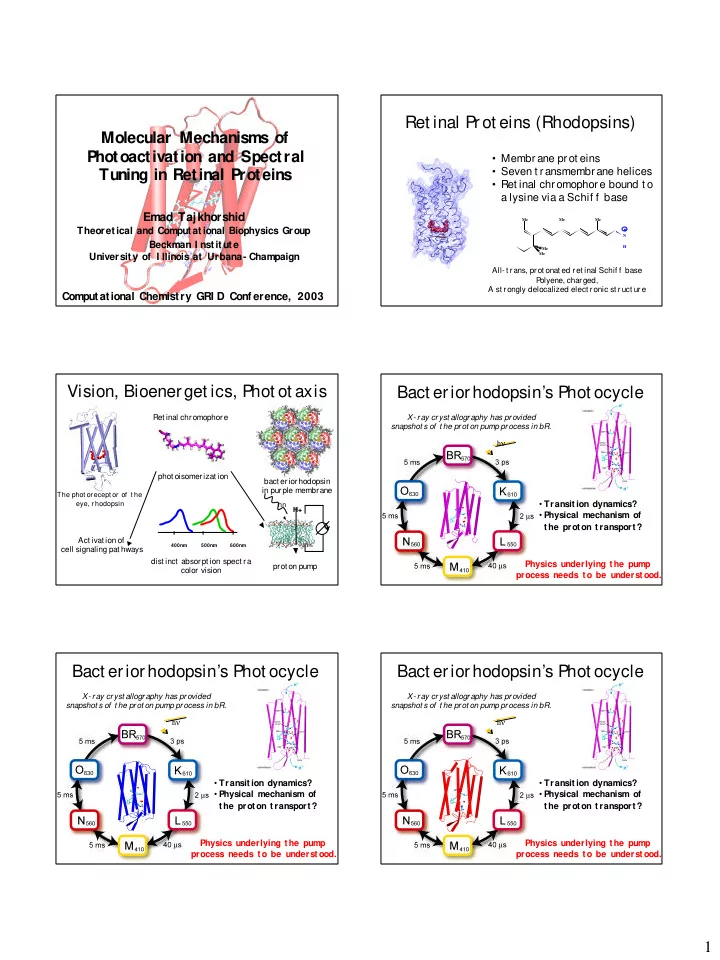

Ret inal Prot eins (Rhodopsins) Molecular Mechanisms of Photoactivation and Spectral • Membrane prot eins • Seven t ransmembrane helices Tuning in Retinal Proteins • Ret inal chromophore bound t o a lysine via a Schif f base Emad Tajkhorshid Me Me Me Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group N Beckman I nst it ut e H Me Me University of I llinois at Urbana- Champaign All- t rans, prot onat ed ret inal Schif f base P olyene, charged, A st rongly delocalized elect ronic st ruct ure Computational Chemistry GRI D Conf erence, 2003 Vision, Bioenerget ics, Phot ot axis Bact eriorhodopsin’s Phot ocycle Ret inal chromophore X- ray cryst allography has provided snapshot s of t he prot on pump process in bR. h ν phot oisomerizat ion bact eriorhodopsin in purple membrane The phot or ecept or of t he eye, r hodopsin • Transit ion dynamics? hn H+ • Physical mechanism of V t he prot on t ransport ? Act ivat ion of 400nm 500nm 600nm cell signaling pat hways dist inct absorpt ion spect ra Physics underlying t he pump prot on pump color vision process needs t o be underst ood. Bact eriorhodopsin’s Phot ocycle Bact eriorhodopsin’s Phot ocycle X- ray cryst allography has provided X- ray cryst allography has provided snapshot s of t he prot on pump process in bR. snapshot s of t he prot on pump process in bR. h ν h ν • Transit ion dynamics? • Transit ion dynamics? • Physical mechanism of • Physical mechanism of t he prot on t ransport ? t he prot on t ransport ? Physics underlying t he pump Physics underlying t he pump process needs t o be underst ood. process needs t o be underst ood. 1
Bact eriorhodopsin’s Phot ocycle Bact eriorhodopsin’s Phot ocycle X- ray cryst allography has provided X- ray cryst allography has provided snapshot s of t he prot on pump process in bR. snapshot s of t he prot on pump process in bR. h ν h ν • Transit ion dynamics? • Transit ion dynamics? • Physical mechanism of • Physical mechanism of t he prot on t ransport ? t he prot on t ransport ? Physics underlying t he pump Physics underlying t he pump process needs t o be underst ood. process needs t o be underst ood. HOOC-D96 Phot ocycle of bR bR 568 + Bact eriorhodopsin’s Phot ocycle K216 N H D85-COO The phot ocycle is init iat ed by HOOC-E204 5ms X- ray cryst allography has provided 3ps phot oisomer izat ion of t he O 645 K 603 snapshot s of t he prot on pump process in bR. r et inal chr omophor e, and HOOC-D96 HOOC-D96 h ν + ef f ect ively pumps a pr ot on in K216 H N N + every cycle (ms). H K216 D85-COOH D85-COO OOC-E204 HOOC-E204 1µ s 5ms + OOC-D96 HOOC-D96 N • Transit ion dynamics? H + K216 N N + • Physical mechanism of H K216 H D85-COOH D85-COO 500 fs t he prot on t ransport ? OOC-E204 HOOC-E204 N 550 L 543 40 µ s 5ms HOOC-D96 + H N Physics underlying t he pump N K216 process needs t o be underst ood. M 410 D85-COOH OOC-E204 Comput at ional Met hodology Quest ions • What det er mines t he maximal absor pt ion of Molecular dynamics simulat ions r et inal in dif f er ent pr ot ein envir onment s? Modif ied f orce f ield paramet ers (spect r al t uning in bact er ial r hodopsins) • What ar e t he dynamics of phot oisomer izat ion and t he mechanism of light ener gy st or age? Combined quant um mechanical / (excit ed st at e QM/ MM MD) molecular mechanical (QM/ MM) calculat ions • How does t he isomer izat ion is coupled t o • Ret inal and several key residues are described by ab initio QM (HF/ C ASSC F). ot her molecular event s in t he pr ot ein? • P rot ein environment is t reat ed by a (pr ot ein act ivat ion mechanism in bR and Rh) molecular mechanics f orce f ield, (AMBER94). 2
Color Vision QM/ MM Calculat ions Lys216-R ET Hamilt onian of t he QM/ MM syst em O cone cells … ∑ 1 ∑∑ Z ∑ 1 ∑ Z Z ˆ = + + + 2 A A B H p N H i 2 r r r N > > i i A iA i j ij A B A B H MM QM ˆ ∑∑ q q ∑∑ Z q + a p + a p g k k ap ap r r a p a p ap ap + + M M M M V V − QM M M M M H H … N H O O Visual recept ors of t he rhodopsin f amily are H Asp85 QM classif ied based on t heir color sensit ivit y H Asp212 O N QM MM dummy H at om Spect ral Tuning in Bact erial Color Vision Rhodopsins Color is sensed by red, green, and blue rhodopsin visual recept ors. Sensory Rhodopsin I I Bact er ior hodopsin ( sRI I ) ( bR ) phot ot axis prot on pump sRI I bR 400nm 500nm 600nm • Large blue shif t of absorpt ion spect rum absor pt ion maximum in sRI I (70 nm) Their chromophores are the same! • A prominent sub-band 11- cis prot onat ed ret inal Schif f base 500nm 600nm How does t he prot ein t une t he absorpt ion maximum? Ver y Similar Binding Sit es St r uct ur es of bRand sRI I Similar st r uct ur e sRI I • Ar omat ic r esidues. • Hydr ogen-bond net wor k. Very similar protein (count er -ion asparat at es, structures; int er nal wat er molecules) Same chromophore: all trans protonated T204A/ V108M/ G130S of retinal Schif f base sRI I pr oduces only 20 nm (30%) spect ral shif t . bR Mut at ion of t he ent ir e binding sit e can account f or only 50% X-ray st ruct ures: of t he spect ral shif t ! sRI I bR: Luecke et al. , Belrhali et al. sRI I : Luecke et al. , Royant et al. bR What is t he main det erminant of spect ral t uning? 3
QM/ MM Calculat ions Excit at ion Ener gies • Ref inement of X - ray st ruct ures by HF (ret inal, 2Asp, 3H 2 O) Spect ral shif t helix G • Excit at ion energy calculat ions by ∆ E(S 1 - S 0 ) : 6.1 (exp. 7.2) kcal/ mol CASSCF f or ret inal retinal- Calculated spectra ∆ E(S 2 - S 0 ): 1.7 (exp. 4.0) kcal/ mol K205/ K216 helix G ∆ E(S 1 - S 0 ) A sub-band in sRI I is due t o t he retinal- sRI I second excit ed st at e (S 2 ). K205/ K216 D201 bR D212 X-ray st ruct ures D201 D212 500nm 600nm QM/ MM-opt imized Hayashi, Taj khor shid, Schult en, J PC- B (2001) Cont r ibut ions f r om Residues Mechanism of Spect r al Tuning St rong elect ronic reorganizat ion upon