Phylogeny Phylogeny Evolutionary history of a species or a group of - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Phylogeny Phylogeny Evolutionary history of a species or a group of species Goal: Resulting phylogeny should match taxonomy (classification of an organism) Phylogeny and Classification Phylogenetic Tree Constructed using
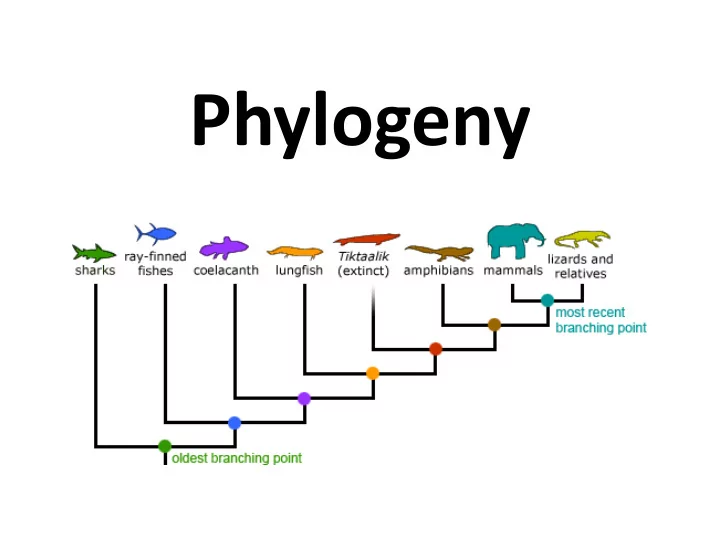
Phylogeny
Phylogeny • Evolutionary history of a species or a group of species • Goal: Resulting phylogeny should match taxonomy (classification of an organism)
Phylogeny and Classification
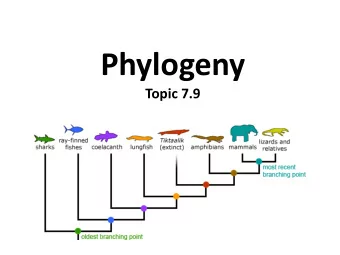
Phylogenetic Tree • Constructed using morphological similarities (homologies) of living or fossil species, DNA and protein sequences • Show evolutionary history and relationships among groups of organisms (hypothesis) • Trees are dynamic (constantly being revised)
Understanding Phylogenies • Click on the hyperlink above for an introduction to phylogenetic trees • Read the first page and then click “next” at the bottom of the page for page 2 of Understanding Phylogenies • Write down 3 things in your notes that you learned about phylogeny by exploring this link
Tree Terminology
Tree Terminology • Sister taxa – groups of organisms that share an immediate common ancestor • Node (branch point) – represents the most recent common ancestor of a group • Root – single branch point from which all branches originate in the tree
Rooted versus Unrooted Trees
Clades • Clade: a group of organisms that consists of a common ancestor and all of its descendants
Monophyletic Group • A clade is also known as a monophyletic group
Phylogenetic Trees vs Cladograms • Sometimes used interchangeably • Branch lengths of trees may show evolutionary time and amount of genetic change
Character • Characters are heritable traits that can be compared across organisms, such as physical characteristics (morphology), genetic sequences, and behavioral traits • Example: wings shown below
Derived versus Ancestral Characters • A derived character is one that evolved in one group but not in the other group (a new trait) • An ancestral character is thought to have evolved in a common ancestor of both groups
Derived versus Ancestral Characters • Identify a derived character for mammals • Identify an ancestral character for mammals
Example of a Derived Trait • Number of heart chambers in animals • Tbx5 protein influences the formation of two ventricles in bird and mammalian hearts
Trees Show Speciation Events and Relatedness • Examine common ancestry in order to determine relatedness • Who is species 5 most closely related to?
Outgroup • An outgroup is a group of organisms that serve as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationship among a monophyletic group of organisms • Used as a point of comparison for the ingroup • Example: - Chordates – Ingroup - Echinodermata - Outgroup
Chordate Evolution
Another Outgroup Example
Trees May Show Time and Extinct Lineages
Extinct versus Extant
Phylogenetic Trees Based on Sequence Data • Use of molecular (i.e. DNA, proteins) genetics to determine evolutionary relationships • Disadvantages – Need common genes – Gene sequences need to be “aligned” first
Sequence Alignment • Goal of Sequence Alignment: Maximize the number of matching nucleotides in all compared sequences • Compare SNPs and Indels
SNPs and Indels • SNPs – single nucleotide polymorphisms • Indels – insertions and deletions
Maximum Parsimony • Choosing a tree that requires the fewest evolutionary events (fewest amount of molecular changes) • The simplest explanation that is consistent with the facts
Which is the most parsimonious tree?
Constructing a Phylogenetic Tree • May require the use of a character table • + or 1 indicates the presence of the character, - or 0 indicates the absence of the character
Now You Try It • Based on the shared characteristics in the table below, build a tree of the most likely evolutionary history of these organisms • + (present), - (absent)
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.