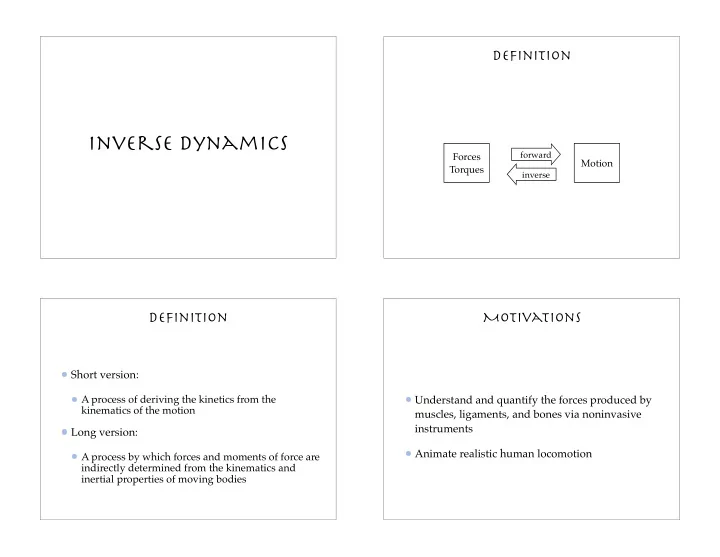

Definition Inverse dynamics forward Forces Motion Torques inverse Definition Motivations Short version: A process of deriving the kinetics from the Understand and quantify the forces produced by kinematics of the motion muscles, ligaments, and bones via noninvasive instruments Long version: Animate realistic human locomotion A process by which forces and moments of force are indirectly determined from the kinematics and inertial properties of moving bodies
Motion and force measurement Motion analysis Interaction of muscle Need to record accurate kinematic properties of the contractions across several motion joints is extremely complex video or infrared based motion analysis systems Most invasive devices can only measure forces in single tissues Need to measure the external forces precisely surgical stables force platforms that measures the ground reaction forces buckle force transducers Motion analysis Joint kinetics Equal in joint forces and moments, but completely Inverse dynamics can only measure the net effect of different in muscle activities the internal forces and torques across several joints Inverse dynamics can compute total load on a system, but can not determine the distribution of the load Inverse dynamics assumes there is no co- contraction of agonist and antagonist muscles
Model reduction Model reduction Reduce complex anatomical structures force from bone-on-bone F ankle triceps surae forces ligament force from F ∗ F ∗ M ankle force tibialis anterior F F M F ground ground contact force contact force − F ∗ gravity gravity Foot with Forces and F ∗ − F ∗ Couple and F muscle added at ankle � replaced by − F ∗ force F center moment M F Equation of motion Limitations ID relies on assumption that are not always valid Given body kinematics and anthropometric joint friction and air friction parameters, derive the kinetics quantities using the non-uniform distribution of mass Newton-Euler equations: movement of joint center of rotation Newton (linear): approximation of body segment parameters Euler (angular): Measurement error and numerical error propagation
Recommend
More recommend