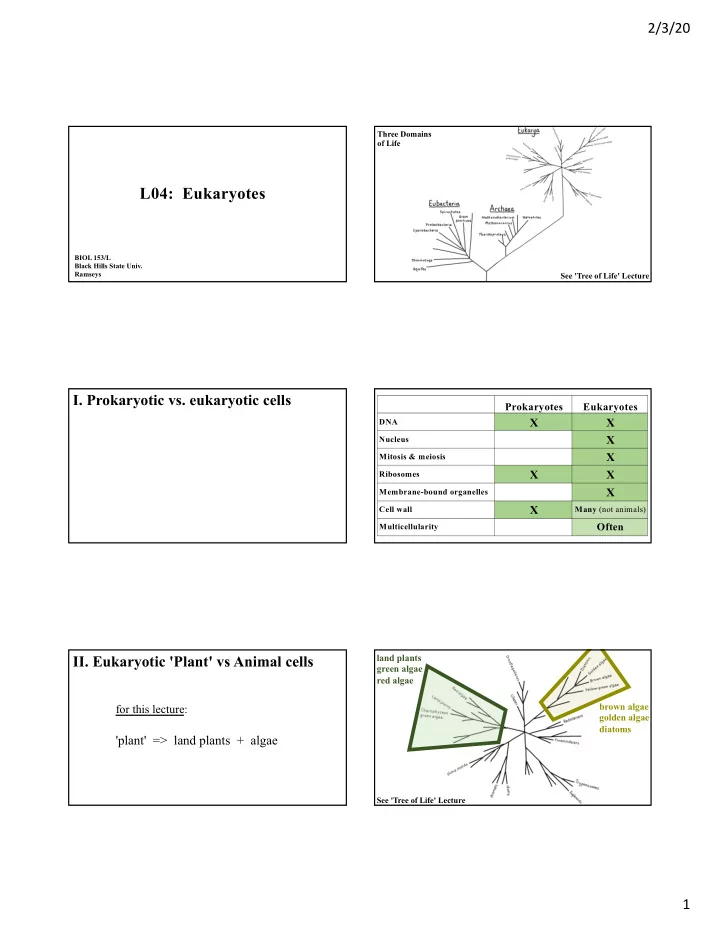

2/3/20 Three Domains of Life L04: Eukaryotes BIOL 153/L Black Hills State Univ. Ramseys See 'Tree of Life' Lecture I. Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells Prokaryotes Eukaryotes X X DNA X Nucleus X Mitosis & meiosis X X Ribosomes X Membrane-bound organelles X Cell wall Many (not animals) Often Multicellularity II. Eukaryotic 'Plant' vs Animal cells land plants green algae red algae brown algae for this lecture: golden algae diatoms 'plant' => land plants + algae See 'Tree of Life' Lecture 1
2/3/20 III. Eukaryotic cell components 'Plant' cells Animal cells Cell wall X Cell type diversity Less More X X Mitochondria X Chloroplasts Always Often Vacuoles (large vacuoles) (small vacuoles) A. Nucleus B. Cytoplasm membrane-bound compartment containing living matter of cell, outside nucleus linear DNA (chromosomes) nucleus disassociates during mitosis and meiosis cytosol is term for the cytoplasm 'goo' C. Organelles cell membrane nucleus cytosol 2
2/3/20 1. Definition of organelle 2. Membrane-bound organelles (examples) • Narrow: membrane-bound structure in cytoplasm • Broad: any cell structure outside nucleus a. Mitochondria b. Chloroplast 2x membrane-bound organelle; 2x membrane-bound organelle; performs aerobic respiration performs photosynthesis c. Vacuole d. Eyespot apparatus membrane-bound space with water, membrane-bound organelle; organic + inorganic molecules, enzymes senses light direction + intensity functions in storage, materials isolation, turgor pressure found in many unicellular photosynthetic organisms 3
2/3/20 3. Non-bound organelles (examples) cell membrane vacuole nucleus chloroplast cytosol mitochondria a. Ribosome b. Flagella threadlike structure protruding from cell; small structure composed of protein + RNA function in movement found in many unicellular photosynthetic organisms, site of protein synthesis in cell cytoplasm sperm of many multicellular photosynthetic organisms D. Cytoskeleton E. Cell wall structural layer outside cell membrane; provides support + protection network of microtubules + actin filaments in cytosol complex composition usually including carbohydrate in-cell movement (cell division, cytoplasmic streaming, etc.) polymers and microfibril structures 4
2/3/20 1. Taxonomic distribution 2. Land Plant cell walls eukaryotes very traditionally called 'plants' (prokaryote cell walls different) land plants, algae, fungi, many protists a. Multiple layers b. Composition • 1º cell wall: cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin • 1º cell wall: flexible, exterior • 2º cell wall: rigid, interior (not always present) • 2º cell wall: lignin, cutin, suberin • middle lamella: interface between cells c. Plasmodesmata cell membrane intercellular space cell wall middle lamella vacuole small channels traversing cells walls nucleus chloroplast cytosol mitochondria allow regulated communication + transport among cells plasmodesmata 5
2/3/20 3. Other cell walls • Fungi: chitin carbohydrate that provides rigidity to fungal cell walls • Diatoms: silica (glass) • Fungi: chitin SiO 2 provides strength and ridigity to cell wall • Diatoms: silica (glass) • Brown algae: alginate reacts with calcium in ocean water, creates flexible gel 6
2/3/20 • Brown algae: alginate • Red algae: carageenan, agar, calcium carbonate reacts with calcium in ocean water, creates flexible gel provide flexibility (carageenan, agar), rigidity (calcium c.) 7
Recommend
More recommend