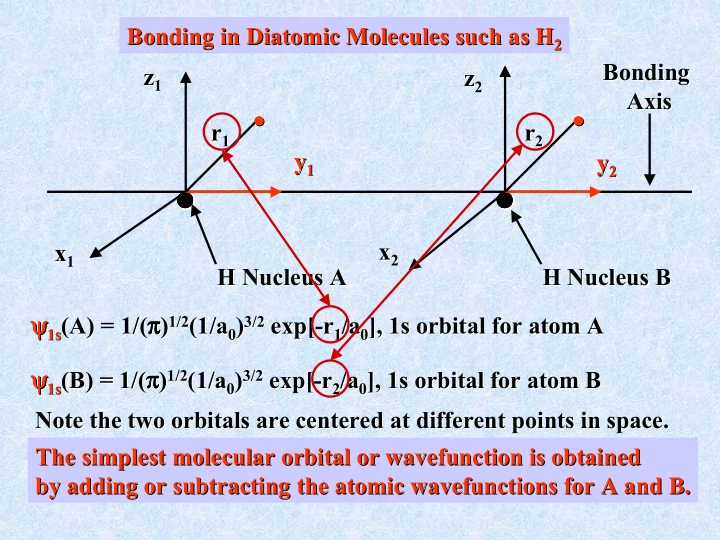

Bonding in Diatomic Molecules such as H 2 Bonding in Diatomic Molecules such as H 2 Bonding Bonding z 1 z z 2 z 1 2 Axis Axis • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • r 1 r 2 r r 1 2 y 1 y y 2 y 1 2 • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • x 2 x 1 x x 2 1 H Nucleus A H Nucleus B H Nucleus A H Nucleus B 3/2 exp ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ (A) = 1/( π π ) π π π π ψ ψ π π ) 1/2 (1/a 0 ) 3/2 exp[ [- -r r 1 /a 0 ], 1s orbital for atom A 1s (A) = 1/( 1/2 (1/a 0 ) 1 /a 0 ], 1s orbital for atom A 3/2 exp ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ (B) = 1/( π π π π ) π π ψ ψ π π ) 1/2 (1/a 0 ) 3/2 exp[ [- -r r 2 /a 0 ], 1s orbital for atom B 1s (B) = 1/( 1/2 (1/a 0 ) 2 /a 0 ], 1s orbital for atom B Note the two orbitals orbitals are centered at different points in space. are centered at different points in space. Note the two The simplest molecular orbital or wavefunction wavefunction is obtained is obtained The simplest molecular orbital or by adding or subtracting the atomic wavefunctions wavefunctions for A and B. for A and B. by adding or subtracting the atomic
σ 1s σ σ σ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ σ σ σ σ [ ψ ψ ψ ψ (A) + ψ ψ ψ ψ = C 1 (B)], Sigma 1s Bonding Molecular Bonding Molecular 1s = C 1 [ 1s (A) + 1s (B)], Sigma 1s orbital. C 1 is a constant. orbital. C 1 is a constant. σ σ 1s σ σ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ - ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ σ σ σ σ [ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ * = C 2 (A) - (B)], Sigma 1s Anti Anti- -bonding Molecular bonding Molecular 1s * = C 2 [ 1s (A) 1s (B)], Sigma 1s orbital. C 2 is a constant. orbital. C 2 is a constant. Note that probabilities for finding electron at some position in Note that probabilities for finding electron at some position in 2 and [ σ σ 1s σ σ σ σ 1s σ σ space scale like [ σ σ σ σ and [ σ σ σ σ ] 2 *] 2 2 : : space scale like [ 1s ] 1s *] 2 = {C 2 = σ σ 1s σ σ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ - ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s [ σ σ σ σ [ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ *] 2 = {C 2 (A) - (B)]} 2 = [ 1s *] 2 [ 1s (A) 1s (B)]} ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s {[ ψ ψ ψ ψ + [ ψ ψ ψ ψ 2[ ψ ψ ψ ψ (A)][ ψ ψ ψ ψ (C 2 ) 2 2 {[ (A)] 2 2 + [ (B)] 2 2 - - 2[ (B)]} } (C 2 ) 1s (A)] 1s (B)] 1s (A)][ 1s (B)] Extra Term Extra Term [ σ σ 1s σ σ σ σ σ σ “Non- -interacting” part of interacting” part of [ *] 2 “Non 1s *] 2 (note difference (note difference “Non- -interacting” part is result for large interacting” part is result for large “Non in sign!). in sign!). separation between nucleus A and B separation between nucleus A and B [Zero for large [Zero for large A, B separation.] A, B separation.] 2 = {C [ σ σ σ 1s σ σ σ [ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ (A) + ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ σ σ ψ ψ ψ ψ ] 2 = {C 1 (B)]} 2 = [ 1s ] 1 [ 1s (A) + 1s (B)]} 2 = ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ {[ ψ ψ ψ ψ + [ ψ ψ ψ ψ + 2[ ψ ψ ψ ψ (A)][ ψ ψ ψ ψ (C 1 ) 2 2 {[ (A)] 2 2 + [ (B)] 2 2 + 2[ (B)]} } (C 1 ) 1s (A)] 1s (B)] 1s (A)][ 1s (B)] σ 1s σ [ σ σ σ σ σ σ “Non- -interacting” part of interacting” part of [ ] 2 “Non 1s ] 2
