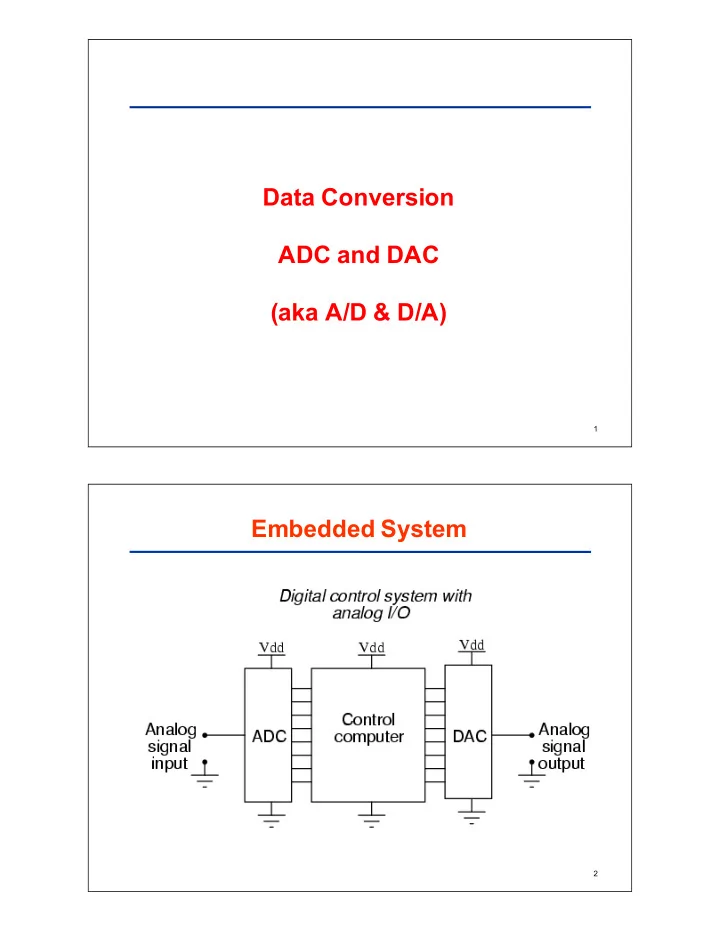

Data$Conversion ADC$and$DAC (aka$A/D$&$D/A) 1 Embedded$System 2
Signal$Conversion$System • Analog+to+Digital • Digital+to+Analog – Conversion+of+Sensor+ – Conversion+of+Binary+ Output+to+Binary+Code Code+to+Analog+Signal 3 Digital$to$Analog$Circuit 4
D/A$Conversion • Operation+Converts+an+ n ?bit+Binary+ value and+ Generates+a+Voltage+ A out • A out is+Proportional+to+ Reference'Voltage' V ref • Reference'Voltage' is+Absolute+Range • Resolution ,+ MRV ,+is+Smallest+non?zero+ Voltage 5 Absolute$Voltage$Range EXAMPLE:+8?bit+Input+Word+with+Output+ Voltage+Ranging+Between++5V+(max)+to+? 5V+(min) TRUE+ BINARY ABSOLUTE RANGE WORD RANGE +5V++++++++++++11111111++++++++++10V Must%add%an%offset%value of%+5%to%Scale%True%Voltages 0V 10000000++++++++++5V to%Absolute%Voltage ?5V++++++++++00000000+++++++++++0V 6
Converter$Varieties • Some+Converters+Utilize+Signed+Binary+while+ Unsigned+Binary+is+Most+Commonly+Used • Negative+ V min is+Common+Since+Many+Sensors+ Produce++/? Voltage+Values – If+ V min =0 ,+then+ V max = V ref • Many+Different+Internal+Architectures+(circuit+ level)+are+Available – Each+has+Different+Strengths+and+Weaknesses • Here+We+Concentrate+only+at+the+System+ Level – Internal+Circuit+Architectures+Studied+in+Analog+and+ Mixed+Signal+Courses 7 Other$Binary$Encodings NOT+ TRUE 2'S+COMPLEMENT 8
D/A$Conversion • Operation+Converts+an+ n ?bit+Binary+ value and+ Generates+a+Voltage+ A out • Resolution is+Number+of+Possible+Output+ Levels+the+DAC+is+Designed+to+Reproduce+– Usually+stated+as+Number+of+bits,+ n • A out is+Proportional+to+ Reference'Voltage' V ref 9 DAC$Parameters$&$Performance • Maximum+ Sampling'Frequency' – measurement+of+maximum+speed+at+which+ DAC+circuitry+can+operate+and+still+produce+ Correct+Output – Aliasing can+Occur+if+Sampling+Frequency+is+Too+ Low • Monotonicity Refers+to+Ability+of+DAC+Output+ to+Move+Only+in+One+Direction+(increasing+or+ decreasing+voltage) – measure+of+the+amount+a+DAC+output+may+ decrease+before+asserting+the+correct+output 10
Analog$to$Digital$Circuit 11 ADC$Waveforms 12
Sampling$Concepts • Ideal+Sampling+Modeled+as+Equally+Spaced+Impulse+ Function+Train • More+Realistic+Model+is+Very+Narrow+Pulses • Contributes+to+ jitter and+ phase'noise • Adds+Harmonics+&+DACs+Usually+use+Low?Pass+Filters+ ( Reconstruction' Filter )+to+Reduce+this+Distortion IDEAL LESS+IDEAL 13 Sampling$&$Accuracy Accuracy is+measure+of+Radial+Distance+of+Sample+Point+from+ True+Point+on+Analog+Signal 14
Data$Converter$Accuracy/Error • An+Accurate+ Sample Point+Perfectly+Overlays+ Corresponding+Point+on+Analog+Signal – Perfect+Accuracy+=+Zero+Error • Roundoff+Error+Contributes+to+ Accuracy – More+ Resolution Decreases+ Roundoff'Error • Horizontal+Distance+is+ Timing'Error – Jitter ,+ Phase'Noise ,+ Skew ,+etc.+Contribute+to+this+Error – Other+Contributors • Vertical+Distance+is+ Amplitude'Error (usually+volt) – Many+Different+Contributors – Step'Recovery ,+ Monotinicity and+Other+Contributors • Noise Sources+are+ Random Contributors 15 Aliasing 16
