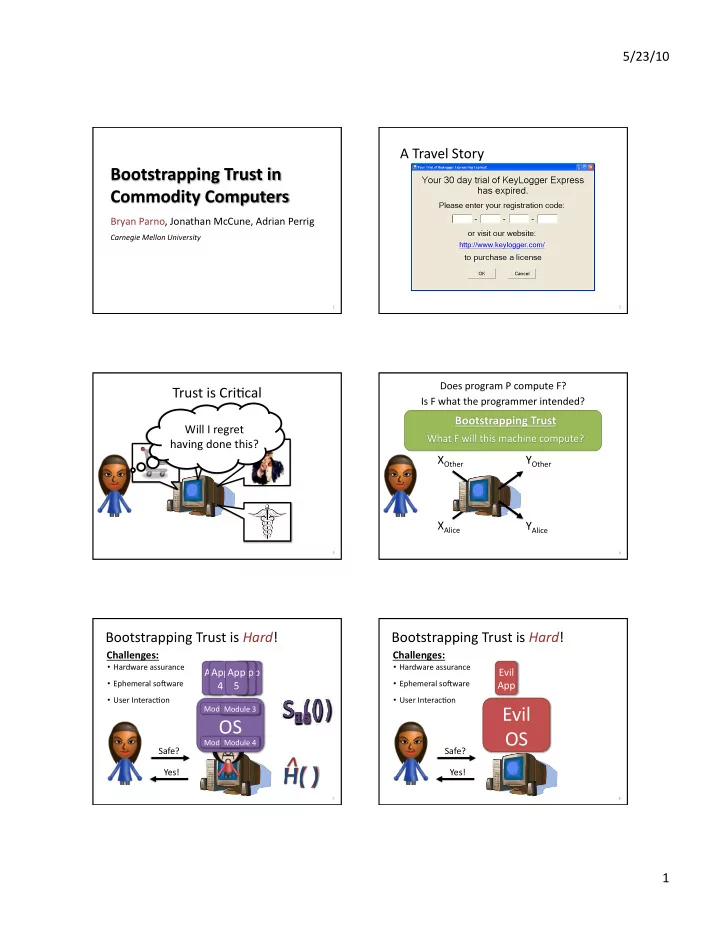

5/23/10 A Travel Story Bryan Parno, Jonathan McCune, Adrian Perrig Carnegie Mellon University 1 2 Does program P compute F? Trust is CriAcal Is F what the programmer intended? Will I regret having done this? X Other Y Other F X Alice Y Alice 3 4 Bootstrapping Trust is Hard ! Bootstrapping Trust is Hard ! Challenges: Challenges: • Hardware assurance • Hardware assurance App App App App App App Evil • Ephemeral soRware 1 4 5 N 2 3 • Ephemeral soRware App • User InteracAon • User InteracAon Evil Module 1 Module 3 OS OS Module 2 Module 4 Safe? Safe? Yes! Yes! 5 6 1
5/23/10 In the paper… 1) Establish Trust in Hardware • Bootstrapping foundaAons • Hardware is durable • TransmiXng bootstrap data • Establish trust via: • InterpretaAon – Trust in the manufacturer • ValidaAon – Physical security • ApplicaAons • Human factors • LimitaAons • Future direcAons • … and much more! 7 8 A Simple Thought Experiment 2) Establish Trust in SoRware • Imagine a perfect algorithm for analyzing control flow • SoRware is ephemeral – Guarantees a program always follows intended control flow App App … • We care about the soRware No! 1 N • Does this suffice to bootstrap trust? currently in control P • Many properAes ma`er: Respects OS Type Safe – Proper control flow control flow – Type safety – Correct informaAon flow … 9 10 What is Code IdenAty? Code IdenAty as Trust FoundaAon • An a`empt to capture the behavior of a program • From code idenAty, you may be able to infer: – Proper control flow • Current state of the art is the collecAon of: – Type safety – Program binary FuncAon f – Program libraries – Correct informaAon flow – Program configuraAon files … Inputs to f – IniAal inputs • Reverse is not true! • ORen condensed into a hash of the above 11 12 2
5/23/10 Establishing Code IdenAty What Can Code IdenAty Do For You? [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Arbaugh et al. ‘97], [Sailer et al. ‘04], [Marchesini et al. ‘04],… • Research applicaAons • Secure the boot process • Thwart insider a`acks X Other Y Other • Count‐limit objects • Protect passwords • Improve security of • Create a Trusted Third Party F network protocols • Commercial applicaAons • Secure disk encrypAon (e.g., Bitlocker) X Alice Y Alice • Improve network access control • Secure boot on mobile phones • Validate cloud compuAng plamorms 13 14 Establishing Code IdenAty Establishing Code IdenAty [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Arbaugh et al. ‘97], [Sailer et al. ‘04], [Marchesini et al. ‘04],… [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Arbaugh et al. ‘97], [Sailer et al. ‘04], [Marchesini et al. ‘04],… Chain of Trust Root of X Other Y Other Trust ? … SoRware SoRware SoRware f 1 f 2 f N . . . N 1 N‐1 X Alice Y Alice 15 16 A`estaAon: Trusted Boot: Recording Code