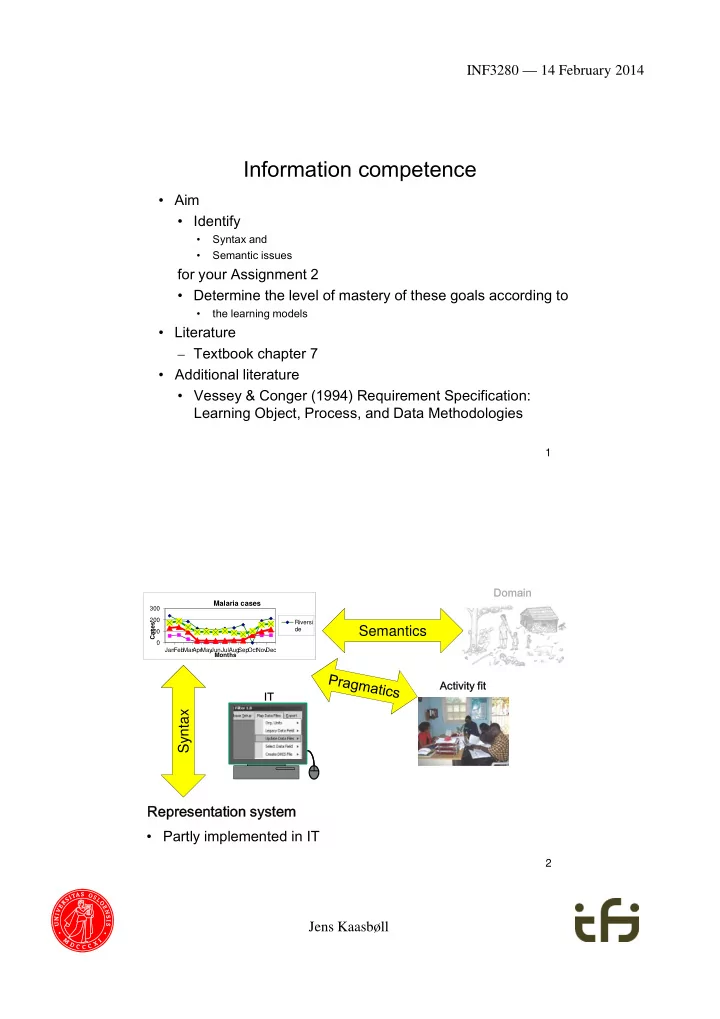

INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Information competence • Aim • Identify Syntax and • Semantic issues • for your Assignment 2 • Determine the level of mastery of these goals according to the learning models • • Literature – Textbook chapter 7 • Additional literature • Vessey & Conger (1994) Requirement Specification: Learning Object, Process, and Data Methodologies 1 Domain Malaria cases 300 200 Riversi Cases Semantics de 100 0 Jan Feb MarApr May JunJulAug Sep Oct Nov Dec Months Activity fit IT Syntax Representation system • Partly implemented in IT 2 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Information • About something • Representing it • Detached in time and space from what it is representing • Expressed in a representation system Information No information 3 Representation system • Semantics • Coupling a domain to a set of symbols • Meaning • Syntax • Symbols • Rules for combining symbols • Combined symbols International Standard Combined meaning Book Number • Examples • Language • Formal language • Arabic number system Musical notation • Roman number system 4 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Syntax Malaria cases 300 200 Riversi Cases de 100 0 Jan Feb MarApr May JunJulAug Sep Oct Nov Dec Months IT Syntax Many syntactic rules implemented in IT 5 Types and Instances Description of a common A unit of data adhering to set of symbols and the type operations Integer 234 -2 1 000 000 Number without decimals Calculation operators :Account Account 18 473.32 Balance Kari Owner :Account Class Objects Deposit 3 292.00 Withdraw Ola 6 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Data structures 1-many relationship between customer and address Not explicitly stated Restrictions on values 7 Aspect Explanation Example – Styles in text processors Semantics What it refers to The format of paragraphs Syntax – Type- Composite of paragraph, character, border Properties and Instance and numbering. operations enabled Syntax – Disabled values and Restrictions operations Syntax – Internal Two level hierarchy How the instances structure are organised. Syntax – External Can be applied to 0 or more paragraphs. How its instantiations structure relate to instantiations of other concepts Similarities and Style and master slides determine layout of Comparisons with distinctions to other portions of a file. Styles apply to paragraphs, other concepts concepts. while master slides apply to slides. Aspects of an information concept 8 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Easiness of making data structures Process modeling Easy Data and object modelling Difficult Vessey & Conger, 1994 9 Learning syntax – levels of mastery Structural Functional understanding understanding of syntax Reflect of syntax Refer to input & output Explain the rules and without doing the operation relate concepts Interpret Navigate Information Syntax skills Reproduction Repeat Fix up representations Skills Imitate which break the rules Reproduce the symbols of the system 10 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Learning syntax – example Because an apostrophe Astrud’s song should precede the Type an ‘ between the genitive s. name and the s Reflect Refer to input & output Explain the rules without doing the operation and how they apply Interpret Navigate Grammar Structure Combining noun, apostrophe and s Fix up representations Reproduce the symbols Repeat which break the rules of the system Imitate Astrud’s song Astruds song 11 Semantics Domain Malaria cases 300 200 Riversi Cases Semantics de 100 0 Jan Feb MarApr May JunJulAug Sep OctNov Dec Months • Users’ Meaning of the Information • Rules and conventions for aligning Information with Domain • Collectively agreed by the group of users 12 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Learning semantics Structural Functional semantic Understanding understanding the ability to express the the ability to express why a Reflect rules and conventions state in the domain is governing the domain- represented by a particular information relation piece of information Interpret Navigate Information Skills Repeat Imitate Semantic Skill the ability to observe the domain and enter appropriate data and to read data and relate it to the domain. Learning semantics – example Tiger I wonder why they wrote The word “tiger” denotes a that, is it a kind of metaphor? large, striped cat. Reflect Functional semantic Structural semantic understanding understanding Interpret Navigate Mammal species Semantic skills Repeat Aligning information and reality Imitate Tiger 14 Lion Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Learning failure – interference • Two concepts with similar properties • Basing learning on the wrong preconception Grammar Word processors A paragraph is a sequence of A paragraph is a sequence of sentences dealing with one point characters ending with Enter Headline. Paragraphs No paragraph Learning failures Learner’s often stumble on their paths to understanding, and we often see that the Paragraph concepts they develop do not correspond to those of the teacher. That does not necessarily mean that one is better than another, but some ways of understanding may be inadequate for certain purposes. 1. Find the data structures Outline views • Data models • Deduce from user interface • 16 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 2. Decide main and sub structure types Sequence Grid (array, matrix) Hierarchy Combinations? Network 17 3. Decide user group • Entering and reporting Only data Visit Visit-ID Patient Visit-type • Setting up data structures Include types 18 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 4. Include abstract entities • Events in the Domain represented by a record Occupancy From date # nights # guests • Planned events Reservation From date # nights # guests Room type 19 5. Include examples • In the model Customer Reservation Name: Fjoralba From date: 24.03.14 Address: Oslo # nights: 3 Phone: 123456 # guests: 2 Email: fj@mail.com Room type: Luxe • Relate to New reservation recognisable places Name Fjoralba in the user interface # guests 2 From 24 March 2014 # nights 2 Room type Luxe 20 Jens Kaasbøll
INF3280 — 14 February 2014 Start Assignment 2 making • A list of 1-3 concepts to include in your teaching • A table of the aspects of the concept(s) • A structural model for Assignment 2 Jens Kaasbøll
Recommend
More recommend