MIT 6.837 - Ray Tracing Ray Tracing MIT EECS 6.837 Most slides are - PDF document
MIT 6.837 - Ray Tracing Ray Tracing MIT EECS 6.837 Most slides are taken from Frdo Durand and Barb Cutler Some slides courtesy of Leonard McMillan 1 2 Ray Tracing Ray Tracing Ray Tracing kills two birds with one stone: Solves the
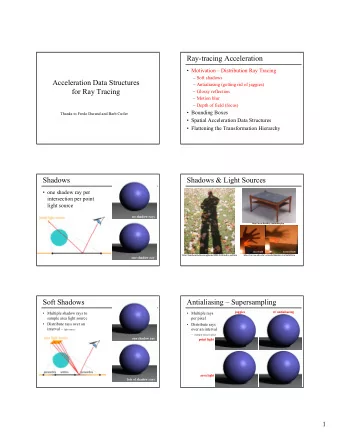
MIT 6.837 - Ray Tracing Ray Tracing MIT EECS 6.837 Most slides are taken from Frédo Durand and Barb Cutler Some slides courtesy of Leonard McMillan 1 2 Ray Tracing Ray Tracing • Ray Tracing kills two birds with one stone: – Solves the Hidden Surface Removal problem – Evaluates an improved global illumination model • shadows • ideal specular reflections • ideal specular refractions – Enables direct rendering of a large variety of geometric primitives • Book: A. Glassner, An Introduction to Ray Tracing • Web: http://www.cs.cf.ac.uk/Ray.Tracing Recursive ray tracing: Turner Whitted, 1980 3 4 Backward Tracing Overview of today • Shadows • Reflection • Refraction • Recursive Ray Tracing 5 6 1
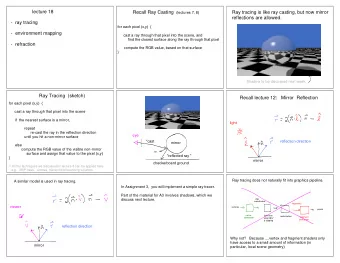
Ray Casting (a.k.a. Ray Shooting) Ray Casting with diffuse shading For every pixel (x,y) Color castRay(ray) Construct a ray from the eye Hit hit(); color[x,y]=castRay(ray) For every object ob ob->intersect(ray, hit, tmin); • Complexity? Color col=ambient*hit->getColor(); For every light L – O(n * m) col=col+hit->getColorL()*L->getColor* – n: number of objects, m: number of pixels L->getDir()->Dot3( hit->getNormal() ); Return col; 7 8 Encapsulating shading Questions? Color castRay(ray) • Image computed using Hit hit(); the RADIANCE For every object ob system by Greg Ward ob->intersect(ray, hit, tmin); Color col=ambient*hit-> getMaterial() ->getDiffuse(); For every light L col=col+hit-> getMaterial()->shade (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); Return col; 9 10 How can we add shadows? Shadows Color castRay(ray) Color castRay(ray) Hit hit(); Hit hit(); For every object ob ob->intersect(ray, hit, tmin); For every object ob Color col=ambient*hit->getMaterial()->getDiffuse(); For every light L ob->intersect(ray, hit, tmin); Ray ray2(hitPoint, L->getDir()); Hit hit2(L->getDist(),,) Color col=ambient*hit->getMaterial()->getDiffuse(); For every object ob For every light L ob->intersect(ray2, hit2, 0); col=col+hit->getMaterial()->shade If (hit->getT> L->getDist()) (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); col=col+hit->getMaterial()->shade (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); Return col; Return col; 11 12 2
Shadows – problem? Avoiding self shadowing Color castRay(ray) Color castRay(ray) Hit hit(); Hit hit(); For every object ob For every object ob ob->intersect(ray, hit, tmin); ob->intersect(ray, hit, tmin); Color col=ambient*hit->getMaterial()->getDiffuse(); Color col=ambient*hit->getMaterial()->getDiffuse(); For every light L For every light L Ray ray2(hitPoint, L->getDir()); Hit hit2(L->getDist(),,) Ray ray2(hitPoint, L->getDir()); Hit hit2(L->getDist(),,) For every object ob For every object ob ob->intersect(ray2, hit2, 0); ob->intersect(ray2, hit2, epsilon ); If (hit->getT> L->getDist()) If (hit->getT> L->getDist()) col=col+hit->getMaterial()->shade col=col+hit->getMaterial()->shade (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); Return col; Return col; 13 14 Shadow optimization Shadow optimization • Shadow rays are special • We only want to know whether there is an intersection, not which one is closest • How can we accelerate our code? • Special routine Object3D::intersectShadowRay() – Stops at first intersection 15 16 Shadow ray casting history Questions? • Image Henrik Wann Jensen • Due to Appel [1968] • First shadow method in graphics • Not really used until the 80s 17 18 3
