100,000 100,000 100,000 0 0 0 0 <41 years <41 years <41 years <41 years 418 41 41 41 8 8 859 years 59 years 59 years 59 years 60+years 60+years 60+years 60+years Age of Household Head Age of Household Head Age of Household Head Age of Household Head 1
9/30/2014 “For People With Down Syndrome, Longer Life “For People With Down Syndrome, Longer Life “For People With Down Syndrome, Longer Life “For People With Down Syndrome, Longer Life Has Complications Has Complications” Has Complications Has Complications Published: June 1, 2008 Published: June 1, 2008 Published: June 1, 2008 Published: June 1, 2008 By Sally Sara How well8prepared is the medical community to care for older adults with I/DD? “Seeking Grown “Seeking Grown8 8up Care” up Care” “Seeking Grown “Seeking Grown 8 8 up Care” up Care” Accelerated Aging in Down syndrome Published: February 2, 2009 Published: February 2, 2009 Published: February 2, 2009 Published: February 2, 2009 By Patricia Wen Alzheimer’s disease Hypothyroidism Sensory deficits Early/aggressive cataracts Sensorineural hearing loss Early menopause Atlantoaxialinstability Obstructive sleep apnea Osteoarthritis Decrease in functional ability Osteoporosis ���������������������������������������������������������������� Common Conditions in Older Adults But what about everything else?? with CP Contractures and worsened – Sturge Weber? spasticity – Congenital hydrocephalus? Neurogenic bowel and bladder – Prader Willi? Osteoarthritis – Autism?? Osteoporosis GERD What is normative aging in I/DD? What is normative aging in I/DD? What is normative aging in I/DD? What is normative aging in I/DD? Poor dental hygiene PAIN http://www.teamhoyt.com/gallery / 2
9/30/2014 Additional lifespan considerations for Challenge unique to adults with I/DD: this current aging generation OVERdiagnosis State institutionalization •Failing to recognize changes Failing to recognize changes or Failing to recognize changes Failing to recognize changes Early and prolonged exposure to attributing them to the patient’s psychoactive medications intellectual disability Lack of formal, expert diagnosis UNDERdiagnosis by either: Poor medical record8keeping •Over Over Over8 Over 8 8 8calling calling calling calling the diagnosis the diagnosiswithout the diagnosis the diagnosis Lack of longitudinal historians exploring all other possibilities Lack of ongoing family contact Fear of support services Prevalence of dementia in I/DD • Historically conflicting data • In adults with I/DD not due to Down Risk of Dementia syndrome: – Longitudinal study from 2004 1 concluded rates of dementia were ≤ rates in the general population – Epidemiologic survey of 281 adults from 2009 2 found that dementia was 283 times more common in the non8DS ID/DD population 1. Zigman et al. Am Journal of MR, 2004. 2. Strydom et al. Psych Med, 2009. Prevalence of AD in adults with DS Genetic link between DS and AD 3 copies of chromosome 21 in DS (trisomy) Gene coding for APP overexpressed on chromosome 21 Other genes on 21 also likely associated with changes of premature AD as well as accelerated aging Prasher, VP. Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia in Down Syndrome and Intellectual Disabilities, 2005. 3
Recommend
More recommend