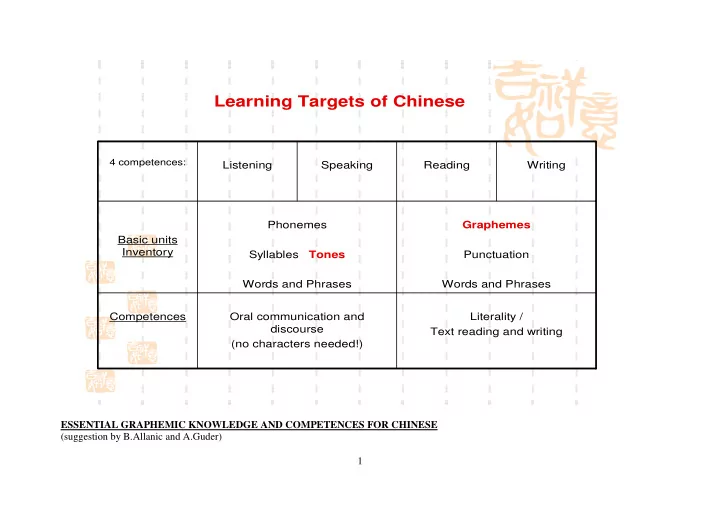

Learning Targets of Chinese 4 competences: Listening Speaking Reading Writing Phonemes Graphemes Basic units Inventory Syllables Tones Punctuation Words and Phrases Words and Phrases Competences Oral communication and Literality / discourse Text reading and writing (no characters needed!) ESSENTIAL GRAPHEMIC KNOWLEDGE AND COMPETENCES FOR CHINESE (suggestion by B.Allanic and A.Guder) 1
knowledge Graphemic receptive Graphemic productive A1 competence competence Writing System Hanyu - knows the function of letters and tone marks - can understand familiar words - can write down isolated of the pinyin alphabet as a transcription and sentences when written in words and short sentences in Pinyin system for the Chinese language Pinyin pinyin - can link Hanyu Pinyin with the - can type characters and texts corresponding Chinese characters with a computer using the if a text or word is given in both pinyin input writing systems - knows the basic principles of stroke order - can write familiar characters Characters Strokes and stroke and stroke direction by hand correctly, respecting directions the imaginary squares to fill in - can type characters and texts with a computer using the pinyin input ( 独体字 ) from complex ( 合体字 ) characters character - knows the main rules of composition of - can recognize about 20 semantic - can write and copy unknown component complex characters, can distinguish simple components if they are parts of characters without mistakes if unknown characters they are composed of familiar structure components - knows the difference between characters and components and does not confuse these two categories pictographic ( 象形字 ), semantic compound - knows the four main categories of ( 会 yi 字 ), phonetic loan ( 假借字 ) and characters (in his/her mothertongue): semantic-phonetic ( 形声字 ) - knows the difference between semantic components and phonetic components - knows about 20 semantic components and 2
can name it in mothertongue 亻 / 人 扌 / 手 饣 / 食 - is familiar with certain graphic variants of important semantic components 忄 / 心 讠 / 言 氵 / 水 3
- can see whether a given text is - can write by hand sentences, sequences of written in Chinese traditional respecting the proportion of characters characters or mainland characters each character and the space or Japanese between characters characters - knows that some characters function as - can understand more characters and lexical single words and others not than he/she can write by hand extensions - knows that most characters have a morphemic function in di- or polysyllabic words knowledge Graphemic receptive Graphemic productive A2 competence competence Writing System Hanyu see A1 see A1 see A1 Pinyin Characters see A1 see A1 see A1 - knows examples of characters that share the - can point out semantic classes of same phonetic components unknown characters with the help of their semantic components - can find unknown characters in dictionaries (with help of radical / key components) or with help of electronic devices Punctuation is able to understand the function of is able to use common Chinese common Chinese punctuation marks, punctuation marks in own short including dunhao 顿号(、) texts, including dunhao 顿号 shenglüehao 省略号(……) , (、) shenglüehao 省略号 shuminghao 书名号(《》〈〉) (……) , shuminghao 书名号 and zhuanminghao 专名号(﹒ (《》〈〉) and ﹒) . zhuanminghao 专名号(﹒ ﹒) . 4
Most frequent and most useful semantic elements : 亻 / 人 person 氵 water, liquid 土 earth, locality 女 woman / female gender 火 / 灬 fire / verbs of cooking 木 wood 扌 / 手 hand / verb of doing sth with hand(s) 辶 / 走 verb of fast movement 口 mouth / (particle of orality) 讠 / 言 words / verbs of speech 饣 / 食 food 忄 / 心 heart / words of emotionality 月 moon // flesh / parts of the human body 贝 shell / money and trade Cf. also the 104 graphic components list of France High frequent xingshengzi , but of high obscurity: 就 到 还 作 在 都 点 High frequent bifunctional components : 马 , 隹 ------------------------------------ Available Reference material about vocabulary in (characters) words for Chinese language levels (Guder 2011) Source basic elementary intermediate advanced Comme 基 基 基 基 础 初 级 初 初 初 中 中 中 中 级 高 高 高 高 级 nt 础 础 础 级 级 级 级 级 级 级 级 级 Old HSK exam 旧汉语 水平考 试 (800) 1033 (1604) (2305) (2905) no 2018 5253 8822 relation to (-2009) CERF Official standard of the PRC for (300) 505 (900) (1800) (2700-3000) no 5
TCFL 汉语国际教 育用音 节汉 字 词 2245 5456 9631-11092 relation to CERF 汇 等 级划 分 (2010) New Practical Chinese Reader 1 : 2 : 4 : no 新 实 用 汉语课 本 (400) (700) (1200) relation to 400 800 1900 CERF Source A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 New HSK exam 新 汉语 水平考 试 (0) (0) (623) (1071) (1709) (2633) A1/ A2 150 300 600 1200 2500 5000 without (2010-) characters New HSK exam in the opinion of (623) (1071) (1709) (2633) (2010-) 在德 国 FaCh 的 说 明 German FaCh 新 汉语 水平考 试 600 1200 2500 5000 Taiwan TOCFL exam 800 1500 5000 8000 A2 = 基 础 华语 文能力 测验 ( 台 湾 2011) „basic“ other languages: German, investigation of FaCh 2009 500 1000 2000 4-5000 8000 Suggestion EBCL project ?? p/a p/a p/a p/a p/a Important observations: - No difference made anywhere between passive (reading) and active (writing) vocabulary - High consistency concerning B2 level and above (except New HSK) - in level A the number of characters is about equivalent to the number of words ----- 6
Recommend
More recommend