Undersampling 17 Nyquist$Sampling$(ADC) • Nyquist'Frequency' is+Absolute+ Maximum+Limit – f Nyq is+2X+Highest+Desired+Frequency+Component+in+ Sampled+Signal • Does+not+Represent+the+Highest+ PRACTICAL+Frequency+Measurable • In+Practice+Cannot+Expect+ADC+to+ Resolve+any+Frequency+Greater+than+1/5+ to+1/10+of+Sample+Frequency • Typically+Sample+Signals+about+7?10+ Times+per+Period 18
Preventing$Aliasing • Insert+Low?Pass+Filter+Between+Signal+Source+ and+ADC+( antiEaliasing'filter ) • Low?Pass+Cutoff+Frequency+set+to: • Practical+Attenuation+Levels+at+Cutoff+are+3?9+ dB+(Gain+=+0.5+(?3+dB)+to+0.125+(?9+dB)) • This+Ensures+no+Signal+Frequency+ Components+Higher+than+Nyquist+Frequency+ are+Sampled+by+the+ADC 19 ADC$Step$Recovery • Measure+of+How+Quickly+ADC+Changes+its+ Output+to+Match+a+Large+Sudden+Change+in+ Analog+Input – eg+a+signal+with+a+near+"step+function?like"+feature+ requires+very+quick+(low?valued)+step+recovery • Ideal+ADC – Large+(infinite)+Output+Word+Size+(high+resolution) – very+fast+(0?delay)+Step+Recovery • Unfortunately+ NO$IDEAL$ADCS$ in+Reality – Resolution+versus+Step+Recovery+is+a+Tradeoff – Continual+R&D+in+ADC+Circuit+Architecture – Always+Taking+Advantage+of+Emerging+Technologies 20
ADC$Circuit$Architecture$Tradeoffs Resolution/Compl Speed Step Recovery exity Ratio Single-slope BEST Flash Flash Integrating Dual-slope Successive- Tracking Integrating Approximation Single-slope Successive Counter Integrating AND Approximation Counter Single-Slope Tracking - Integrating AND Counter Successive Dual-slope - Approximation Integrating Dual-slope WORSE Flash Tracking Integrating (assumptions+made+here+– not+absolute+– such+as+analog+comparator+complexities) 21 DAC$Performance$Measures • Total'Harmonic'Distortion' (THD)+– measurement+of+the+amount+of+noise+and/or+ distortion+introduced+into+output+signal+by+the+ DAC – expressed+as+percentage of+total+power+of+ unwanted+signal+components+versus+total+power+of+ ideal+signal+component • Dynamic'Range' – Measurement+of+Difference+ Between+Largest+and+Smallest+Signal+DAC+ can+Reproduce – usually+expressed+in+decibels+(dB) – dB+is+convenient+for+exponentially+varying+values+ since+it+reduces+them+to+a+linear+relationship 22
DAC$Performance$Measures • Jitter – Deviation+from+Precise+Sample+Timing+ Intervals • Phase'Distortion' – Distortion+Occuring+due+to+ non?linear+Filter+Phase+Response+over+the+ Frequency+Range+of+Interest • Causes+Dependent+on+Particular+Circuit+ Architecture: – Clock+Skew+and+Drift – Reconstruction+Filter+Nonlinearaties – Sampling+Circuit+Architecture – Noise+(White,+Flicker,+etc.) 23 Resolution$and$ MRV • MRV (Minimum+Representable+ Voltage) – MRV =+Full+Scale+ • For+n+bits+Binary Resolution – Resolution+:+ 2 - n – Example • Full+Scale+of+10V,+4?bit+ Encoding • MRV+=+10/16+=+625mV • Impossible+to+represent+a+ voltage+lower+than+625mV – To+improve+ accuracy of+ conversion,+Increase+ n • Example:+ n = 8 • MRV+=+10+/+2 8 =+39mV 24
