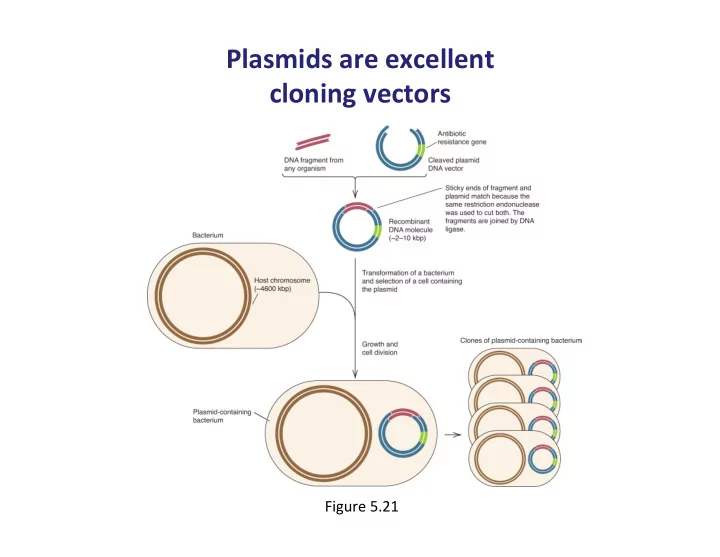

Plasmids ¡are ¡excellent ¡ ¡ cloning ¡vectors ¡ Figure ¡5.21 ¡
Figure 11.11 Order of restriction enzyme cut sites in polylinker Ampicillin lacZ ʹ″ ʹ″ resistance Apo I - Eco RI Ban II - Sac I Acc 651 - Kpn I Ava I - Bso BI - Sma I - Xma I Bam HI Polylinker Xba I Acc I - Hin cII - Sal I Bsp MI - Bfu AI pUC19 Sbf I 2686 base pairs Pst I Sph I Hin dIII lacI Origin of DNA replication
Figure 11.12 lacZ ʹ″ ʹ″ AmpR Foreign DNA Vector Digestion with restriction enzyme Join with DNA ligase Opened vector Recyclized vector without insert Vector plus foreign DNA insert Transform into Escherichia coli and select on ampicillin plates containing Xgal Transformants blue Transformants white ( β -galactosidase ( β -galactosidase active) inactive)
Figure 11.18 J Capsid genes att int xis N QSR cos cos Wild-type Replaceable region lambda Charon 4A (replacement β -Gal gene Another vector) substitution Charon 16 (insertional Another β -Gal gene vector) substitution
Figure 11.19 Replaceable region R L Digestion with cos restriction enzymes L R Ligation with foreign DNA Foreign DNA L R Hybrid Packaging cloned DNA DNA into phage head R L Phage assembly Infective lambda virion
Figure 11.13 Eukaryote Bacteria Escherichia coli Bacillus subtilis Saccharomyces cerevisiae Easily transformed Well-developed Well-developed Nonpathogenic genetics genetics Naturally secretes Nonpathogenic Many strains proteins Can process mRNA available Endospore formation and proteins Best known simplifies culture Easy to grow bacterium Potentially Genetically unstable Plasmids unstable pathogenic Genetics less Will not replicate Periplasm traps developed than most bacterial proteins in E. coli plasmids Advantages Disadvantages
Figure 11.15 oriC Ampicillin resistance t/pa ESM Promoter oriY t/pa CEN Polylinker Promoter (cloning site)
Figure 11.20 Bam HI Sma I Kpn I Eco RI Xba I Sal I Pst I Hin dIII Polylinker lacP M13 genomic DNA lacZ ʹ″ ʹ″ Phage in clear plaques have cloned DNA Phage in blue plaques do not have cloned DNA
X-‑gal ¡Cloning ¡Results ¡
Three ¡major ¡types ¡of ¡ ¡ restric8on ¡endonucleases ¡
Restric8on ¡endonucleases ¡ produce ¡blunt ¡or ¡s8cky ¡ends ¡ Type ¡II ¡enzymes ¡cut ¡at ¡ palindromic ¡sequences ¡
Restric8on ¡endonucleases ¡cleave ¡DNA ¡at ¡specific ¡ sites ¡
Restric8on ¡maps ¡ Figure ¡5.18ab ¡ Photo ¡courtesy ¡of ¡FOTODYNE ¡Incorporated. ¡
Construc8ng ¡a ¡restric8on ¡map ¡ Figure ¡5.19ab ¡
Figure 11.5 Foreign DNA Cut with restriction enzyme Add vector cut Sticky with same ends restriction enzyme Vector Add DNA ligase to form recombinant molecules Cloned DNA Introduction of recombinant vector into a host
Figure 11.9
cDNA ¡synthesis ¡by ¡ ¡ reverse ¡transcriptase ¡ Figure ¡5.45 ¡
Figure 11.14 Before gas release After gas release Plunger Helium gas Gas vent Disc Microprojectiles with transfecting nucleic acid Fine screen Rough screen Target tissue
Figure 11.6 Transformant colonies growing on agar surface Replica-plate onto membrane filter Lyse bacteria and denature Partially lyse cells; add DNA; add RNA or DNA specific antibody; add agent probe (radioactive); wash to detect bound antibody in out unbound radioactivity radiolabeled form Autoradiograph to detect radioactivity X-ray film Positive colonies
Polymerase ¡chain ¡ reac8on ¡(PCR) ¡ to ¡amplify ¡DNA ¡ Figure ¡5.31 ¡
Southern ¡bloHng ¡is ¡used ¡ to ¡detect ¡specific ¡DNA ¡ fragments ¡ Figure ¡5.22 ¡
Recommend
More recommend