Oat basics and Cooking with oats Roseline Yap WK and Tee E-Siong - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Oat basics and Cooking with oats Roseline Yap WK and Tee E-Siong Outline Whole grains and oats Oat basics and types of oats Oat nutrition Oats existing and emerging benefits Cooking with oats Conclusion 2 Whole grains
Oat basics and Cooking with oats Roseline Yap WK and Tee E-Siong
Outline Whole grains and oats Oat basics and types of oats Oat nutrition Oats – existing and emerging benefits Cooking with oats Conclusion 2
Whole grains and Oats • Whole Grains are Wholesome • Rich in macro- and micro-nutrients and phytonutrients • High in dietary fiber (soluble and/or insoluble) • Provide several health benefits, including lowering risk to chronic diseases OAT IS A WHOLE GRAIN! 3
Oat is a whole grain 4
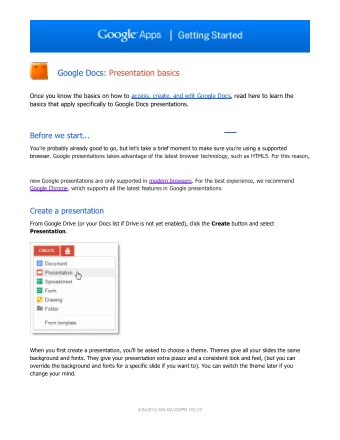
Oat Basics and Types of Oats 5
Variety of Oat Products Cookies Ready-to-eat cereals Flavoured sweet and savoury porridge Cereal beverages 6
Oat Nutrition Nutritional Value of Oats Per 100g 7
Nutrients in Oats Magnesium Phosphorus Vitamin B1 Iron Zinc Vitamin B12
Health Benefits Existing and Emerging Blood cholesterol and Heart disease Blood pressure Cardiovascular function - antioxidant Blood Sugar Satiety Gut health 9
Oats and Lower Risk to Heart Disease EXISTING BENEFIT Oats may help to: lower total blood cholesterol lower LDL-cholesterol reduce the risk of heart disease Thies et al. 2014 FDA – ‘Eating ≥ 3 grams beta-glucan from oats or barley per day, as part of a diet low in saturated fat and cholesterol may reduce the risk of coronary heart disease’ . Food and Drug Administration, Fed Regist. 1996;61:296-313. 10
“Other function” claim Beta glucan from (state the source) helps lower or reduce cholesterol* *Component Minimum Other Conditions amount required Beta-glucan 0.75g per I. Source of beta glucan shall be serving from oat and barley II. The food to be added with beta-glucan shall also contain total dietary fiber for not less than amount required to claim as “source” : 3g per 100 g (solids) 1.5g per 100 ml (liquids) III. There shall be written in the label this following statement, ‘Amount recommended for cholesterol lowering effect is 3 g/day’ However, Malaysia does not allow a claim on reducing risk to heart disease 11
1. Oats and Blood Pressure Relate to: • Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) – diet rich in whole grains • Inverse association between high whole grains intake and lower prevalence of hypertension Jacobs et al. 1998, Steffen 2005 • However, the link is unresolved: - Some studies showed improved blood pressure with oats, while others showed no significant effect - Similar with large trials • Hence, more studies are needed Fonseca 2003, He et al. 2004, Kotchen 1996, Keenan et al. 2002, Pins et al. 2002, Saltzman et al. , 2001, Tighe et al. 2010, Davy et al . 2002, Charlton et al. 2011, Maki et al. 2007 12
2. Oats and Cardiovascular Function Oats may help: • improve heart muscle function, and slow development of atherosclerosis Katz et al. 2004, Liu et al. 2004, Nie et al. 2006 • reduce inflammation and improve blood flow - due to the antioxidants (called avenanthramides) Bratt et al. 2003, Chen et al . 2007, Ji et al. 2003 However, insufficient evidence at this time, and further exploration is required, looking at the antioxidant properties of oats. 13
3. Oats and Blood Sugar Oats may help to control blood sugar : • delay sugar uptake in gastrointestinal tract • improve insulin sensitivity / response • Behall et al . 2005, De Angelis et a l. 2007, Wood et al . 1994, Hlebowicz et al . 2008, Regand et al. 2009, Alminger et al. 2008, Granfeldt et al. 2008 Also, permitted “other function” claim in Malaysia: Oat soluble fibre (beta-glucan) helps to lower the rise of blood glucose provided it is not consumed together with other food However, more research is still needed on the effects of oats on blood sugar when consuming a meal mixed with other foods. 14
4. Oats and Satiety Oats may help one to feel full longer: • due to the viscosity of its fibres • food leaves the stomach at a slower rate • able to regulate / control appetite Kristensen et al. 2011, Wanders et al. 2011 Evidence is still growing , which requires more studies. 15
5. Oats and Gut Health High in dietary fibre (both soluble & insoluble) • which may help to support digestive health Hallert et al. 2003, Hogberg et al. 2004, Junoven et al. 2009, Janatuinen et al. 2002 Emerging area of research in oats’ prebiotic capacity to benefit gut health Kedia et al. 2009, Connolly et al. 2010, Duncan et al. 2004 16
Oats in your daily diet • Oats have been recommended to be included in daily diet in a variety ways, for the preparation of various meals. • For example, oatmeal (oats cooked with water) is an excellent choice for breakfast , and • Due to its flexibility of either eaten as raw or cooked, oats can be incorporated as an ingredient into several foods. 17
Cooking with Oats Video presentation 18
Cooking with Oats Variety of ways to include OATS into your diet: Shakes and smoothies Gravies and sauces Binder in patties or to coat meat or fish nuggets Cookies, muffins, cakes, etc Salads Others - pancakes • Rolled oats can also be used instead of rice! 19
Cooking with Oats Oats Fish Fingers Fruit salad with oats and yoghurt 20
Oat Recipes from Junior Chef Granola Cookbook – Nutrition Society Bar of Malaysia Oatmeal Chocolate Chip Cookies 21
Conclusion • At least half of the recommended intake for grains should be derived from whole grains . • Consumption of oats can help consumers meet their daily whole grain requirement. • With the several health benefits of oats, let’s start including oats in the family menu ! OATS ARE YUMMY! 22
Acknowledgements e-Learning Academy and Laboratory Officer Embe ber Mohd ohd Radzy dzy Izan 23
t hank You
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.