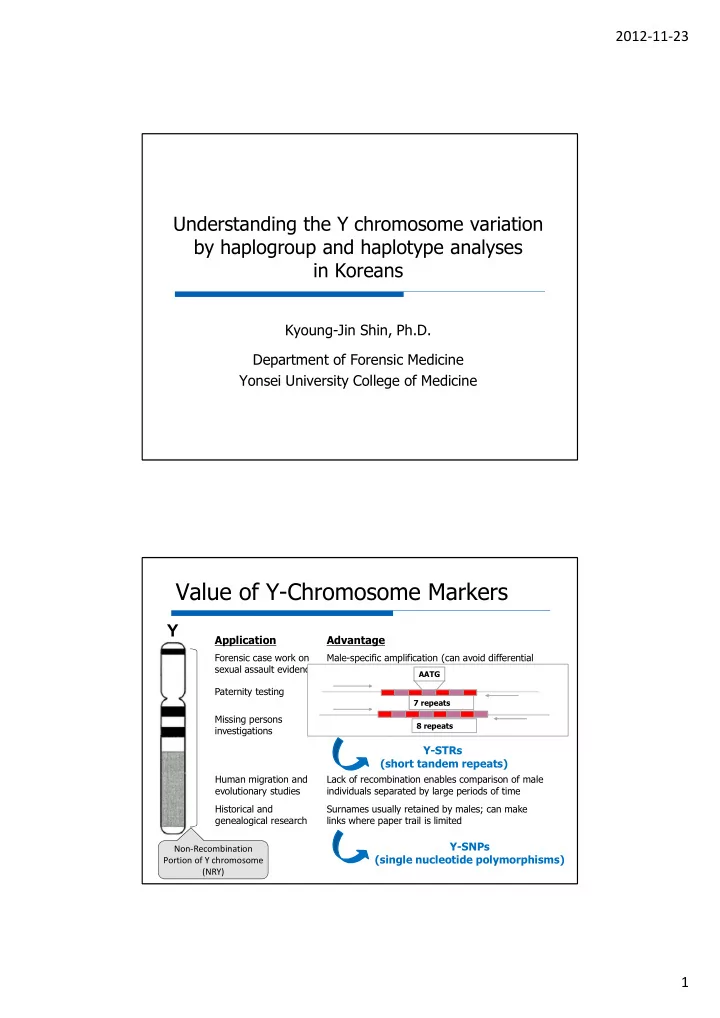

2012-11-23 Understanding the Y chromosome variation by haplogroup and haplotype analyses in Koreans Kyoung-Jin Shin, Ph.D. Department of Forensic Medicine Yonsei University College of Medicine Value of Y-Chromosome Markers Y Application Advantage Forensic case work on Male-specific amplification (can avoid differential sexual assault evidence extraction to separate and epithelial cells) AATG Paternity testing Male children can tied to fathers in motherless cases 7 repeats Missing persons Patrilineal male relatives may be used for 8 repeats investigations reference samples Y-STRs (short tandem repeats) Human migration and Lack of recombination enables comparison of male evolutionary studies individuals separated by large periods of time Historical and Surnames usually retained by males; can make genealogical research links where paper trail is limited Y-SNPs Non-Recombination (single nucleotide polymorphisms) Portion of Y chromosome (NRY) 1
2012-11-23 Focusing on Y-SNPs n Increasing requests for information regarding ethnic and geographical origin from specimens left at a crime scene. n Globalization of crime suspects and victims n Increase of movement from East-southern population n Increase of excavation of Korean War victims and ancient mummies n Individual identification in mass disaster such as airplane crashes, tsunamis or terrorist attacks where people from various geographical areas are involved n Y-haplogroup ß combination of allelic states at SNPs n Set of haplotypes defined by slowly mutating markers (mainly SNPs) which have more phylogenetic stability n Unique event polymorphisms (UEP) record history of Y chromosome Y chromosome haplogroup 2
2012-11-23 Y chromosome phylogenetic tree F A n In 2008, Karafet TM et al. G H - Genome Res 2008;18:830-838 B n 20 major clades D I n 311 haplogroups based on 599 binary markers J E n In 2011, Yan et al. - Eur J Hum Genet 2011;19:1013-1015 L n An updated tree of haplogroup O M n Redefined marker KL2, JST002611, N PK4 and P164 C K O Need for development of Y-SNP Q typing method according to the P revised tree R S T Relationships between haplogroup and haplotype n Y-STR haplotype mainly used in forensic field 693 population studies from 105 countries 9 loci haplotype (Minimal haplotype): 87440 haplotypes 11 loci haplotype (+ DYS438, DYS439): 59736 haplotypes http://www.yhrd.org 12 loci haplotype (+ DYS437): 39349 haplotypes 17 loci haplotype (Yfiler): 27532 haplotypes n The Y-STR variability within haplogroup Number Name Haplogroup DYS DYS DYS DYS DYS DYS DYS DYS DYS DYS 19 389I 389II 390 391 392 393 437 438 439 N2341 Khan J2 13 13 30 24 9 14 14 14 12 11 N2350 Khan J2 13 14 29 24 9 15 14 14 12 11 N2351 Khan J2 14 13 29 24 9 14 14 14 12 12 N2984 Khan J2 13 14 30 26 9 15 14 14 12 12 N2990 Khan J2 13 14 30 23 9 14 14 14 12 11 3
