Forward and Flyback (Converters with isolation ) 4.1 Transfer of DC - PDF document
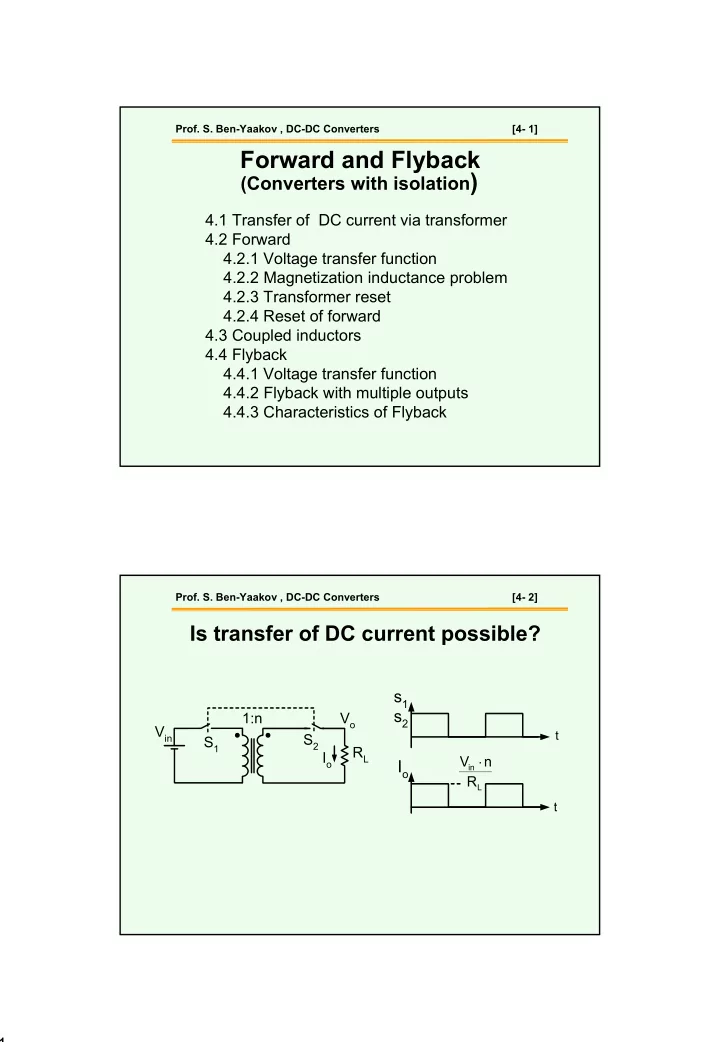
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 1] Forward and Flyback (Converters with isolation ) 4.1 Transfer of DC current via transformer 4.2 Forward 4.2.1 Voltage transfer function 4.2.2 Magnetization inductance problem 4.2.3 Transformer
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 1] Forward and Flyback (Converters with isolation ) 4.1 Transfer of DC current via transformer 4.2 Forward 4.2.1 Voltage transfer function 4.2.2 Magnetization inductance problem 4.2.3 Transformer reset 4.2.4 Reset of forward 4.3 Coupled inductors 4.4 Flyback 4.4.1 Voltage transfer function 4.4.2 Flyback with multiple outputs 4.4.3 Characteristics of Flyback Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 2] Is transfer of DC current possible? s 1 s 2 1:n V o V in t S 2 S 1 R L I o V ⋅ n I o in R L t 1
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 3] Replacing S 2 by a Diode 1:n S 1 D V o V in R L I o Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 4] Forward Converter L 1:n V o V in D 1 I L C I R D 2 R I C T S Forward : � T is a transformer � Output section: Buck � Buck derived 2
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 5] Voltage transfer function S L D 1 V X 1:n V o ON ON V in t I L C I R V 2 T s D 2 R I C V in ⋅ n V 2 S t V X V − V 2 D 1 At steady state, over one switching cycle: t = V 0 ; L ≈ − ⋅ S ( nV V ) t ; V + in o on + = ⇒ = S S 0 o nD + − ≈ − o ⋅ on S ( V ) t ; V − off in Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 6] Magnetization Inductance Problem 1:n V in L m ideal S V Lm V in t ? 3
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 7] Transformer Reset V in V in V L t off t L m t on V in V L S V reset t t on reset − ( V V ) in = − V D ( V V ) D in on reset in off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 8] Applying a Reset Winding V in ON n 1 n 2 OFF I L V in n 3 L m1 V reset S V reset V V reset in Reset Requirements ≥ D D off on n n 3 1 4
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 9] Applying same source V in n 2 n 1 n 3 V reset S n D V V in in 3 on < > D D off on n n n D 3 1 1 off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 10] Assignment V in n 1 n 2 n 3 V reset S Given: 0.1<D on <0.7 What will be the voltage stress on S? 5
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 11] Reset of Forward D 1 L V in I L C I R n 1 D 3 D 2 R n 2 I C n 3 Calculation of n 3 S � Calculation can be done by looking at any of the windings n 1 , n 2 , n 3 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 12] Fundamental requirement: V V n 1 in S 1 =S 2 S 1 t off n 2 t L m n 1 t on S 2 n 1 V 1 in n I 3 Lm n 3 t V V n 1 v winding = in o S 1 t off t t on S 2 2 � Example: Looking at n 1 I Lm t 6
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 13] VT V V n 1 n in S 1 =S 2 S 1 ≥ V D 1 V D t off t in off in on n 3 t on S 2 1 n V 1 in n I 3 Lm D t n ≤ n off 3 1 D on V V n 1 in S 1 D t off ≤ t n n off 3 1 − 1 D t on S 2 off 2 I Lm t Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 14] VT Voltage on switch when “off” n = + V V 1 V V V s in in D off t n n 1 in 3 D on D n = + on max V V [ 1 ] V 1 in n s in − 1 D on max 3 7
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 15] Reset winding I 1 I 2 L V in D 1 I L C I R n 1 D 3 D 2 R n 2 I C Switch Current I 2 I pk n n = 1 t on t off t n 3 n 2 S T S n I I 1 pk � primary current is a reflection n 2 I t off t pk of I 2 plus I m Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 16] Taking into account Lm I 2 L V in I Lm n 1 D 1 I Lm C R D 3 t L m D 2 n 2 I 2 n t n 3 I S I 2 n+I Lm S t 8
