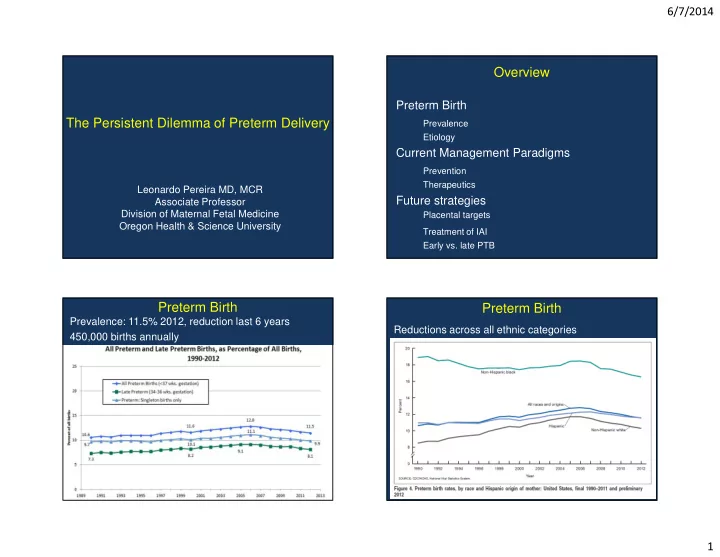

6/7/2014 Overview Preterm Birth The Persistent Dilemma of Preterm Delivery Prevalence Etiology Current Management Paradigms Prevention Therapeutics Leonardo Pereira MD, MCR Future strategies Associate Professor Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Placental targets Oregon Health & Science University Treatment of IAI Early vs. late PTB Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Prevalence: 11.5% 2012, reduction last 6 years Reductions across all ethnic categories 450,000 births annually 1
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Prevalence: Globally 15 million infants per year Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Etiology Removed IAI from the OB distribution Group A - Normal Distribution Group B – IAI/Pathology Births (thousands ) Analyzed distribution of remaining births Remaining births showed normal distribution 2
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Etiology Late PTB and Early PTB – always pathologic Postterm Late Preterm pregnancy are Postterm Births (thousands ) opposite ends of normal Late PTB – normal distribution of labor onset, parturition spectrum non-pathologic Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Late PTB Current Management Paradigms: Prevention 35-37 weeks gestation ~8% of pregnancies; ¾ of all PTB IM 17-OHP: prior PTB 20-34 weeks Growing population Impact is increasing Vaginal Progesterone: CL < 25 mm Neonatal risks Healthcare costs Cerclage: prior mid trimester losses, dilated cervix Maternal risks ALPS trial Pessary: multifetal gestations 3
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Current Management Paradigms: Prevention Current Management Paradigms: Prevention 17-OHP: Prior PTB 20-36 weeks [20-34] 17-OHP: Prior PTB 20-36 weeks [20-34] 250 mg IM injection weekly Begin 16-20 weeks Continue through 36 weeks Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Current Management Paradigms: Prevention Current Management Paradigms: Prevention Cerclage: Vaginal Progesterone: CL < 25 mm [15-24 mm]* History-indicated cerclage: 3 prior mid trimester losses or 2 90-200 mg micronized progesterone with no live births; 12-14 wga Ultrasound-indicated cerclage: cervical shortening < 25 Begin at time of diagnosis mm in patient with prior PTB, subsequent shortening despite progesterone therapy; 16-24 wga Continue through 36 weeks Physical-exam indicated cerclage: dilated cervix, any patient before 24 wga; consider amniocentesis *Regardless of obstetric history Bias - Shirodkar over McDonalds RCT: 17-OHP vs. vaginal progesterone for RPTB 4
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Prevention of Current Management Paradigms: Prevention Ascending infection - ? role for probiotics Modulation of inflammatory pathway signaling Pessary: multifetal gestations with premature Premature cervical changes cervical shortening Modulation of actin cytoskeletal signaling Not advocating for screening TVUS CL in multifetal gestations but if identified recommend pessary Preterm Birth Preterm Birth 5
