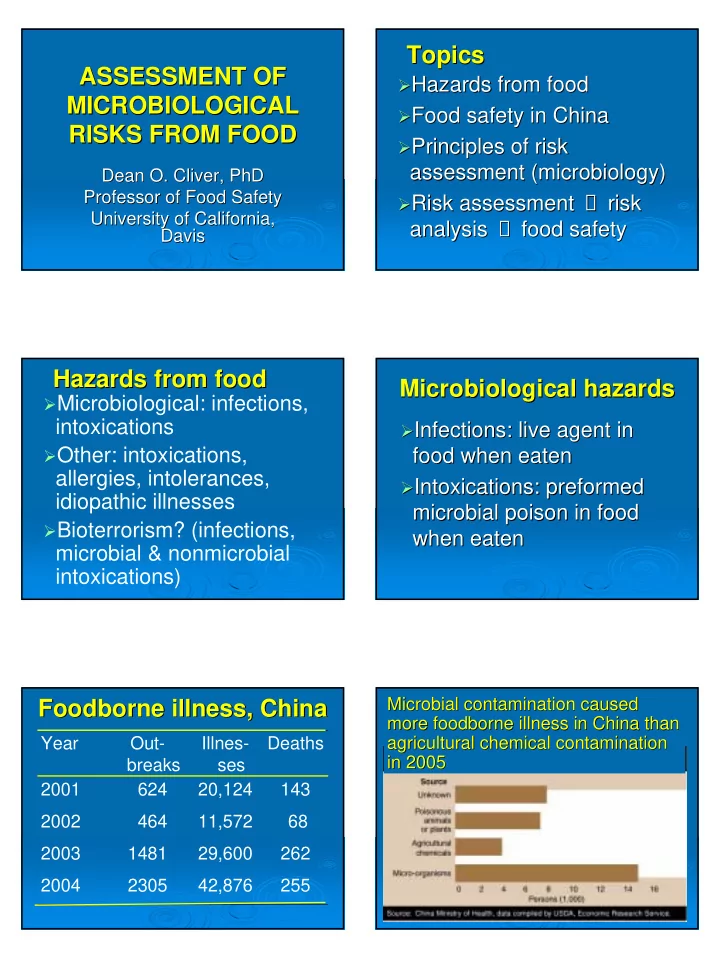

Topics Topics ASSESSMENT OF ASSESSMENT OF Hazards from food � � Hazards from food MICROBIOLOGICAL MICROBIOLOGICAL Food safety in China � Food safety in China � RISKS FROM FOOD RISKS FROM FOOD Principles of risk � Principles of risk � assessment (microbiology) assessment (microbiology) Dean O. Cliver Dean O. Cliver, PhD , PhD Risk assessment → → risk Professor of Food Safety Professor of Food Safety risk � Risk assessment � University of California, University of California, → food safety analysis → analysis food safety Davis Davis Hazards from food Hazards from food Microbiological hazards Microbiological hazards � Microbiological: infections, intoxications Infections: live agent in � � Infections: live agent in � Other: intoxications, food when eaten food when eaten allergies, intolerances, � Intoxications: preformed Intoxications: preformed � idiopathic illnesses microbial poison in food microbial poison in food � Bioterrorism? (infections, when eaten when eaten microbial & nonmicrobial intoxications) Microbial contamination caused Microbial contamination caused Foodborne illness, China illness, China Foodborne more foodborne more foodborne illness in China than illness in China than agricultural chemical contamination Year Out- Illnes- Deaths agricultural chemical contamination in 2005 in 2005 breaks ses 2001 624 20,124 143 2002 464 11,572 68 2003 1481 29,600 262 2004 2305 42,876 255
Foodborne disease disease Schools in Sichuan, Foodborne Schools in Sichuan, in China September 2006 in China September 2006 � Chongzhou Chongzhou 1 1º º: 300/1100 : 300/1100 2d quarter 2006: 5696 � � 2d quarter 2006: 5696 � students ( Shigella Shigella ) ) students ( cases; 1950 in schools cases; 1950 in schools Chengdu 1º º: ~90 ill : ~90 ill � Chengdu 1 � � Safety of school food? � Safety of school food? (same- -day onset?) day onset?) (same � China Daily: official data, � China Daily: official data, Chengdu teachers now eat � Chengdu teachers now eat � ann. avg. ~300 million/yr ann. avg. ~300 million/yr 30 minutes before students. 30 minutes before students. Risk assessment Risk assessment Pathogens in food (1) Pathogens in food (1) to predict: to predict: � Sources: humans (food Sources: humans (food � Probability, severity � Probability, severity � handlers?), animals, handlers?), animals, Disease agent, vehicles, � Disease agent, vehicles, � environment environment “at “ at- -risk risk” ” population population Bacteria & fungi may � � Bacteria & fungi may � Exposure assessment: Exposure assessment: multiply in food; multiply in food; viruses viruses � (Shanghai clams, 1988, (Shanghai clams, 1988, frequency & levels of frequency & levels of 300k ill) & parasites cannot 300k ill) & parasites cannot ingestion via food ingestion via food Risk characterization Risk characterization Pathogens in food (2) Pathogens in food (2) parameters: parameters: Persistence: freezing, � Persistence: freezing, � � Prevalence (time & Prevalence (time & � refrigeration, processing, refrigeration, processing, place of occurrence) place of occurrence) preparation preparation � Severity (bias) Severity (bias) � � Hazard characterization: Hazard characterization: � � Susceptibility of hosts Susceptibility of hosts � dose vs. severity dose vs. severity Social (& economic?) � Social (& economic?) � impact impact
Records needed for Records needed for Information for Information for risk assessment risk assessment risk assessment: risk assessment: � Illnesses & etiologies World’ ’s scientific literature s scientific literature � World � (diagnosis, field work, Incidence of present illness lab analyses) � Incidence of present illness � in targeted population in targeted population � Vehicles (sampling, testing, traceback) � Update as new information � Update as new information � Preventive measures becomes available becomes available in place (resources) The zero- -risk goal risk goal The zero Risk management Risk management by HACCP: by HACCP: � Cost of incremental improvement � Prevent contamination Prevent contamination � � The not-eating option � Undo contamination by Undo contamination by � � Cost “no object” — processing (CCP) processing (CCP) food elitism � Last resort: test Last resort: test � System design for risk System design for risk Applying risk analysis: Applying risk analysis: analysis and safety analysis and safety � Risk assessment — greater � Responsibility shared by accuracy (> data collection & sharing) government, industry, � Risk management — consumers government leadership, � Assessment, management, industry execution communication � Risk communication — � Costs, public perceptions government, industry, public
Recommend
More recommend