2012-11-23 Relationships between haplogroup and haplotype n Haplogroup prediction from Y-STR values The possibility of haplogroup prediction based on the Y-STR haplotype information Presentation Outline n Development of multiplex systems for determination of East Asian Y haplogroups for large reference samples n Presentation of Y-haplogroup distributions in Koreans n Elucidation of relationships between Y-haplogroups and Y-STR haplotypes in a Korean population n Evaluation of haplogroup affiliation for Y-STR allele/haplotype n Representation of the substructure within haplogroup n Evaluation of possibility for haplogroup prediction based on Y-STR haplotypes 4
2012-11-23 Materials and methods Multiplex SBE reaction Exo-SAP Electrophoresis Multiplex PCR SBE reaction SAP treatment purification ddATP A A 5’ 3’ 3’ 5’ T 3’ T 5’ ddGTP G 5’ 3’ T C A 3’ C 5’ G 3’ 5’ G T 5’ 3’ C 3’ A 5’ C ddCTP 5’ 3’ ddTTP 3’ G 5’ C T 3’ 5’ G 3’ A 5’ Multiplex allele-specific PCR Multiplex PCR Electrophoresis C G F primer F primer F primer T C A C T G C 5’ 3’ T R primer R primer A R primer M174 M9 M231 PCR Size 78 81 130 156 127 153 SNP C T G C A T Results – Development of multiplex PCR systems n Multiplex AS-I 5
2012-11-23 Results – Development of multiplex PCR systems n Multiplex allele-specific PCR assay Haplogroup A, B A,B DE (xD) DE M145 M174 D D C RPS4Y 711 C3 (xC3c, C3d, C3e) C M48 3 M217 c C3c d M407 C3d P53.1 e C3e G,H,I J1 M267 F M89 J1 K (xP, NO) P M9 P Q M242 K Q R M207 R NO* N NO M214 M231 N M175 O O* O1* 1 O1a* Multiplex AS-I M119 1 P203 a O1a1 2 M110 O1a2 O2* O2a* a PK4 2 P31 M95 1 O2a1 O2b* SRY 465 b 47z 1 O2b1 O3* M122 3 O3a* O3a1 (xO3a1c) M324 1 KL2 a JST002611 c O3a1c O3a2* M159 AS-II a O3a2a P201 b M7 2 O3a2b O3a2c* P164 c O3a2c1* 1 M134 M117 O3a2c1a* a M162 1 O3a2c1a1 b P101 O3a2c1b Results – concordance test Multiplex SBE reactions Multiplex allele-specific PCR All SNPs genotypes were concordant between multiplex SBE reaction and multiplex allele-specific PCR 6
2012-11-23 Results – concordance test n Discordance haplogroup O3a2c1a designation between M133 (multiplex SBE reaction) and M117 (multiplex allele-specific PCR) in one sample M133 M117 SBE reactions M133 - ATCT Wild deletion Allele-specific PCR Confirm the allelic state of M133 and M117 by sequencing analysis M117 + Results – distribution of haplogroups n Distribution of Y haplogroups in 1006 Korean males O2b 24.2% C3 O3a2c1a* 13.4% 12.3% P164 JST002611 21 different haplogroups were identified by 33 Y-SNPs KL2 The haplogroup diversity : 0.8830 The phylogenetic position Discriminatory capacity : 2.1 % of newly redefined markers KL2, JST002611 and P164 was confirmed 7
2012-11-23 Results – distribution of haplogroups n Comparing known haplogroup frequencies from other study for Korean Wild JST002611 P > 0.05 The mutation of JST002611 is observed in frequently in East Asia. This study reported the presence of the haplogorup O3a1c-JST002611 Mutant P < 0.05 Results – combined analysis with haplotype n Non-equivalence between M117 and M133 markers n Combined haplogroup and haplotypes analyses in 706 samples with known 22-YSTR genotypes. n M117 and M133 designate the haplogroup O3a2c1a n Non-equivalence M117(+) M133(-) samples were found. n A median-joining network was constructed to evaluate the relationships of these samples based on 17 Y-STR haplotype information 8