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Current Management Paradigms: Therapeutics Current Management Paradigms: Therapeutics Tocolysis: Neuroprotection MgSO4: 24-32 weeks Indomethacin 24-28 weeks Reduction in cerebral palsy MgSO4: 24-32 weeks Protocol from NICHD trial recommended in the U.S. Calcium channel blockers: 24-34 weeks Oxytocin receptor antagonists Load 6 gm then 2 gm/hr continuous Indomethacin 24-28 If delivery not imminent in 12 hours the D/C 50-100 mg load, then 25 mg q 4-6 hrs PO/PR MgSO4 24-32 Restart when PTL restarts at 2 gm/hr 6 gm load, then 2 gm/hr Ca Channel Blockers 24-34 Repeat loading dose if > 6 hours from D/C 10-20 mg PO q4-6 hrs Indomethacin 24-28 MgSO4 28-32 Ca 32-34 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Placental targets Future strategies Functional MRI – placental modeling, flow, adaptation P lacental targets Microbubble infusion – measure flow, delivery of therapeutic targets Treatment of IAI Modulation of - Early/Late PTB innate immune response apoptosis 6
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Treatment of IAI: treating U. parvum in rhesus model of IAI with Placental targets maternal IV Azithromycin therapy Placental villous hypermaturation (PVH) in late PTB – common finding in idiopathic PTB waited until after PTL/IAI Late PTB: analysis of 82 placentas: acute chorioamnionitis 40%, clinically other 22%, idiopathic PTB 38% evident (6-8 days after innoculation); Frequency of PVH in idiopathic PTB 84% sterilized AF Similar to cases with IUGR or preeclampsia 89% within 4 days Chorioamnionitis 30% , p<0.001 Grigsby PL, AJOG Morgan TK. J Mat-Fetal & Neonatal Med 26:647-53, 2013 207(6) 2012 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Treatment of IAI Treatment of IAI in humans pregnancies: Treatment of U. parvum in rhesus IAI with maternal IV Azithromycin Eradication of Ureaplasma urealyticum from the amniotic fluid with transplacental antibiotic treatment Eradication of U parvum in AF within 4 days erythro, amp, gent, clinda x 6 days Romero RR et al, AJOG 166(2) 1992 Prolongation of pregnancy: 20.9 vs. 13.7 days Successful treatment of preterm labour by eradication of Ureaplasma urealyticum with erythromycin Prevention of lung injury: reduction in intraalveolar leukocytes, erythro x 10 days alveolar wall thickening, peribronchial lymphocytic aggregates, Mazor M et al, Arch Gyn Obstet 253(4) 1993 Type II pneumocyte hyperplasia Antibiotic treatment of intra-amniotic infection with Ureaplasma urealyticum. A case report and literature No additional benefit from Dexamethasone/indomethacin review Survival studies ongoing – cognitive and pulmonary function erythro x 7 days, fluoroquinolone and clinda x 10 days Smorgick N et al, Fetal Diag Ther 22(2) 2007 Grigsby PL et al, AJOG 207(6) 2012 7
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Clinical treatment of IAI/PTL limited by Late PTB and Postterm Lack of large well designed trials Late Preterm pregnancy are Postterm Births (thousands ) opposite ends Necessity to perform amniocentesis of normal parturition spectrum Inability to determine chronicity of IAI *Need for noninvasive markers or subclinical infection Preterm Birth Preterm Birth Proteins related to premature or failed initiation of labor Challenges of proteomics in late PTB The concept is not novel in medicine: Findings on pooled samples may not apply to Endocrinology Hematology individual cases (thyroid, diabetes) (platelets, clotting factors) Misidentification of proteins is possible TSH Factor VIII Cost and time of analysis Need to reproduce findings/validate on separate, large cohorts Hypothyroidism Graves Disease Hemophilia Thrombophilia (hyperthyroidism) (stroke) 8
6/7/2014 Preterm Birth Clouseau’s postulate Limitation – always get results You may get the right answer, but are you asking the right question? Need to ask the right question, in the right way Importance of validation studies 9
Recommend
More recommend