to the left B out of the page C into the page D to the top of - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
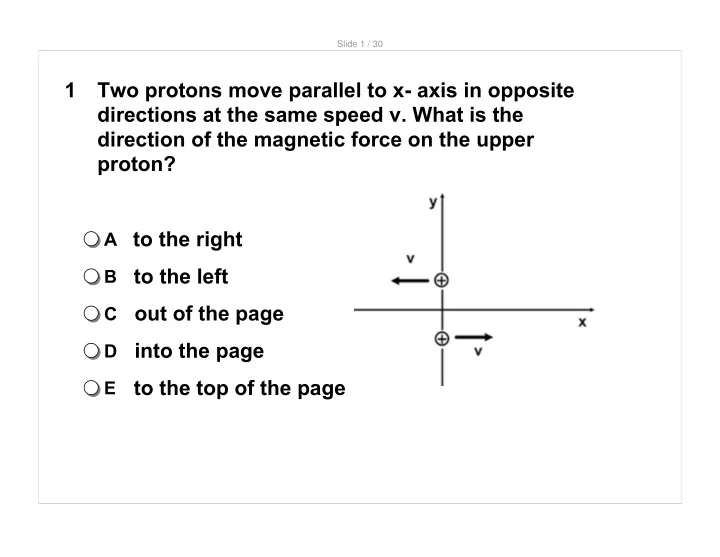
Slide 1 / 30 1 Two protons move parallel to x- axis in opposite directions at the same speed v. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the upper proton? A to the right to the left B out of the page C into the page D to the top of
Slide 1 / 30 1 Two protons move parallel to x- axis in opposite directions at the same speed v. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the upper proton? A to the right to the left B out of the page C into the page D to the top of the page E
Slide 2 / 30 2 A positive charge q moves at a constant speed v in the direction presented by the above diagram. What is the direction of the magnetic field due to the moving charge at point P? A to the right to the left B out of the page C into the page D to the top of the page E
Slide 3 / 30 3 A negative charge q moves at a constant speed v in the direction presented by the above diagram. What is the direction of the magnetic field due to the moving charge at point P? A to the right to the left B out of the page C into the page D to the bottom of the page E
Slide 4 / 30 4 A positive charge q moves at a constant speed v parallel to the x-axis. At which of the following points is the magnetic field strongest in magnitude? A A B B C C D D E E
Slide 5 / 30 5 Two positive charges of equal magnitude move in a reference frame shown on the above diagram. What is the direction of the net magnetic field at the origin? A into the page out of the page B to the left C to the right D zero E
Slide 6 / 30 6 Two opposite charges of equal magnitude move in a reference frame shown on the diagram. What is the direction of the net magnetic field at the origin? A into the page out of the page B to the left C to the right D zero E
Slide 7 / 30 7 A long, straight wire, shown above, carries an electric current I. What is the direction of the magnetic field at point P? A into the page out of the page B to the right C to the left D to the top of the page E
Slide 8 / 30 8 A long, straight wire carries an electric current I directed into the page. If B0 is the magnitude of magnetic field due the current at point A, what is the magnitude of the field at point B? A B C D E
Slide 9 / 30 9 Two long, straight wires carry equal currents directed into the page. What is the direction of the magnetic field at the midpoint between the wires? A into the page out of the page B to the top of the page C to the bottom of the page D zero E
Slide 10 / 30 10 Two long, straight wires carry equal currents directed into the page. The wires are placed at two corners of an equilateral triangle. Which of the following is the correct direction of the net magnetic field at point P? A B C E D
Slide 11 / 30 11 Two long, straight wires carry equal, but opposite, currents perpendicular to the page as shown above. The wires are placed at two corners of an equilateral triangle. Which of the following is the correct direction of the net magnetic field at point P? A B C E D
Slide 12 / 30
Slide 13 / 30
Slide 14 / 30 14 Two long, straight wires carry equal currents perpendicular to the page. There is an attractive magnetic force between the wires of magnitude F0. What is the new force between the wires if the magnitude of each current is doubled? A B C D E
Slide 15 / 30 15 Two long, straight wires carry equal currents perpendicular to the page. There is an attractive magnetic force between the wires of magnitude F0. What is the new force between the wires if the distance between the wires is doubled? A B C D E
Slide 16 / 30 16 Three parallel wires are each carrying a current I in the direction shown on the diagram. What is the direction of the net magnetic force on the bottom wire? A out of the page into the page B to the top of the page C to the bottom of the page D zero E
Slide 17 / 30 17 Two circular loops of wire each carry a current I. Loop A has twice the radius of loop B. What is the ratio of the magnetic field at the center of loop A to that of loop B? A B C D E
Slide 18 / 30 18 A circular conductor carries an electric current I. The loop is placed in the x-y-z reference frame in such way that the center of the loop is at the origin. The plane of the loop is parallel to the y-z axes and perpendicular to the x-axis. Which one of the following graphs represents the magnetic field strength along the x-axis? C A B D E
Slide 19 / 30
Slide 20 / 30
Slide 21 / 30
Slide 22 / 30
Slide 23 / 30 23 A uniform magnetic field B is created by the electric current flowing through a long solenoid. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid with the same current and twice the radius? A B C D E
Slide 24 / 30
Slide 25 / 30
Slide 26 / 30 26 A uniform magnetic field B is created by an electric current I flowing through a long solenoid with n turns per unit length and radius R. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field inside the solenoid? A B C D E
Slide 27 / 30 27 A cylindrical conductor with radius a carries an electric current I. The current is uniformly distributed over the cross-sectional area of the cylinder. Which of the following graphs represents the magnetic field B as a function of distance r, both inside and outside the conductor? A C B E D
Slide 28 / 30 28 A solid conductor with radius a is surrounded by a tube with an inner radius b and outer radius c. The conductor and tube carry equal currents in opposite directions (conductor - out of the page, tube - into the page). An electron e travels to the right in the space between the conductor and tube at point P. What is the direction of the magnetic force on the electron at point P? A Into the page out of the page B to the bottom of the page C to the top of the page D to the left E
Slide 29 / 30
Slide 30 / 30
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.