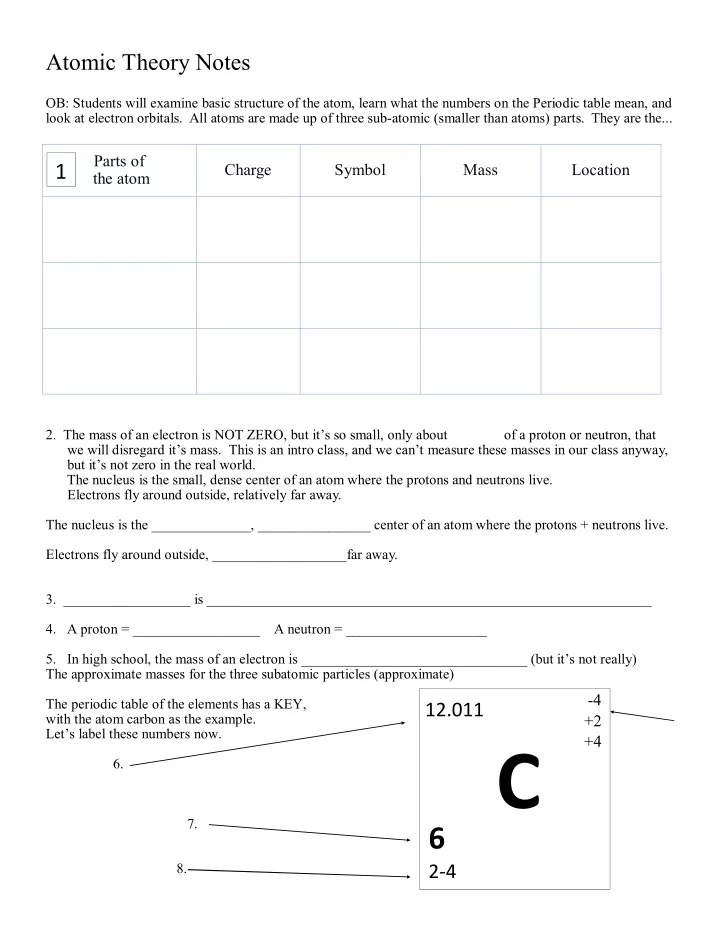

Atomic Theory Notes OB: Students will examine basic structure of the atom, learn what the numbers on the Periodic table mean, and look at electron orbitals. All atoms are made up of three sub-atomic (smaller than atoms) parts. They are the... Parts of 1 Charge Symbol Mass Location the atom 2. The mass of an electron is NOT ZERO, but it’s so small, only about of a proton or neutron, that we will disregard it’s mass. This is an intro class, and we can’t measure these masses in our class anyway, but it’s not zero in the real world. The nucleus is the small, dense center of an atom where the protons and neutrons live. Electrons fly around outside, relatively far away. The nucleus is the ______________, ________________ center of an atom where the protons + neutrons live. Electrons fly around outside, ___________________far away. 3. __________________ is _______________________________________________________________ 4. A proton = __________________ A neutron = ____________________ 5. In high school, the mass of an electron is ________________________________ (but it’s not really) The approximate masses for the three subatomic particles (approximate) -4 The periodic table of the elements has a KEY, 12.011 with the atom carbon as the example. +2 Let’s label these numbers now. +4 C 6. 7. 6 8. 2-4
9. Atomic Mass Numbers will be rounded to the _______________________________________ (they are not really whole numbers, we’ll get to that later) 10. Mass Number = mass of _____________________ + ____________________________ 11. The mass of mercury is 201 amu, so mercury has a total of 201 protons plus neutrons. How many of each??? Let’s learn how to figure this out 12. How many protons, neutrons, and electrons in the element TIN? 14. All atoms are electrically neutral, The number of _____________ = the number of _________________ The positives = the negatives. Always. Every atom is neutrally charged. The positive protons + negative electrons always BALANCE. Determine how many protons, neutrons, and electrons are in these three atoms In, Nb, and Ba. Write in their NAMES too. 15. In 16a. Nb 16b. Ba Name Name name
There are several ways to “write” symbols that stand for atoms, here’s another, more formal method. Copy calcium and label the numbers Ca 17. Write the formal symbols, with the proper numbers, in the RIGHT PLACE, for mercury chlorine copper 18. Electrons do not fly around randomly. They stay in ________________________________, which are also called _________________________________. 19. The closer to the nucleus, the ____________________ the energy level is. The further away from the nucleus, the _____________________ the energy level that orbital is. 20. The orbitals are only so big, they fit ________________________________________________________ Orbital Noble gases Configurations 2 1 st He ex 2 nd Ne 21 3 th Ar 22 4 th Kr 23 5 th Xe 24 6 th Rn 25
26. The 1 st orbital holds a maximum of ______ electrons. The 2 nd orbital holds a maximum of ______ electrons The 3 rd orbital is weird. The 3 rd orbital can “fill up” with _____ electrons, or stretch out to hold up to ______ electrons. The 4 th , 5 th , and 6 th orbitals can stretch too. 27. Find silver, how many electrons does it have? _________ 28. Find hafnium, how many electrons, how many neutrons in this element? _____e _____n 29. What element has 16 protons and 16 electrons ? ________ 30. What’s the symbol for tungsten? _____ How many electrons are in this element? _____ ———————- 31. Democritus said: the INDIVISIBLE PARTICLE is called the __________________________. 32. John Dalton’s Atomic Theory… 33. Dalton imagined his atom to look like a _______________________ __________________ 34. Around 1837 J. J. Thomson discovers the ________________________ (and later gets a Nobel Prize). 35. Thomson did a variety of experiments, some using what’s called the _______________________________ to detect and measure electrons. He found the first subatomic particle, which was ___________________ charged. 36. Thomson describes the atom as ______________ ________________________________!