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 17] Reset Current n D n D = = = 1 on V V 1 V on reset in in − − n 1 D n 1 D 3 on 3 on I I pk ? Question 1: How does I n3 look ? n 3 t t off T S Question 2: If D max =0.3 2.1 Calculate n 1 /n 3 2.2 Find maximum voltage on switch Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 18] Coupled inductor n 1 L 1 L 1 L 2 n 2 L 2 2 L n = 1 1 L n 2 2 9
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 19] Current in a Winding CAN be Interrupted ! S 1 t S 2 t S 1 S 2 1:1 I 1 I 2 V 1 V 2 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 20] Energy stored in core (not in wires) S 1 t S 1 S 2 1:1 S 2 I 1 I 2 V 2 V 1 t I 1 V 1 I pk 1 L At transition t t S = I I I 2 I pk pk pk V 2 1 2 2 = N I N I L 1 pk 2 pk 1 2 t t S 10
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 21] Coupled windings S 1 S 2 S 1 1:n I 1 I 2 V 1 V 2 L t S 2 t Problem: Leakage inductance I 1 (will be discussed later) V I 1 pk 1 L t ⋅ = ⋅ I 1 I n t S pk pk 1 2 I 2 I pk V 2 I 2 pk = 2 I 2 n L t pk 1 n t S Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 22] Diode replace a switch S 2 1:n V 1 V 2 = ⋅ V 10 V n V 10 1 S 1 1:n 1 = V V 20 2 n V 1 V 2 V 20 (negative voltage) S 1 1:n V 1 11
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 23] Buck Boost D S V o V in C R L Polarity Reversal + = V D V D 0 in on o off V D o = − on V D in off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 24] Flyback D S V o V in C R L Buck Boost D S Isolated Back-Boost V o V in C R Flyback 12
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 25] Flyback converter D 1 1:n V o V in R C S 1:n V o 1:n V o V in V in V o C R C R I n nV in t on t off S S V o V in n Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 26] Voltage transfer function The average voltage method D 1 Voltage across primary 1:n V o V in R C V 1 V 1 -V in t off t S t on V o n T s V ⋅ = o ⋅ V t t in on off n V D V o = on o n ⋅ = ⋅ V D D in on off V D n in off 13
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 27] Voltage transfer function The ∆ I method n 2 D 1 n 1 V o t on V in R L 1 C t I 2 T s L 2 I 1 I 1 ∆ I 1 S t n 2 I ∆ 2 I n 1 1 V V t ∆ = ∆ = n I n I n in t n o t ; 1 1 2 2 1 on 2 off L L 1 2 2 V = n L V t D n n V D n D = = = 2 1 o on on 2 1 o on o 2 on n L V t D n n V D V n D 1 2 in off off 1 2 in off in 1 off Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 28] Flyback with multiple outputs V in V o1 D 1 R 1 n 1 C 1 V o2 D 2 R 2 C 2 n 2 S 14
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 29] Flyback t on t off n 1 n 1 V in V in V o1 V o1 R 1 C 1 R 1 C 1 n 2 n 2 V o2 V o2 C 2 C 2 R 2 R 2 = n V n V 1 o 2 o 1 2 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 30] Characteristics of Flyback � Isolation � Step-up or Step-down � Discontinuous current at input and output (Buck-Boost Derived) � Multiple outputs (economical) 15
Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 31] Exercise 10meg R4 D1 out Dbreak L1 L2 V1 {L1} C1 RL {Vin} {L1*(n*n)} 220u {Load} IC = 6 out_gnd drain S1 K K1 0 gate PARAMETERS: K_Linear + + COUPLING = 1 n = 0.5 - - L1 = l1 Vin = 12 V1 = 0 Sbreak L1 = 300u V2 L2 = l2 V2 = 15 Load = 10 TD = 0 0 TR = 0.01u TF = 0.01u PW = 10u PER = 20u 0 � Find by simulation Llkg and Lm of the magnetic body if k=.9 � Calculate Ap of magnetic element 16
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.

![1 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [4- 4] Forward Converter L 1:n V o V in D 1 I L C I](https://c.sambuz.com/702678/1-s.webp)








![Drivers Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [8- 2] Driving a MOSFET L D V in V o R L C 1](https://c.sambuz.com/1030065/drivers-s.webp)
![1 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [8- 4] Gate Current V S 15V L D V in V o t V gs R g](https://c.sambuz.com/1030433/1-s.webp)
![1 Prof. S. Ben-Yaakov , DC-DC Converters [10- 4] Closed Loop V o Power v o stage R 1 - MOD](https://c.sambuz.com/839741/1-s.webp)








