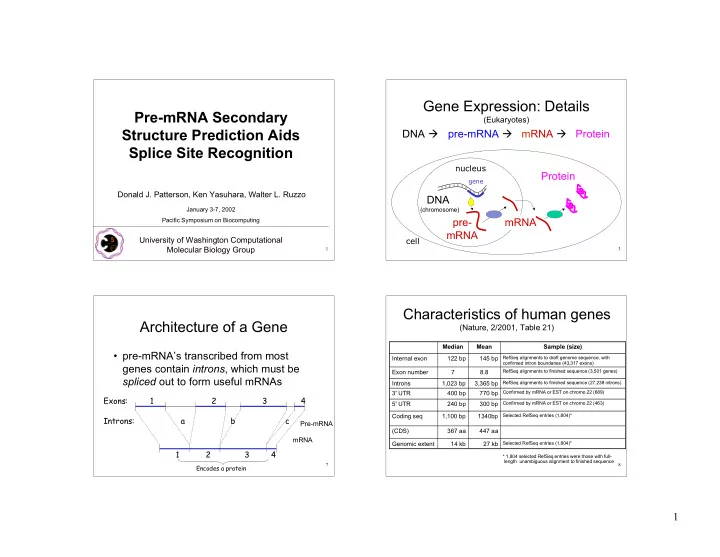

Gene Expression: Details Pre-mRNA Secondary (Eukaryotes) Structure Prediction Aids DNA pre-mRNA mRNA Protein Splice Site Recognition nucleus Protein gene Donald J. Patterson, Ken Yasuhara, Walter L. Ruzzo DNA January 3-7, 2002 (chromosome) pre- mRNA Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing mRNA University of Washington Computational cell Molecular Biology Group 1 3 Characteristics of human genes Architecture of a Gene (Nature, 2/2001, Table 21) Median Mean Sample (size) • pre-mRNA’s transcribed from most Internal exon 122 bp 145 bp RefSeq alignments to draft genome sequence, with confirmed intron boundaries (43,317 exons) genes contain introns , which must be Exon number 7 8.8 RefSeq alignments to finished sequence (3,501 genes) spliced out to form useful mRNAs Introns 1,023 bp 3,365 bp RefSeq alignments to finished sequence (27,238 introns) 3' UTR 400 bp 770 bp Confirmed by mRNA or EST on chromo 22 (689) Exons: 1 2 3 4 5' UTR 240 bp 300 bp Confirmed by mRNA or EST on chromo 22 (463) Coding seq 1,100 bp 1340bp Selected RefSeq entries (1,804)* Introns: a b c Pre-mRNA (CDS) 367 aa 447 aa mRNA Genomic extent 14 kb 27 kb Selected RefSeq entries (1,804)* 1 2 3 4 * 1,804 selected RefSeq entries were those with full- length unambiguous alignment to finished sequence 7 8 Encodes a protein 1
Relevance of Splice Prediction • Splice site prediction is critical to eukaryotic gene prediction. – Average human gene has 8.8 exons – Genes with over 175 exons known Mechanical Devices of the Spliceosome: Jonathan P. Staley and Christine Guthrie Cell, Vol. 92, 315–326, February 6, 1998 – Current primary sequence models do Motors, Clocks, Springs, and Things not display the same discriminatory power that cells exhibit in vivo – Small per-site error rate compounds 9 10 Possible acceptor splice sites Pre-mRNA sequences Hypothesis Secondary Structure Prediction (MFOLD) Primary Sequence Model • Secondary structure contains (WAM) information useful for predicting splice Secondary … site location. Structure Predictions Summary Statistics • This information is in addition to primary sequence information. Summary – Specific instances of secondary structure Statistics variation affecting the splicing process. Threshold Machine Learner Classifier 11 12 2
Possible acceptor splice sites Pre-mRNA sequences Data Set Secondary Structure Prediction (MFOLD) Primary • Drawn from 462 unrelated, annotated, multi- Sequence Model exon human genes with standard splicing. (WAM) (Reese 97) Secondary … Structure • 1,980 acceptor splice sites (3’ end of intron) Predictions Summary Statistics • 1,980 non-sites selected randomly – Aligned to an “AG” consensus Summary – Located within 100 bases of an annotated Statistics acceptor splice site. Threshold Machine Learner Classifier 13 14 Possible acceptor splice sites Pre-mRNA sequences What's in the Primary Sequence? Secondary Structure Prediction exon 5’ (MFOLD) Primary Sequence Model (WAM) Secondary … Structure Predictions Summary intron Statistics Summary Statistics Threshold Machine Learner Classifier 15 exon 16 3
What's in the Primary Sequence? Sequence-based Metric • 1 st order Weight Array Matrix (WAM) / Markov Model -4 -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3 – P i (N i ={A,C,G,U} | N i-1 ={A,C,G,U} ) A 22 4 100 0 25 25 27 • Training C 33 74 0 0 13 21 27 – Generate two conditional probability tables for G positions (–21,+3), one from positive examples and 22 0 0 100 52 22 24 one from negative examples. T 22 21 0 0 9 32 23 • Testing intron exon – For each sequence, x, calculate its likelihood ratio: acceptor splice site ( ) P + x � � log WAM � � Weight Matrix Model (0 th order Markov Model) 10 � ( ) � P x � � � WAM 17 18 Possible acceptor splice sites Acceptor Pre-mRNA sequences Splice Site Secondary Structure Secondary Sequence Model Prediction (MFOLD) (MFOLD) Primary Sequence Model (WAM) Secondary … Structure Predictions Summary Statistics Secondary Summary 0 Statistics Structure 100 Threshold Machine Learner Classifier 19 20 4