2012-11-23 Results – combined analysis with haplotype Relationships between haplotypes within haplogroup O3a2c1-M134 17 Y-STR loci (DYS19, DYS388, DYS390, DYS391, DYS392, DYS393, DYS437, DYS438, DYS439, DYS446, DYS456, DYS458, DYS635 and GATA H4) O3a2c1a O3a2c1 M117 + M117 - M133 + M133 - Allocation of the M133 marker within phylogeny should be considered. non-equivalence More reliable M117 marker for designating M117 + haplogroup O3a2c1a M133 - Results – combined analysis with haplotype Diversity, mutation rate and AMOVA analysis for each Y-STR marker and haplotype Y-STR Gene/haplotype di Mutation rate % Variance versity (x10 -3 ) a Among Within haplogroups haplogroups DYS19 0.7115 1.76 44.82 55.18 DYS392-DYS393-DYS438-DYS437-DYS448-DYS388 DYS385 0.9595 2.09 15.00 85.00 Y-STR Gene/haplotyp Mutation rate % Variance DYS389-I 0.6675 2.44 46.07 53.93 DYS389-II 0.7244 2.60 19.04 80.96 e diversity (x10 -3 ) a Among Within DYS390 0.6733 2.29 44.43 55.57 DYS391 0.2667 3.11 24.87 75.13 haplogroups haplogroups DYS392 0.6789 0.68 76.17 23.83 6 Y-STRs DYS393 0.9317 0.6281 0.81 - 66.17 71.15 33.83 28.85 DYS437 0.4320 2.02 65.59 34.41 9 Y-STRs 0.9966 - 42.09 57.91 DYS438 0.6330 0.33 84.84 15.16 DYS439 0.6329 5.37 12.80 87.20 17 Y-STRs 0.9995 - 41.52 58.48 DYS448 0.7510 0.00 61.27 38.73 22 Y-STRs 0.9999 - 38.95 61.05 DYS456 0.5108 5.59 31.34 68.66 DYS458 0.7779 8.38 10.91 89.09 DYS635 0.6857 5.66 26.24 73.76 GATA H4 0.6115 3.43 38.28 61.72 DYS388 0.4850 0.00 72.33 27.67 DYS446 0.7886 2.71 31.95 68.05 DYS447 0.7520 5.41 42.78 57.22 DYS449 0.8523 18.97 14.86 85.14 DYS464 0.9668 3.99 16.71 83.29 9
2012-11-23 Results – combined analysis with haplotype YHRD database release 39 Haplotype N % Haplogroup (392-393-438-437-448-388) DE D C C3 F Q N O 11-13-10-14-17-12 10 55.6 D-M174 88 88 1 1 11-13-10-14-19-12 2 11.1 222 208 3 2 11-13-11-14-17-12 2 11.1 29 28 11-15-10-14-21-12 (or 13) 23 26.4 C3-M217 115 38 11-14-10-14-21-12 (or 13) 19 21.8 2 74 29 11-14-10-14-22-13 12 13.8 45 15 1 11-13-11-14-0-13 4 4.6 11 5 3 14-14-12-14-19-12 7 53.8 Q-M207 20 18 15-14-12-14-19-12 3 23.1 8 5 14-13-10-14-20-13 5 18.5 N-M231 17 14 2 14-13-10-14-19-12 (or 13) 4 14.8 39 27 10 15-13-10-14-19-12 (or 13) 4 14.8 15 14 16-14-11-14-19-12 3 11.1 10 10 14-13-10-14-18-12 3 11.1 60 8 52 Results – combined analysis with haplotype YHRD database release 39 Haplotype N % Haplogroup (392-393-438-437-448-388) O O1a O1a1 O2 O2b O2b1 14-13-10-14-18-12 13 68.4 O1a1-P203 52 44 13 1 16-13-10-14-18-12 2 10.5 3 3 2 13-13-10-14-18-12 3 30.0 O2*-P31 15 1 11 13-14-10-14-18-12 2 20.0 45 37 13-13-13-14-18-12 (or 13) 124 80.0 O2b*-SRY 465 714 398 398 128 13-13-13-14-18-12 46 64.8 O2b1-47z 714 398 398 128 10
Recommend
More recommend