1. In 1908, my chemical hero, Ernest J. Rutherford discovers the nucleus! He gets the Nobel Prize as well. 37. Rutherford’s ______________ _______________ experiment helps him discover the nucleus, and figure out the physical structure of the modern atom. 38. Listen first, then draw. This drawing is online, you can add details later if you need to. 39. What does the Gold Foil Experiment prove? 1. Atoms are mostly __________________ ____________________ (since most of the alpha particles pass though the foil like it’s not really there.) 2. Atoms are neutral (he knew this) so the nucleus must be ________________________________________. since the alpha particles which are positive didn’t stick, and they dinged off of something big every once in a while. 3. Neutral atoms must therefore have the negatively charged electrons ________________________________ flying around outside (like planets?) made sense.
40. The Rutherford model is named the ______________________ model. He perceives the electrons flying around the atom’s nucleus like the ____________________________________. 41. But there were serious PROBLEMS with this new theory, even though he was RIGHT. How can atoms be mostly _________________________________? How can they be mostly “not” there? How can these negative electrons fly around a positive center, but they ________________________________________________________________? Why not? They just keep flying? They never use up their energy? Ever? Really? How far away are these electrons from the nucleus? Do they just fly willy-nilly, or _________________________________________ to them? 42. _______________ ______________________ is able to do some very funky math, and he proves the Rutherford model of the atom is correct. He too wins a Nobel Prize. The Bohr Model - the Planetary model with more detail 43. He expands on the simple planetary model of Rutherford, and put the electrons into ______________________________ _________________________, or energy levels. 44. He proves that for hydrogen, if the electron flies at the right speed, and the right distance, it will mathematically _____________________________________________________________________, and stay in orbit forever around the nucleus. 45 . His math only works for the simplest atom _________________ with its single electron. 46. Nitrogen Draw a simple Bohr or Planetary Model of the atom has…
47. Niels Bohr further determines that electrons could gain a specific amount of energy, an amount called a ______________________________________________, which enables the electrons to “jump” up to a higher than normal energy level or excited state. 48. The excited state is __________________________________, and the electron will soon move back to the lower energy, more stable, ground state. 49. Since every atom was ___________________ (they all have different numbers of protons and different electron configurations) it takes unique amounts of energy to make these upward “jumps” possible. 50. The electrons, in this new excited state, were less stable than the were in the normal or ground state. To get back to normal, or back to the ground state, electrons would have to give back or _______________________________________________________________of energy they just gained to get excited. 51. The energy they give back is also unique, and we can see it with our own eyes! It’s called ____________ 52. The modern model …. 53. It’s called the __________________________________________________________________ because the electrons sometimes act like waves of energy, and sometimes like little bits of mechanical matter with a negative charge. 54. This model is more about the _________________________________________________________ of finding an electron’s location MOST OF THE TIME, not all of the time. 55. ___________________ are like teenagers, they are where they should be most of the time, but not always.
Symbol Name Ground State Excited State 56 Li 57 Na 58 Mg 59 Ca 60 He 61 Ne 62 Ar 63. Ground + Excited State electron configurations have the number of electrons, the electrons are just in __________________________________ places. 64. How do electrons get excited? They absorb __________________ amounts of ____________________, called a ______________________________________ of energy. A quantum means a specific amount. 65. Spectra is produced when this unique, quantum of energy is ____________________________________ as ________________________________ __________________________________. 66. The color of light, or the SPECTRA that we see, is a _____________________________ of many colors of light that our eyes blur together. 67. A refractive lens can break up this mixture of colors into a unique _______________________________. 68. The orange light given off by the neon lamp is the _________________________.
Recommend
More recommend