+ H 2 Wave Func t i o ns Wave Func t i o ns El e c t ron Den s i t i e s El e c t ron Den s i t i e s ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ] 2 (A) 1s (A) * ] [ σ [ σ [ σ [ σ ] ] σ * = C A B [ ψ ψ − ψ ψ − − ψ − ψ ψ ψ ] σ σ σ 2 1s 1s 1s 1s + B ANTIBONDING - away from - Pushes e - away from Pushes e A A B region between region between ψ ψ 1s - ψ ψ ψ ψ - 2[ ψ ψ ψ 1s (A)][ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s (B)] ψ ψ ψ (B) - 1s (B) nuclei A and B nuclei A and B A B [ ψ + ψ ψ + ψ ψ + ψ ] ψ + ψ σ σ σ σ + 2[ ψ ψ 1s (A)][ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s (B)] ψ = C ] 2 [ σ [ σ [ σ [ σ ] ] ] 1 1s 1s 1s 1s BONDING + + - between Pushes e - between Pushes e A B nuclei A and B A B nuclei A and B 2 2 2 2 ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s ψ ψ ψ [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] ψ ψ ψ ψ 2 (n.i.) [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] [(ψ ) + (ψ ) ] A B (A) (B) ψ 2 ~ A B 1s (A) 1s (B) ψ (n.i.) ~ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ ψ 1s 1s 1s 1s + + N ON-INTERACTING A B A B
+ Potential Energy of H 2 H R H R V(R) Separated H, H + σ * σ σ σ * 1s H + H + H + H + R R 0 ∆ E d = ∆ E d = 255 kJ mol mol - -1 1 255 kJ σ σ 1s σ σ Single electron Single electron + together + holds H 2 together holds H 2 1.07 Å 1.07 Å
CORRELATION DIAGRAM CORRELATION DIAGRAM Energy Ordering: H 2 H σ 1 σ σ 1 σ σ σ σ σ s < 1s < σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ * σ σ 1s s * ( σ σ σ σ σ σ For H 2 ) 2 , Bond order = For H 2 ( 1s ) 2 , Bond order = 2 1 s 1 1 s 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 (1/2)(2- -0) = 1 0) = 1 (1/2)(2 σ σ 1 σ σ σ σ σ σ * s * 1 s 1 1 1 1 1 1 E 1s 1s (H Atom A) (H Atom B) Atomic Orbital Atomic Orbital σ 1 σ σ σ σ σ σ σ 1 1 1 1 1 s 1 1 s H 2 Molecular Orbitals Orbitals H 2 Molecular Bond order =(1/2)[# electrons in bonding orbitals orbitals - - Bond order =(1/2)[# electrons in bonding #electrons in antibonding orbitals antibonding orbitals] ] #electrons in H-H Bond Length = 0.74Å; Bond Energy = 431 kJ/mole. Strong + (255 kJ/mole) bond! Note: is about 1/2 bond Energy of H 2
CORRELATION DIAGRAM CORRELATION DIAGRAM 2 Bond Z for He =2 σ 1s σ σ σ 1s ( σ σ σ σ ( σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ For He 2 ) 2 *) 2 Bond He 2 For He 2 ( 1s ) 2 ( 1s *) He 2 order = (1/2)(2- -2) = 0 2) = 0 order = (1/2)(2 σ 1 σ σ σ σ σ σ σ * s * 1 s 1 1 1 1 1 1 E 1s 1s (He Atom A) (He Atom B) Atomic Orbital Atomic Orbital σ 1 σ σ σ σ σ σ σ 1 1 s 1 1 1 1 1 s He 2 Molecular Orbitals Orbitals He 2 Molecular He 2 barely exists under the most extreme He 2 barely exists under the most extreme ± ± ± ± 4Å!! Bond He bond length 52 ± ± ± ± conditions: He- -He bond length 52 4Å!! Bond conditions: He Energy ~ 0.008 Joules/mole!!!! Energy ~ 0.008 Joules/mole!!!! (Phys. Rev. Letts Letts. . 85 85, 2284 , 2284- -87(2000)) 87(2000)) (Phys. Rev.