Example$Problem A+water+tank+has+a+maximum+height+of+40+ feet.++If+a+perfect+sensor+can+measure+the+ water+height,+how+much+resolution+is+ required+for+the+ADC+to+give+values+with+a+ measurement+error+of+no+more+than+1/10+ of+an+inch?+(Assume+all+other+error+ sources+are+zero) 25 Example$Problem$1 1) First+determine+the+number+of+1/10+inch+ steps+in+maximum+value: 2) Compute+Number+of+Bits+Needed+to+ Represent+4800+Steps: 26
Example$Problem$2 A+decoded+MP3+audio+stream+is+to+be+ scaled+between++/? 1V+for+input+to+the+final+ output+amplifier.+If+the+DAC+outputs+16?bit+ samples,+what+is+the+minimum+(non?zero)+ representable+voltage+(MRV)?+Assume+ perfect+accuracy+? an+ideal+DAC.++This+ means+ideal+jitter+(0),+perfect+step+recovery+ (infinite),+etc.+ 27 Example$Problem$2 Use+Resolution+Equation,+ MRV = A out when+ value =1 and+ V ref is+Full+Scale+Voltage: 28
Example$Problem$3 What+is+the+dynamic+range+of+the+DAC+in+ Example+Problem+2? 29 Example$Problem$3 What+is+the+dynamic+range+of+the+DAC+in+ Example+Problem+2? This%is%a%BIG%Dynamic%Range!!! DVD+Audio+Sounds+Better+than+CD+Audio (24?bit+versus+16?bit+– More+Accurate) 30
Example$Problem$4 What+is+the+resolution+of+a+DAC+with+a+70+ dB+dynamic+range+and+a+reference+voltage+ of+5V? 31 Example$Problem$4 What+is+the+resolution+of+a+DAC+with+a+70+ dB+dynamic+range+and+a+reference+voltage+ of+5V? 1) First+find+MRV 32
Example$Problem$4 What+is+the+resolution+of+a+DAC+with+a+70+ dB+dynamic+range+and+a+reference+voltage+ of+5V? 2) Use+Resolution+Equation+to+find+ n 33 Example$Problem$5 An+8?bit+DAC+outputs+?2.2V+with+ V max =+5V and+ V min =-5V .++What+is+the+8?bit+input+ value (in+unsigned+binary ) ? 34
Example$Problem$5 An+8?bit+DAC+outputs+?2.2V+with+ V max =+5V and+ V min =-5V .++What+is+the+8?bit+input+ value (in+unsigned+binary ) ? +5V++++11111111++++++++++10V Must%add%an%offset%value of%+5%to%Scale%True%Voltages 0V 10000000++++++++++5V to%Absolute%Voltage ?2.2V+++???????? +2.8V ?5V+++00000000++++++++++++0V 35 Example$Problem$5 An+8?bit+DAC+outputs+?2.2V+with+ V max =+5V and+ V min =-5V .++What+is+the+8?bit+input+ value (in+binary ) ? 1)Use+the+resolution+equation+(ONE+WAY) 36
Example$Problem$5 An+8?bit+DAC+outputs+?2.2V+with+ V max =+5V and+ V min =-5V .++What+is+the+8?bit+input+ value (in+binary ) ? 1)Use+proportions+(ANOTHER+WAY) 37 Example$Problem$6 An+audio+signal+is+sampled+at+3+times+the+ Nyquist+frequency+and+processed+by+a+16? bit+DAC.++The+resulting+bitstream+is+then+ transmitted+serially.++What+is+the+bandwidth+ of+the+serial+transmission? 38
Example$Problem$6 An+audio+signal+is+sampled+at+3+times+the+ Nyquist+frequency+and+processed+by+a+16? bit+DAC.++The+resulting+bitstream+is+then+ transmitted+serially.++What+is+the+bandwidth+ of+the+serial+transmission? 1) First+Identify+Frequency+Range+of+ Human+Auditory+System.++This+Varies+ from+Human+to+Human+but+is+Generally+ Considered+to+be+20Hz+to+40kHz. 39 Example$Problem$6 An+audio+signal+is+sampled+at+3+times+the+ Nyquist+frequency+and+processed+by+a+16? bit+DAC.++The+resulting+bitstream+is+then+ transmitted+serially.++What+is+the+bandwidth+ of+the+serial+transmission? 2) Only+Need+to+Worry+about+High+ Frequency+Component+for+our+Problem,+ 40kHz. 40
Recommend
More recommend