Overview of today Mirror Reflection • Shadows • Compute mirror contribution • Cast ray – In direction symmetric wrt normal • Reflection • Multiply by reflection coefficient (color) • Refraction • Recursive Ray Tracing 19 20 Mirror Reflection Reflection • Cast ray • Reflection angle = view angle – In direction symmetric wrt normal • Don’t forget to add epsilon to the ray Without epsilon N R V � R � V With epsilon 21 22 Reflection Amount of Reflection • Reflection angle = view angle • Traditional (hacky) ray tracing – Constant coefficient reflectionColor � � � � � 2 R V V N � N � � � � – Component per component multiplication N R V � R � V V N N N V R � R � V V N N V 23 24 4
Amount of Reflection Fresnel reflectance demo • More realistic: • Lafortune et al., Siggraph 1997 – Fresnel reflection term – More reflection at grazing angle – Schlick’s approximation: R( � )=R 0 +(1-R 0 )(1-cos � ) 5 N R V � R � V metal Dielectric (glass) 25 26 Questions? Overview of today • Image by Henrik Wann Jensen • Shadows • Reflection • Refraction • Recursive Ray Tracing 27 28 Transparency Qualitative refraction • From “Color and Light in Nature” by Lynch and Livingston • Compute transmitted contribution • Cast ray – In refracted direction • Multiply by transparency coefficient (color) 29 30 5
Refraction Refraction ˆ ˆ ˆ N cos I N � � i ������������������� ˆ ˆ N cos I � i � i ˆ M � t ˆ T ˆ N � ������������������������������� ���������������� 31 32 Refraction Total internal reflection ˆ ˆ ˆ N cos I N • From “Color and Light in Nature” by Lynch and Livingstone sin � � � � i i t ������������������� � � � r sin ˆ � � N cos t i ˆ I � i � i ˆ M � t ˆ T ˆ N � ������������������������������� ���������������� 33 34 Cool refraction demo Cool refraction demo • Enright, D., Marschner, S. and Fedkiw, R., • Enright, D., Marschner, S. and Fedkiw, R., 35 36 6
Refraction and the lifeguard problem Wavelength • Refraction is wavelength-dependent • Running is faster than swimming Lifeguard • Newton’s experiment Water Beach • Usually ignored in graphics Run Digression Person in trouble Swim Pittoni, 1725, Allegory to Newton , 1725, Allegory to Newton Pittoni Pink Floyd, The Dark Side of the Moon 37 38 Rainbow Rainbow Digression Digression • From “Color and Light in Nature” by Lynch and Livingstone • Refraction depends on wavelength • Rainbow is caused by refraction+internal reflection+refraction • Maximum for angle around 42 degrees From “Color and Light in Nature” by Lynch and Livingstone 39 40 Questions? 41 42 7
Overview of today • Shadows • Reflection • Refraction • Recursive Ray Tracing 43 44 Recap: Ray Tracing Recap: Ray Tracing Color traceRay(ray) traceRay For every object ob Intersect all objects ob-> intersect (ray, hit, tmin); Color col=ambient*hit->getMaterial()->getDiffuse(); Ambient shading For every light L For every light If ( not castShadowRay ( hit->getPoint(), L->getDir()) col=col+hit->getMaterial()-> shade Shadow ray (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); If (hit->getMaterial()->isMirror()) shading Ray rayMirror (hit->getPoint(), getMirrorDir(ray->getDirection(), hit->getNormal()); If mirror Col=col+hit->getMaterial->getMirrorColor() Trace reflected ray * traceRay (rayMirror, hit2); If (hit->getMaterial()->isTransparent() If transparent Ray rayTransmitted(hit->getPoint(), Trace transmitted ray getRefracDir(ray, hit->getNormal(), curentRefractionIndex, hit->Material->getRefractionIndex()); Col=col+hit->getMaterial->getTransmittedColor() * traceRay (rayTransmitted, hit3); Return col; 45 46 Does it end? The depth of reflection Color traceRay(ray) For every object ob ob-> intersect (ray, hit, tmin); Color col=ambient*hit->getMaterial()->getDiffuse(); For every light L If ( not castShadowRay ( hit->getPoint(), L->getDir()) col=col+hit->getMaterial()-> shade (ray, hit, L->getDir(), L->getColor()); If (hit->getMaterial()->isMirror()) Ray rayMirror (hit->getPoint(), getMirrorDir(ray->getDirection(), hit->getNormal()); Col=col+hit->getMaterial->getMirrorColor() * traceRay (rayMirror, hit2); If (hit->getMaterial()->isTransparent() Ray rayTransmitted(hit->getPoint(), getRefracDir(ray, hit->getNormal(), curentRefractionIndex, hit->Material->getRefractionIndex()); Col=col+hit->getMaterial->getTransmittedColor() * traceRay (rayTransmitted, hit3); Return col; 47 48 8
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.