sRI I excit at ion S 2 Me Me Me S 1 + + N H S 2 Me S 0 Me bR S 1 S 0 isolat ed T142 T204 in sRI I gives a blue- shif t T142 in bR gives a red- shif t Consistent with mutagenesis experiment s St r uct ur al Det er minant of t he Mechanism of Spect r al Tuning Spect ral Shif t St rong elect ronic reorganizat ion upon excit at ion Dist ance bet ween t he Schif f retinal- K205/ K216 base and t he count er ion is S 2 shor t er in sRI I . helix G S 2 S 1 N 16 –C γ (Asp201: sRII) : 4.5 A Me Me Me S 1 D201 + + N 16 –C γ (Asp212: bR) : 5.2 A D212 N S 2 H Decomposed elect r onic r eor ganizat ion ener gies Me S 0 O Same residue!!!! Me O C S 1 S 0 Asp (Glu) S 0 isolat ed in protein This is why mut agenesis experiments cannot Excit ed st at es and t he ground st at e restore the maximal receive dif f erent st abilizat ion f rom a absorpt ion. count erion inside t he prot ein Hayashi, Taj khor shid, Schult en, J PC- B (2001) 4
Ab I nit io Excit ed St at e QM/ MM Phot oisomer izat ion of Ret inal MD Simulat ion One of t he f ast est r eact ions in nat ur e Femt osecond r esolut ion spect r oscopy measur ement s QM + N energy H <500 f s all-trans 13-cis • Two low- lying st at es (S 0 and S 1 ) in bR • An analogue of ret inal (t hree double bonds, 13 • Ult raf ast rat e (240- 500 f s) 14 20 at oms) wit h CASSCF(6,6)/ DZV + H • High bond select ivit y in prot ein: N • AMBER94 f orce f ield f or t he prot ein 100% 13 - cis phot oproduct • 11 t raj ect ories st art ing f rom init ial • I n solut ion: conf igurat ions generat ed by classical MD 9- cis (2%), 11 - cis (14%), 13 - cis (1 %) Hayashi, Taj khor shid, Schult en, Biophys. J . (2003) Dynamics of Curve Crossing Ensemble of Tr aj ect or ies A t ypical t r aj ect or y in bR Emission and absor pt ion ener gies cis Gas phase dynamics energy trans •Fast isomerizat ion •A single crossing event all- t r ans 13- cis I n sit u dynamics + N •Relat ively slow isomerizat ion H •Mult iple crossing event s I somerizat ion event s •Larger energy dif f erences • Bond select ive and smaller nonadiabat ic • Unidirect ional isomerizat ion cis trans couplings at crossing point s P roduct f ormat ion: • Cis product f ormat ion is dominant at t he f irst crossing point . Hayashi, Taj khor shid, Schult en, Biophys. J . (2003) Hayashi, Taj khor shid, Schult en, Biophys . J . (2003) Dynamic Spect r al Modulat ions Pr ot ein Act ivat ion Pr ocess in Time evolut ion of emission spect rum along a non- isomerizing t raj ect ory Bact eriorhodopsin Ye et al. (pump-probe) emission energy Stimulated emission at 800 nm 200 fs oscillation Rocking around ps the isomerizing bond Kobayashi et al. (pump-probe at 610 nm) Spectrogram of fast oscillations on a decay curve Low freq. shift of C 13 =C 14 str Time dependent coupling between C-C str. (in-plane H 14 bending) and H 14 -HOOP Gate delay time ( fs) Hayashi, Taj khor shid, Schult en, Biophys . J . (2003) 5
Recommend
More recommend