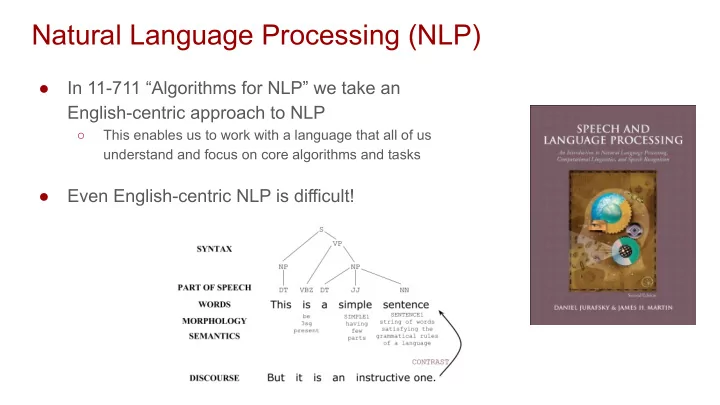

Natural Language Processing (NLP) ● In 11-711 “Algorithms for NLP” we take an English-centric approach to NLP ○ This enables us to work with a language that all of us understand and focus on core algorithms and tasks ● Even English-centric NLP is difficult!
English Natural Language Processing (NLP) A conversational agent contains ● Speech recognition ● Language analysis ○ Language modelling, spelling correction ○ Syntactic analysis: part-of-speech tagging, syntactic parsing ○ Semantic analysis: named-entity recognition, event detection, word sense disambiguation, semantic role labelling ○ Longer range semantic analysis: coreference resolution, entity linking ○ etc. ● Dialog processing ○ Discourse analysis, user adaptation, etc. ● Information retrieval ● Text to speech
But most of the world today is multilingual Source: US Census Bureau Source: Ethnologue
World’s Englishes
NLP beyond English ● ~7,000 languages ● thousands of language varieties
Tokenization
Part-of-speech tagging
Tokenization + disambiguation
Tokenization + disambiguation
Morphosyntactic analysis
Morphological processing
Syntactic parsing
Semantic analysis ● Every language “sees” the world in a different way ● For example, it could depend on cultural or historical conditions ● Russian has very few words for colors, Japanese has hundreds ● Multiword expressions, e.g. it’s raining cats and dogs or wake up and metaphors, e.g. love is a journey are very different across languages
Multilingual NLP ● Levels of linguistic structure ● Categorization of languages and processing of linguistic structures across languages ● Multilingual modeling
Recommend
More recommend