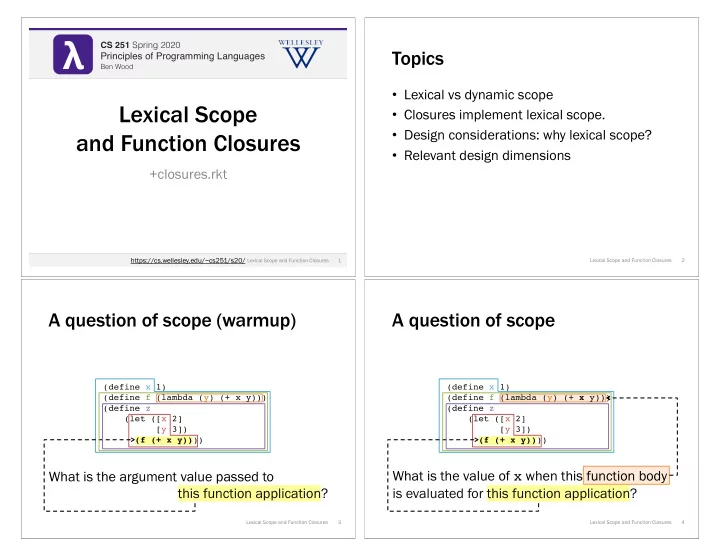

λ λ CS 251 Fall 2019 CS 251 Spring 2020 Topics Principles of Programming Languages Principles of Programming Languages Ben Wood Ben Wood • Lexical vs dynamic scope Lexical Scope • Closures implement lexical scope. • Design considerations: why lexical scope? and Function Closures • Relevant design dimensions +closures.rkt https://cs.wellesley.edu/~cs251/s20/ 1 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 2 Lexical Scope and Function Closures A question of scope (warmup) A question of scope (define x 1) (define x 1) (define f (lambda (y) (+ x y))) (define f (lambda (y) (+ x y))) (define z (define z (let ([x 2] (let ([x 2] [y 3]) [y 3]) (f (+ x y)) )) (f (+ x y)) )) What is the value of x when this function body What is the argument value passed to this function application? is evaluated for this function application? Lexical Scope and Function Closures 3 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 4
A question of free variables Answer 1: lexical (static) scope A variable, x , is fr free in an expression, e , if x is referenced in e A variable, x , is fr free in an expression, e , if x is referenced in e outside the scope of any binding of x within e . outside the scope of any binding of x within e . x is a free variable x is a free variable of the lambda expression. of the lambda expression. (define x 1) (define x 1) (define f (lambda (y) (+ x y))) (define f (lambda (y) (+ x y))) (define z (define z (let ([x 2] (let ([x 2] [y 3]) [y 3]) (f (+ x y)) )) (f (+ x y)))) To what bindings do free variables of a function Free variables of a function refer to bindings in refer when the function is applied? the environment where the function is de defined , regardless of where it is applied. Lexical Scope and Function Closures 5 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 6 Answer 2: dynamic scope Answer 2: dynamic scope A variable, x , is fr free in an expression, e , if x is referenced in e A variable, x , is fr free in an expression, e , if x is referenced in e outside the scope of any binding of x within e . outside the scope of any binding of x within e . x is a free variable x is a free variable of the lambda expression. of the lambda expression. (define x 1) (define x 1) (define f (lambda (y) (+ x y))) (define f (lambda (y) (+ x y))) (define z (define z (let ([ x 2] (let ([x 2] [y 3]) [y 3]) (f (+ x y)) )) (f (+ x y)))) Free variables of a function refer to bindings in Free variables of a function refer to bindings in the environment where the function is ap applied , the environment where the function is ap applied , regardless of where it is defined. regardless of where it is defined. Lexical Scope and Function Closures 7 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 8
Anonymous function definition expressions Closures implement Week 1 Syntax : Sy ( lambda ( x1 … xn ) e ) lexical scope. – pa parameters: x1 through xn are identifiers – bo body: e is any expression Ev Evaluation : closure , ⟨ E, (lambda (x1 … xn) e) ⟩ , 1. The result is a fu function c holding the current environment, E , and the function. Closures allow functions to use any binding in [closure] the environment where the function is defined, E ⊢ (lambda (x1 … xn) e) ↓ ⟨ E, (lambda (x1 … xn) e) ⟩ regardless of where it is applied. Note: – An anonymous function definition is an expression. – A function closure is a new kind of value. Closures are not expressions. – This is a de definition , not a call . . The body, e , is no not evaluated now. – lambda from the λ -ca calcu culus . Lexical Scope and Function Closures 9 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 10 Function application (call) Function application (call) Week 1 Week 1 Sy Syntax : ( e0 e1 ... en ) Synta Sy ntax : ( e0 e1 … en ) Evalu Ev luati tion : 1. Under the current dynamic environment, E , Evaluation : Ev evaluate e0 through en to values v0, …, vn. E ⊢ e0 ↓ ⟨ E', (lambda (x1 … xn) e) ⟩ 2. If v0 is a function closure of n arguments, E ⊢ e1 ↓ v1 ⟨ E', (lambda (x1 … xn) e) ⟩ then … The result is the result of evaluating the closure E ⊢ en ↓ vn body, e , under the closure environment, E' , x1 ⟼ v1, …, xn ⟼ vn, E' ⊢ e ↓ v extended with argument bindings: [apply] x1 ⟼ v1, …, xn ⟼ vn . E ⊢ (e0 e1 … en) ↓ v Otherwise, there is a type error. Functions 11 Functions 12
