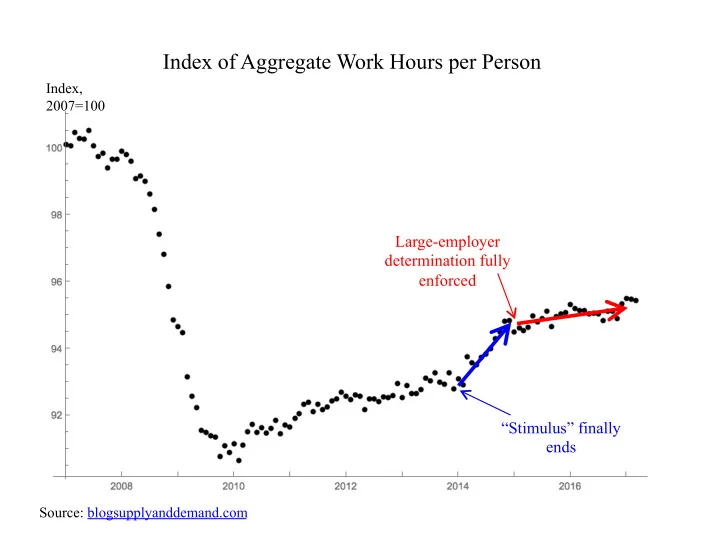

Index of Aggregate Work Hours per Person Index, 2007=100 Monthly data available as of Feb-2016 Apr 2017 Large-employer determination fully enforced “Stimulus” finally ends Source: blogsupplyanddemand.com
The Employer Mandate • Beginning in 2015, employers are designated as small or large based on 50 full-time-equivalent (FTE) employees – Each part-time worker is a partial FTE in proportion to his monthly hours worked – Large designation creates a mandate for the subsequent year • Offer compliant and “affordable” coverage or pay a monetary penalty • Penalty applies only to full-time employees, only during the months that they are on the payroll • Indexed to health insurance costs • Unlike salaries, penalties are not deductible from business taxes. Salary equivalent of $2k penalty is about $3k.
Table 1. The salary equivalent of the 2017 employer penalty Scenario: Expense items Penalty imposed Salary raised 2017 ACA penalty 2,265 0 Salaries 0 3,449 Payroll tax 0 264 7.65% rate Business income taxes 0 -1,448 39% rate Net result for employer expenses including taxes: $2,265 $2,265 At the threshold, one more hire costs 20 penalties: $68,980 annually, plus salary and benefits. Source Side Effects: The Economic Consequences of the Health Reform . acasideeffects.com
Figure 1. The employer penalty's hour-equivalent distribution .3 minimum wage workers average .2 Density .1 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Hours per week
Measurement challenges • Evaders do not want to be measured – Confidential sample of people at corps, rather than corps. • How to know when a regulation is binding? – Literature solution: look at France! Or tax payments. Or both. – Measure size and compliance together • The enforcement probability function is often unpublished • Even bright-line thresholds apply to size measures that are not readily available – Get good (enough) measures of size; a bit of econometrics.
Source: French data via Garicano et al.
Source: Garicano et al. Year is 2003.
Figure 1. Share of private-sector MEPSnetIC firms sized 25-99 0.51 with fewer than 50 employees (FT and PT counted equally) First year of large-employer determination without transition relief applicable in the 0.50 subsequent (i.e., coverage) year In theory, this masks a number of small employers (< 50 FTEs) with more than 50 0.49 employees 0.48 0.47 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016
MEPS suggests that most 49ers have less than 49 FTEs
Hanover survey subscription • One year of unlimited surveys = $45k – Only one survey at a time • Variable cost per respondent – Related to the respondent value of time – E.g., business managers cost more than generic household – Mercatus paid $19k for 745 respondents • i.e., our respondents got about $100 per hour – Survey took 10-15 minutes – Reward system (e.g., sporting tickets, hotel, airline tickets) • Other purchase plans would also be about $40k
Non-ESI firms stay below 50 March 2017 national sample of 745 employers with 2-199 FT employees ESI firms do not About 38,000 Non-ESI firms “move”
Non-ESI firms stay below 50 ESI firms do not Num. obs. in green 20 49 Avg. of the 81 12
Growth in the number of businesses, by size from 2013-14 to 2015-16 1000 or more employees 100-999 employees 50-99 employees 25-49 employees 10-24 employees Less than 10 employees 0% 1% 2% 3% 4% 5% 6%
Duggan, Goda, Jackson • Their regression table shows that the ACA reduced the labor force by 349,190 on average 2014-15 • Their regional-comparisons study is not designed to measure labor market effects of the employer mandate – The employer mandate is federal – The prevalence of 49ers is similar in Medicaid expansion states as in the other states • Their regional comparisons do not measure labor market effects on near-elderly people • Need to add these effects to their 349,190
Recommend
More recommend