Possible acceptor splice sites Pre-mRNA sequences Secondary Structure Statistics Secondary Structure Prediction (MFOLD) Primary • Optimal Folding Energy Sequence Model (WAM) • Max Helix score Secondary • Neighbor Pairing Correlation Model … Structure Predictions Summary Statistics Summary Statistics Threshold Machine Learner Classifier 21 22 1. Optimal Folding Energy 2. Max Helix ...CUGCUUUCUCCCCUCUCAGGGACUUACAGUUUGAGAUGC... What is the highest probability that a helix will form nearby? Secondary Sequence Prediction (MFOLD) • Calculate P HStart , x • Calculate P … HEnd , x MaxHelix max ( P , P ) = Free Energy Free Energy Free Energy i HStart , x HEnd , x Helix x ( i 5 , i 5 ) � � + -35.2 kcal/mole -34.0 kcal/mole -2.0 kcal/mole 23 24 5
3. Neighbor Pairing Correlation 3. Neighbor Pairing Correlation Model Model O O P S P S O S O P S P O O O Change the pre- Change the pre- Unpaired base Unpaired base Unpaired base Unpaired base O O O O mRNA alphabet from mRNA alphabet from Paired base Paired base Paired base Paired base P P P P nucleotides to nucleotides to Paired and stacked base Paired and stacked base Paired and stacked base Paired and stacked base structural symbols S S structural symbols S S 25 26 Possible acceptor splice sites 3. Neighbor Pairing Correlation Pre-mRNA sequences Model Secondary Structure • 2 nd order Markov Model Prediction (MFOLD) Primary – P i (N i ={O,P,S} | N i-1 ={O,P,S} ^ N i-2 ={O,P,S} ) Sequence Model • Training (WAM) – Generate two conditional probability tables for Secondary … Structure positions (–50,+3), one from positive examples Predictions Summary and one from negative examples. Statistics • Testing – For each sequence, x, calculate its log likelihood Summary ratio: Statistics ( ) P + x � � log NPCM � � 10 � ( ) � Threshold P x � Machine Learner � � NPCM Classifier 27 28 6
Possible acceptor splice sites Pre-mRNA sequences Machine Learners Secondary Structure Prediction • Decision Trees (MFOLD) Primary Sequence Model – Quinlan’s C4.5 (WAM) Secondary • Support Vector Machines … Structure Predictions Summary – Noble’s svm 1.1 Statistics – Radial Basis Kernel degree 2 Summary • Both take a vector of statistics and Statistics produce a yes/no binary classifier. Threshold Machine Learner Classifier 29 31 Results LLR of Base Pairing (Decision Trees) Features Mean % Error p Accuracy (%) Reduction 25% more likely for acceptor splice sites to WAM (baseline) 92.73 pair at position -2 WAM,OFE 93.13 5.5 0.066 WAM,OFE,NPCM 93.16 5.9 0.022 WAM,OFE,MH 93.21 6.6 0.009 WAM,OFE,NPCM,MH 93.13 5.5 0.016 WAM = Weight Array Matrix (Primary Sequence Method) Wilcoxon p-value OFE = Optimal Free Energy under 10-fold MH = Max Helix cross-validation NPCM = Neighbor Pairing Correlation Matrix 32 33 7
Results LLR of Helix Continuation LLR of Helix Initiation 45% more likely for 35% more likely for acceptor splice sites acceptor splice sites to to continue a helix initiate a helix at through the splice site. position –2 and -1 34 35 36 37 8
Helix Formed at Splice Site Conclusions • Secondary structure statistics correlate Acceptor Non-Acceptor with splice site location. Pr(No Helix) 0.37 0.48 • Our models (Max Helix, NPCM) can Pr(Helix) 0.63 0.52 represent some of the relevant Pr(Folds Left) 0.35 0.26 secondary structure. Pr(Folds Right) 0.28 0.26 • These models capture correlations that current primary sequence models don’t capture. 38 39 Acknowledgements Future Work • Don Paterson • Other organisms • Ken Yasuhara – Oryza sativa ( rice) in progress • Jeff Stoner • Donor splice sites • Kevin Chu • Other features? • More structure models More Info – Stochastic Context Free Grammars? http://www.cs.washington.edu/homes/ruzzo 40 UW CSE Computational Biology Group 41 9
Recommend
More recommend