When computer arithmetic and signal processing meet Anastasia - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG When computer arithmetic and signal processing meet Anastasia Volkova, Thibault Hilaire , Christoph Lauter Metalbim workshop, March
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG When computer arithmetic and signal processing meet Anastasia Volkova, Thibault Hilaire , Christoph Lauter Metalbim workshop, March 12th, 2018 Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 1/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Plan 1 Context and problematics 2 Determining the Most Significant Bit 3 Compute the quantized transfer function 4 WCPG Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 2/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Applications: reliable systems Digital filters: Algorithms that transform digital signals • Do not need guarantee in the majority of applications • A guarantee is necessary in other applications. Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 3/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Applications: reliable systems Digital filters: Algorithms that transform digital signals • Do not need guarantee in the majority of applications • A guarantee is necessary in other applications. We are interested in guarantees related to the implementation of numerical algorithms, especially in the embedded systems. Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 3/23
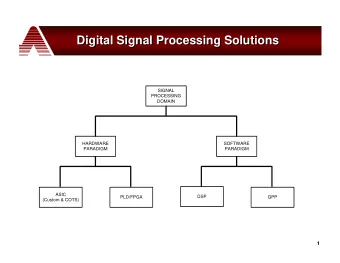
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Automation The implementation is done in several steps: Constraints Software Mathematical Numerical Code algorithm algorithm generation Specifications Numerous constraints: • performance • energy consumption • surface • memory • accuracy • etc. We are interested in the automated process of reliable implementation. Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 4/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Arithmetics 2 w − 1 2 0 • Integer arithmetic: y = Y w Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 5/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Arithmetics 2 w − 1 2 0 • Integer arithmetic: y = Y w 2 0 2 − 1 − 2 m 2 ℓ • Fixed-Point arithmetic: y = Y · 2 ℓ m + 1 − ℓ where ℓ is an implicit factor w Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 5/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Arithmetics 2 w − 1 2 0 • Integer arithmetic: y = Y w 2 0 2 − 1 − 2 m 2 ℓ • Fixed-Point arithmetic: y = Y · 2 ℓ m + 1 − ℓ where ℓ is an implicit factor w • Floating-Point arithmetic: s y = ( − 1 ) s · Y · 2 e exponent mantissa where e is an explicit factor Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 5/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Arithmetics 2 w − 1 2 0 • Integer arithmetic: y = Y w 2 0 2 − 1 − 2 m 2 ℓ • Fixed-Point arithmetic: y = Y · 2 ℓ m + 1 − ℓ where ℓ is an implicit factor w • Floating-Point arithmetic: s y = ( − 1 ) s · Y · 2 e exponent mantissa where e is an explicit factor • Interval arithmetic: � � [ y , y ] = y ∈ R | y � y � y Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 5/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Arithmetics 2 w − 1 2 0 • Integer arithmetic: y = Y w 2 0 2 − 1 − 2 m 2 ℓ • Fixed-Point arithmetic: y = Y · 2 ℓ m + 1 − ℓ where ℓ is an implicit factor w • Floating-Point arithmetic: s y = ( − 1 ) s · Y · 2 e exponent mantissa where e is an explicit factor • Interval arithmetic: � � [ y , y ] = y ∈ R | y � y � y • Multiple-Precision arithmetic: the size of the mantissa varies dynamically Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 5/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Arithmetics • Fixed-Point arithmetic: y = Y · 2 ℓ For the implementation where ℓ is an implicit factor • Floating-Point arithmetic: y = ( − 1 ) s · Y · 2 e For the error analysis where e is an explicit factor • Interval arithmetic: � � For the error analysis [ y , y ] = y ∈ R | y � y � y • Multiple-Precision arithmetic: the size For the error analysis of the mantissa varies dynamically Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 5/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG State-space representation State-space representation of an LTI filter H : � x ( k + 1 ) = Ax ( k ) + b u ( k ) H y ( k ) = cx ( k ) + du ( k ) Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 6/23
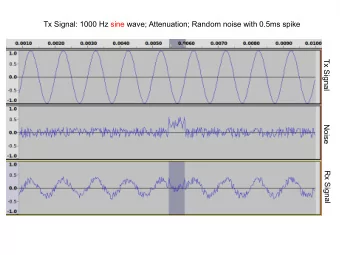
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Range of variables Worst-Case Peak Gain Input u ( k ) Output y ( k ) Stable filter Amplitude Amplitude H Temps Temps Amplification/Attenuation ∀ k , | u ( k ) | � ¯ u ∀ k , | y ( k ) | � � �H� � ¯ u � � � ∞ � cA k b � Worst-Case Peak Gain: � �H� � = � h � 1 = | d | + k = 0 Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 7/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Plan 1 Context and problematics 2 Determining the Most Significant Bit 3 Compute the quantized transfer function 4 WCPG Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 8/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Reliable numerical algorithms H ( z ) SIF H ( z ) C to SIF Code generation SIF Fixed-Point Software algorithm formats Simulink SIF Simulink to graph SIF Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 9/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Reliable numerical algorithms H ( z ) SIF H ( z ) C to SIF Code generation SIF Fixed-Point Software algorithm formats Simulink SIF Simulink to graph SIF Most Significant Bit Least Significant Bit Fixed-Point format Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 9/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Problem of the format choice • Constraints : wordlength w y is fixed for the output variable y • Goal : no overflows, rigorous error bounds • Bonus : minimize the errors Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 10/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Problem of the format choice • Constraints : wordlength w y is fixed for the output variable y • Goal : no overflows, rigorous error bounds • Bonus : minimize the errors � x ( k + 1 ) = Ax ( k ) + b u ( k ) H y ( k ) = cx ( k ) + du ( k ) Problem : find the smallest MSB position m y such that for all k 2 m y � 1 − 2 − w y + 1 � | y ( k ) | � Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 10/23
Context and problematics Determining the Most Significant Bit Compute the quantized transfer function WCPG Problem of the format choice • Constraints : wordlength w y is fixed for the output variable y • Goal : no overflows, rigorous error bounds • Bonus : minimize the errors � x ( k + 1 ) = Ax ( k ) + b u ( k ) H y ( k ) = cx ( k ) + du ( k ) Problem : find the smallest MSB position m y such that for all k 2 m y � 1 − 2 − w y + 1 � � �H� � ¯ u = | y ( k ) | � Mathematical solution : � � 1 − 2 1 − w y �� m y = log 2 ( � �H� � ¯ u ) − log 2 Signal processing / computer arithmetic – Metalibm workshop T. Hilaire (thibault.hilaire@lip6.fr) 10/23
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.















![3-BODY QUANTIZATION CONDITION IN UNITARY FORMALISM [Eur.Phys.J. A53 (2017) no.9] [Eur.Phys.J.](https://c.sambuz.com/1009688/3-body-quantization-condition-in-unitary-formalism-s.webp)