Example: Example: env pointer env pointer shows env structure, by pointing to shows env structure, by pointing to “rest of environment” “rest of environment” returning a function returning a function binding binding maps variable name to value maps variable name to value de def (define x 1) (define x 1) 1 x def de def Current evaluation step: de (define (f y) (define (f y) def de (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) Current environment: (lambda (z) (lambda (z) (+ x y z)) ) (+ x y z)) ) (define z (let ([x 3] (define z (let ([x 3] [g (f 4)] [g (f 4)] [y 5]) [y 5]) (g 6) )) (g 6) )) Lexical Scope and Function Closures 13 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 14 Example: Example: env pointer env pointer shows env structure, by pointing to shows env structure, by pointing to “rest of environment” “rest of environment” returning a function returning a function binding binding maps variable name to value maps variable name to value (define x 1) 1 (define x 1) 1 x x (define (f y) (lambda (y) (define (f y) (lambda (y) f f def def de env de env (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (lambda (z) (lambda (z) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (+ x y z)) ) ) let (+ x y z)) ) ) le (lambda (z) (lambda (z) (+ x y z)) ) (+ x y z)) ) (define z (let ([x 3] (define z (let ([x 3] [g (f 4)] [g (f 4)] def def let de de le [y 5]) [y 5]) (g 6) )) (g 6) )) Lexical Scope and Function Closures 15 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 16
Example: Example: env pointer env pointer shows env structure, by pointing to shows env structure, by pointing to “rest of environment” “rest of environment” returning a function returning a function binding binding maps variable name to value maps variable name to value (define x 1) 1 (define x 1) 1 x x a a p p p p (define (f y) (lambda (y) (define (f y) (lambda (y) a a f f p p def def de env p p de env (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (lambda (z) (lambda (z) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (+ x y z)) ) ) (+ x y z)) ) ) (lambda (z) (lambda (z) app app 4 y (+ x y z)) ) (+ x y z)) ) 3 3 x x let let le le (define z (let ([x 3] (define z (let ([x 3] [g (f 4)] [g (f 4)] def def de de [y 5]) [y 5]) let let le le (g 6) )) (g 6) )) Lexical Scope and Function Closures 17 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 18 Example: Example: env pointer env pointer shows env structure, by pointing to shows env structure, by pointing to “rest of environment” “rest of environment” returning a function returning a function binding binding maps variable name to value maps variable name to value (define x 1) 1 (define x 1) 1 x x (define (f y) (lambda (y) (define (f y) (lambda (y) f f def def de env de env (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (lambda (z) (lambda (z) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) (let ([x (+ y 1)]) p p p p (+ x y z)) ) ) (+ x y z)) ) ) a a (lambda (z) (lambda (z) app app p p p p 4 4 a a y y (+ x y z)) ) (+ x y z)) ) 3 3 x x let let le le app app (define z (let ([x 3] (define z (let ([x 3] 5 5 x x app app app app [g (f 4)] [g (f 4)] def def de de [y 5]) [y 5]) (lambda (z) let let le le env (+ x y z)) (g 6) )) (g 6) )) Lexical Scope and Function Closures 19 Lexical Scope and Function Closures 20
Recommend
More recommend