
1
Middle Pleistocene hominins -Europe becomes more permanently and densely populated -Middle Pleistocene hominins remained and expanded ranges of H. erectus 2
Late Pleistocene: 125-10 kya -Last glaciations -Neandertal emerges in Europe H. heidelbergensis in Europe gave rise to Neandertal H. heidelbergensis in Africa gave rise to Homo sapiens 3
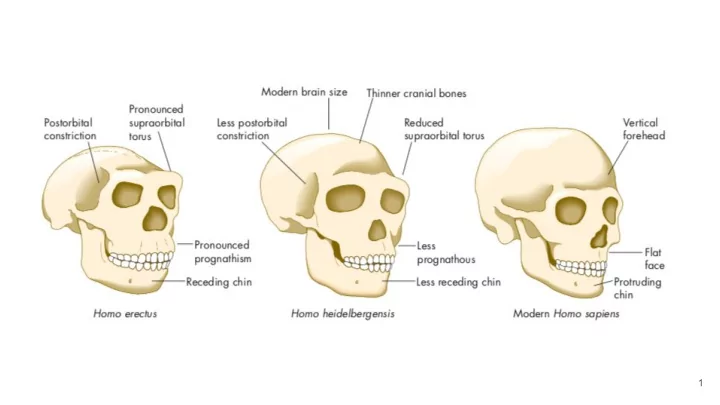
Homo heidelbergensis 850,000-200,000 ya Widely dispersed in Africa and Europe 4
Homo heidelbergensis Morphological changes from Homo erectus -Increased brain size, rounded braincase 5
The Pleistocene Epoch 6
Pleistocene epoch 1.8 mya-10 kya The Ice Age Middle Pleistocene: 780-125 kya -Numerous glacial and interglacial s occurred -Climatic oscillations affected African, European, and Asian hominins Late Pleistocene: 125-10 kya -Last glaciations - Neandertal emerges in Europe 7
Middle Pleistocene African setting Interglacial periods: more rainfall Glacial periods: more arid 8
Middle Pleistocene European setting Interglacial periods: Open migration routes to Europe thru Eurasia Glacial periods: Colder and inaccessible to migrating hominins thru Eurasia 9
Homo heidelbergensis 850-200 kya Widely dispersed in Africa and Europe Morphological changes from Homo erectus -Increased brain size, rounded braincase 10
Middle Pleistocene hominins (MPh) sites Europe 500-400 kya Atapuerca, Spain -80% of MPh remains found here -Evidence of early Neandertal transition 11
Middle Pleistocene culture -Still using Acheulian tools Levallois technique -More control over flake size/shape -Suggests increased cognitive capabilities 12
Middle Pleistocene hominin culture -Caves and open-air campsites -Made temporary structures Subsistence: increased variety in food resources: fruits, vegetables, seeds, nuts, eggs, and... Unique: marine resources: fish, mussels, shellfish, etc. 13
Middle Pleistocene hominins sites Africa 600 kya Bodo, Ethiopia -Earliest H. heidelbergensis site 14
Neandertal 130-30 kya 15
Neandertal -Most neandertal sites are in Europe 16
Neandertal morphology Cranial -Occipital bun CC=1520 cm 3 17
Neandertal morphology Postcranial -Robust, muscular, stockier -Shorter limbs Morphology = adaptations to colder European climate 18
Neandertal culture Mousterian tool industry (125-40 kya) -More flake tools vs core tools -Tools for skinning and making clothes -Regular fire use 19
Neandertal culture Confrontational hunters -Close-proximity hunting with thrusting spears -Pattern of trauma on Neandertal skeletons matches pattern of trauma on rodeo performers 20
Neandertal culture and behavioral traits Symbolic behavior -Intentional burials -Personal art: applied pigment to shells -Capable of making human-like sounds -No evidence of human-like language 21
Neandertal sites Western Asia 70-60 kya Shanidar, Iraq -Burial of disabled man 22
Neandertal sites Western Asia 70-60 kya Shanidar, Iraq -Burial of disabled man 23
Denisovans -Genetic evidence of an extinct hominin 24
Neandertal culture recap -Confrontational hunters -Infrequent intentional burials -Capable of symbolic behavior -Adapted to cold climates -No evidence of human-like language 25
Recommend
More recommend