Bonding for Second Row Diatomics Diatomics Bonding for Second Row Involves the n=2 Atomic Shell Involves the n=2 Atomic Shell Lithium atomic configuration is 1s 2 2s 1 (Only the 2s electron is a valence electron.) 2 = [KK]( σ σ 1s σ σ 1s σ 2s σ σ σ 2s [( σ σ σ σ ( σ σ σ σ ] ( σ σ σ σ ( σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ σ ) 2 *) 2 ) 2 ) 2 Li 2 dimer has the configuration: [( 1s ) 2 ( 1s *) 2 ] ( 2s ) 2s ) 2 CORRELATION DIAGRAM CORRELATION DIAGRAM σ σ 2s ( σ σ σ σ σ σ For Li 2 ) 2 , Bond order = For Li 2 ( 2s ) 2 , Bond order = Li 2 Li (1/2)(2- -0) = 1 0) = 1 (1/2)(2 2 σ σ 2 σ σ σ σ σ σ * s * 2 2 s 2 2 2 2 2 E 2s 2s (Li Atom A) (Li Atom B) Atomic Orbital Atomic Orbital σ σ σ σ 2 σ σ σ σ 2 2 s 2 2 2 2 2 s Li 2 Molecular Orbitals Orbitals Li 2 Molecular
Bonding for Second Row Diatomics: the Role of 2p Orbitals Once the σ σ 2s , σ σ 2s * molecular orbitals formed from the σ σ σ σ 2s atomic orbitals on each atom are filled (4 electrons, Be 2 ), we must consider the role of the 2p electrons (B 2 is first diatomic using 2p electrons). There are 3 different sets of p orbitals (2p x , 2p y , and 2p z ), all mutually perpendicular. If we choose the molecular diatomic axis to be the z axis (this is arbitrary), we have a picture like this:
Bonding x 1 2p z z obital on x 2 2p 2p z orbitals 2p z orbitals Axis atom 1 and atom 2 point at at point each other. each other. z 1 z z 2 z 1 2 • • • • • • • • - - + + y 2 y 1 Nucleus A Nucleus B 2p x orbitals 2p x orbital on 2p x orbital on Bonding x 1 x 2 are atom 1 and atom 2 atom 1 and atom 2 Axis parallel to each + + z 1 z z 2 z other. 1 2 • • • • • • • • - - y 2 y 1 Nucleus A Nucleus B
z Axis is taken to be line through A, B z Axis is taken to be line through A, B Nodal Plane - z - - - + + + + axis A B A B 2p 2p z z * ( (Antibonding Antibonding) ) σ σ σ σ 2p z 2p z (A) + 2p z (B) 2p z (A) + 2p z (B) z - - - - + + + axis A B A B 2pz -2pz σ σ σ σ (Bonding) (Bonding) 2p z 2p z (A) - - 2p 2p z (B) 2p z (A) z (B) Molecular Orbitals Orbitals Molecular Atom ic Orbitals Orbitals Atom ic Bonding with 2p Orbitals Orbitals Bonding with 2p of Atom s A,B of Atom s A,B
⊥ to bond (z) axis ⊥ ⊥ ⊥ Note: orbital is ⊥ ⊥ ⊥ ⊥ to bond (z) axis Note: orbital is Nodal Plane x - + - + A B A B z - + - + 2p x -2p x π π * π π (antibonding) 2p 2p x (A) - - 2p 2p x (B) 2p x (A) x (B) x A,B Nodal Plane + + + A B z A B - - - 2p x 2p x π π π π (bonding) 2p 2p x (A) + 2p x (B) 2p x (A) + 2p x (B) Molecular Orbitals Orbitals Molecular Atom ic Orbitals Orbitals Atom ic Bonding with 2p Orbitals Orbitals ( (cont cont) ) Bonding with 2p of Atom s A,B of Atom s A,B
Recommend
More recommend