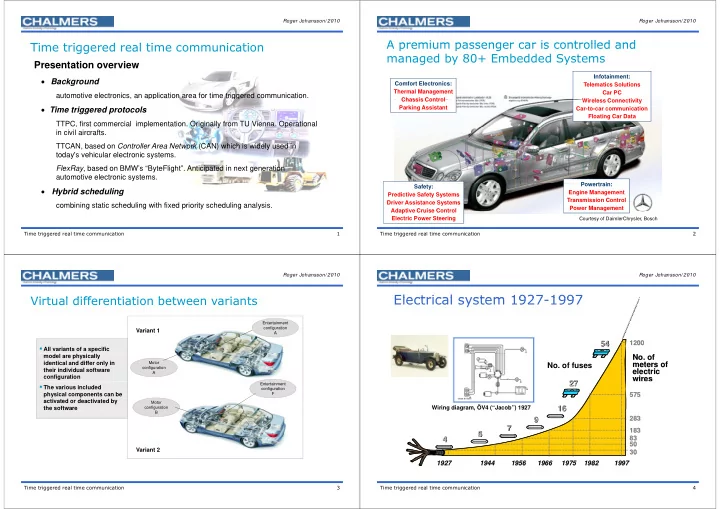

Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 A premium passenger car is controlled and A premium passenger car is controlled and Time triggered real time communication Ti t i d l ti i ti managed by 80+ Embedded Systems Presentation overview Infotainment: Background Comfort Electronics: Telematics Solutions Thermal Management Car PC automotive electronics, an application area for time triggered communication. Chassis Control Chassis Control Wireless Connectivity Wireless Connectivity Time triggered protocols Parking Assistant Car-to-car communication Floating Car Data TTPC, first commercial implementation. Originally from TU Vienna. Operational p g y p in civil aircrafts. TTCAN, based on Controller Area Network (CAN) which is widely used in today s vehicular electronic systems. today's vehicular electronic systems FlexRay , based on BMW’s “ByteFlight”. Anticipated in next generation automotive electronic systems. Powertrain: Po ertrain Safety: Hybrid scheduling Engine Management Predictive Safety Systems Transmission Control Driver Assistance Systems combining static scheduling with fixed priority scheduling analysis. Power Management g Adaptive Cruise Control Adaptive Cruise Control Electric Power Steering Courtesy of DaimlerChrysler, Bosch Time triggered real time communication 1 Time triggered real time communication 2 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Electrical system 1927 1997 Electrical system 1927-1997 Virtual differentiation between variants Vi t l diff ti ti b t i t Entertainment configuration Variant 1 A 54 54 1200 1200 All variants of a specific model are physically No. of No. of identical and differ only in meters of meters of No. of fuses Motor configuration their individual software electric electric A configuration wires wires wires 27 27 27 27 Entertainment The various included configuration 575 physical components can be 575 F activated or deactivated by Motor Wiring diagram, ÖV4 (“Jacob”) 1927 Wiring diagram, ÖV4 ( Jacob ) 1927 16 16 16 16 the software the software configuration g B 283 283 9 9 7 7 183 183 5 5 83 83 4 4 4 4 83 83 50 50 Variant 2 30 30 1927 1927 1927 1927 1944 1944 1944 1944 1956 1956 1956 1956 1966 1966 1966 1966 1975 1975 1975 1975 1982 1982 1982 1982 1997 1997 1997 1997 Time triggered real time communication 3 Time triggered real time communication 4
Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Automotive electronics roadmap A t ti l t i d The evolution of the electrical system Features Power production and distribution 450 Architecture Simple Optimisation on many 400 components levels 350 Standardised interfaces 300 # of More complex functions 250 functions stand-alone systems 200 ABS, Airbag 150 # of 100 100 Integration of systems integrated functions Optimisation of information 50 Common data busses 0 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 1995 2000 2005 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Time triggered real time communication 5 Time triggered real time communication 6 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 The current electrical system The current electrical system Multiplex Networks Mirror Lock Lock Conventional Window Lift Universal Light Network Data Data Identifier Identifier Control Control Command Command system system Light Light CAN CAN Seat Htng Instruments Htng g Wiper p Power Train Central WHtg Interior Roof Body Ctrl ITS Light Engine Control Trunk Htng Climate x6 Seat Module Driver Information Light Seat Htng Control units CAN St-Wheel Panel Automatic Transmission Universal Motor Central Module Lock Lock Sub-Bus Universal Panel Mirror Mirror Time triggered real time communication 7 Time triggered real time communication 8
Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Electronics in distributed control Electronics in distributed control B By-wire control i t l Electronic Electronic information carrier Hydraulic information carrier The F-8 Digital Fly-By-Wire (DFBW) flight research project validated the principal research project validated the principal ((( ))) ((( ))) ((( ))) ((( ))) concepts of all-electric flight control traffic control traffic control systems now used on nearly all modern train (consist) control train (consist) control high-performance aircraft and on military high performance aircraft and on military local control local control and civilian transports. The first flight of the 13-year project was on May 25, 1972. ((( ))) ((( ))) ((( ))) ((( ))) wayside control wayside control Courtesy of Dryden Flight Research Center Time triggered real time communication 9 Time triggered real time communication 10 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Control system implementation strategies Control system implementation strategies Drive-by-wire Local control Local information processing Independent control objects Independent control objects Centralized global control Centralized global control Local and central information processing Interconnected control objects Distributed global control Local and distributed information processing Interconnected control objects Time triggered real time communication 11 Time triggered real time communication 12
Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 N Non-functional requirements f ti l i t Tradeoffs from Safety/Reliability requirements T d ff f S f t /R li bilit i t The extremes from reliability requirements leads to safety requirements. y q y q System life System life Maintainability Maintainability time Extendability Safety requirements implies redundancy, (Fail-Operational, Fail-Safe, etc). Interoperability Changeability Portability Safety Testability Restructuring Safety requirements also demands predictability, we has to show, a priori, that the system will fulfill it’s mission in every surrounding at every time. Performance/ Usability Efficiency In a distributed environment, only time triggered protocols and System System redundant buses can provide this safety. Contemporary TTP’s are: d d t b id thi f t C t TTP’ Security Availability Architecture TTP/C, first commercial implementation. Originally from TU Vienna. Operational Robustness Cost-effectiveness Reliability y in civil aircrafts. in civil aircrafts. Fault tolerance Fault tolerance TTCAN, based on Controller Area Network (CAN) which is widely used in Produceability Understandability today's vehicular electronic systems. Timeliness Variability (variants configurations) Variability (variants, configurations) Conceptual FlexRay , based on BMW’s “ByteFlight”. Anticipated in next generation integrity automotive electronic systems. Time triggered real time communication 13 Time triggered real time communication 14 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 TTCAN TTCAN TTCAN TTCAN – Based on the CAN protocol ”Exclusive” – guaranteed service – Bus topology ”Arbitration” – guaranteed service (high ID), best effort (low ID) ”Reserved” – for future expansion... p – Media: twisted pair Media: twisted pair – 1Mbit/s Transmission Columns Nod A Node 3 CPU/mem Basic cycle 0 /CC Node 1 Node 6 Node 7 S S Basic cycle 1 S Basic cycle 2 Node 5 Node 4 Basic cycle 3 Basic cycle 3 Node 2 t A second controller is required to implement the redundant bus A second controller is required to implement the redundant bus Time is global and measured in network time units (NTU’s) Time triggered real time communication 15 Time triggered real time communication 16
Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 TTP/C TTP/C TTP/C TTP/C – Double channels (one redundant). Bus topology or ”star” (optical) All communication is statically scheduled – Media: twisted pair, fibre Guaranteed service – 10 Mbit/s for each channel ”TDMA-round” CNI works as a “firewall” Nod Nod Nod Nod 3 Nod Nod Status , global time, membership 1 6 6 ”message slots” message slots Control , clock interrupt Watchdog , checking consensus Data the actual message Nod Nod Nod Nod Nod Nod 5 5 4 4 2 Nod A Nod Nod Nod Nod CPU/mem C CNI 1 1 4 4 /CC A Nod Nod Nod Nod S S 2 5 S S Nod Nod B Nod Nod t 3 6 Non periodical messages has to been fitted into static slots by the application N i di l h t b fitt d i t t ti l t b th li ti A network is built on either twin buses or twin stars. Time triggered real time communication 17 Time triggered real time communication 18 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Roger Johansson/ 2010 Flexray Flexray Flexray Flexray – Double channels, bus or star (even mixed). – Media: twisted pair, fibre ”Static segment” (compare TTCAN ”Exclusive”) – guaranteed service – 10 Mbit/s for each channel ”Dynamic segment” (compare TTCAN ”Arbitration”) – guaranteed service (high ID), ”best effort” (low ID) Nod 3 N d 3 Nod 1 Nod 63 Nod 6 Nod 7 A 62 CPU/mem/ B B N Network Idle CC CC Symbol win Guaranteed periodical Guaranteed ”Best-effort” periodical/ aperiodical S S A aperiodical S e Time ndow 3 Nod 5 2 Nod 4 Nod 2 1 0 0 Static segment Dynamic segment (m slots) (n mini-slots) Redundant channel can be used for an alternative schedule R d d t h l b d f lt ti h d l Max 64 nodes on a Flexray network. M 64 d Fl t k Time triggered real time communication 19 Time triggered real time communication 20
Recommend
More recommend