IdenAty Conveying Records to an External EnAty Root of [Gasser et al. ’89], [England et al. ‘03], [Sailer et al. ‘04],… [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Arbaugh et al. ‘97], [England et al. ‘03], [Sailer et al. ’04]… Trust SoRware SoRware SoRware SoRware SoRware SoRware . . . . . . random # N‐1 N N‐1 N 1 1 Sign ( ) SW SW SW SW 1 2 N‐1 N K priv random # SW SW SW SW SW SW SW SW 1 2 N‐1 N 1 2 N‐1 N Controls K priv 17 18 3
5/23/10 InterpreAng Code IdenAty InterpreAng Code IdenAty TradiAonal TradiAonal App 1…N [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Sailer et al. ‘04] [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Sailer et al. ‘04] Drivers 1…N Policy Enforcement Policy Enforcement Virtual [Marchesini et al. ‘04], [Jaeger et al. ’06] [Marchesini et al. ‘04], [Jaeger et al. ’06] Machine OS VirtualizaAon [England et al. ‘03], [Garfinkel et al. ‘03] Virtual Machine Monitor Bootloader Bootloader OpAon ROMs OpAon ROMs BIOS BIOS 19 20 InterpreAng Code IdenAty InterpreAng Code IdenAty TradiAonal TradiAonal [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Sailer et al. ‘04] [Gasser et al. ‘89], [Sailer et al. ‘04] VMM Flicker Policy Enforcement Policy Enforcement Virtual [Marchesini et al. ‘04], [Jaeger et al. ’06] [Marchesini et al. ‘04], [Jaeger et al. ’06] Machine OS VirtualizaAon OS VirtualizaAon [England et al. ‘03], [Garfinkel et al. ‘03] [England et al. ‘03], [Garfinkel et al. ‘03] S Late Launch Late Launch Virtual Machine Monitor [Kauer et al. ‘07], [Grawrock ‘08] [Kauer et al. ‘07], [Grawrock ‘08] Flicker Bootloader Targeted Late Launch [McCune et al. ‘07] OpAon ROMs A`ested BIOS 21 22 InterpreAng Code IdenAty Load‐Time vs. Run‐Time ProperAes App 1…N • Code idenAty provides load‐Ame guarantees Drivers 1…N • What about run Ame? • Approach #1: StaAc transformaAon [Erlingsson et al. ‘06] OS S Run‐Time Policy A`ested Flicker Bootloader Code Code’ OpAon ROMs BIOS 23 24 4
5/23/10 Roots of Trust Load‐Time vs Run‐Time ProperAes Cheaper • Code idenAty provides load‐Ame guarantees • What about run Ame? 0 0 4 2 • Approach #1: StaAc transformaAon [Erlingsson et al. ‘06] • General • General • Special • Timing‐based • Approach #2: Run‐Time Enforcement layer purpose purpose purpose a`estaAon [Haldar et al. ‘04], [Kil et al. ‘09] • Tamper • No physical • Require responding defenses detailed HW Run Time A`ested knowledge Code [Weingart ‘87] [ARM TrustZone ‘04] [Chun et al. ‘07] [Spinellis et al. ‘00] [White et al. ‘91] [TCG ‘04] [Levin et al. ‘09] [Seshadri et al. ‘05] Load Time [Yee ‘94] [Zhuang et al. ‘04] … Enforcer [Smith et al. ‘99] … … 25 26 Human Factors Conclusions • Code iden>ty is criAcal to bootstrapping trust SW SW SW SW 1 2 N‐1 N • Assorted hardware roots of trust available • Many open ques>ons remain! SW SW SW SW 1 2 N‐1 N 27 28 5
Recommend
More recommend