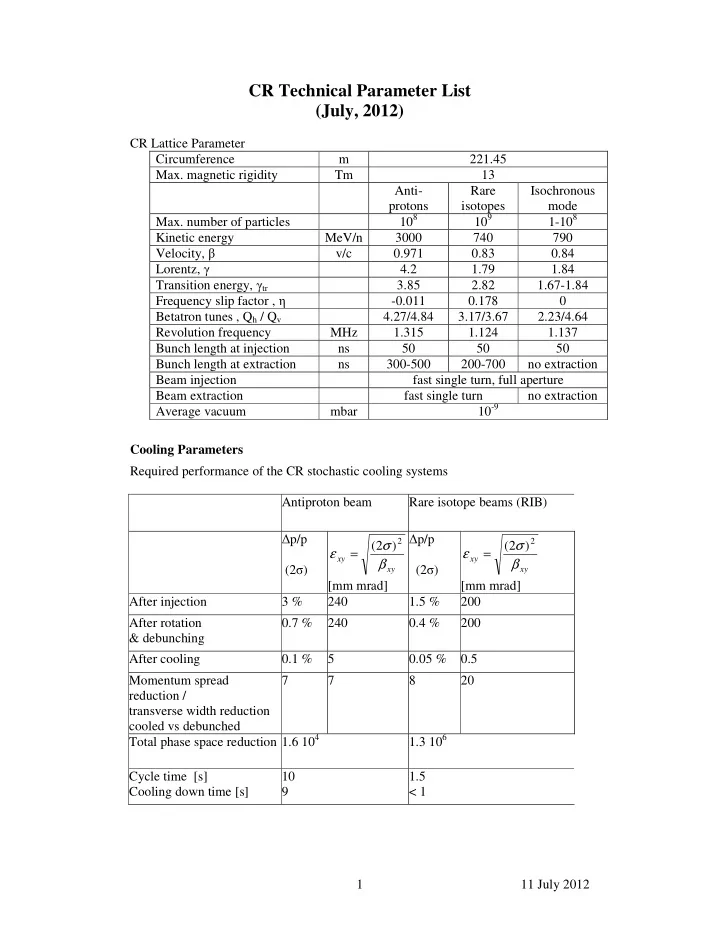

CR Technical Parameter List (July, 2012) CR Lattice Parameter Circumference m 221.45 Max. magnetic rigidity Tm 13 Anti- Rare Isochronous protons isotopes mode 10 8 10 9 1-10 8 Max. number of particles Kinetic energy MeV/n 3000 740 790 Velocity, β v/c 0.971 0.83 0.84 Lorentz, γ 4.2 1.79 1.84 Transition energy, γ tr 3.85 2.82 1.67-1.84 Frequency slip factor , η -0.011 0.178 0 Betatron tunes , Q h / Q v 4.27/4.84 3.17/3.67 2.23/4.64 Revolution frequency MHz 1.315 1.124 1.137 Bunch length at injection ns 50 50 50 Bunch length at extraction ns 300-500 200-700 no extraction Beam injection fast single turn, full aperture Beam extraction fast single turn no extraction 10 -9 Average vacuum mbar Cooling Parameters Required performance of the CR stochastic cooling systems Antiproton beam Rare isotope beams (RIB) � p/p � p/p 2 2 σ σ ( 2 ) ( 2 ) ε = ε = xy xy β β (2 σ ) (2 σ ) xy xy [mm mrad] [mm mrad] After injection 3 % 240 1.5 % 200 After rotation 0.7 % 240 0.4 % 200 & debunching After cooling 0.1 % 5 0.05 % 0.5 Momentum spread 7 7 8 20 reduction / transverse width reduction cooled vs debunched Total phase space reduction 1.6 10 4 1.3 10 6 Cycle time [s] 10 1.5 Cooling down time [s] 9 < 1 1 11 July 2012
2.5.1 System Design General Layout 2 11 July 2012
Beam envelopes in the antiproton mode for half of the ring Horizontal beam envelope in antiproton (Ex=240 mm mrad, for orbits with momentum deviations dp/p=±2.5%) Vertical beam envelope in antiproton mode (Ey=240 mm mrad) 3 11 July 2012
Beam envelopes in the RIB mode for half of the ring Horizontal beam envelope in RIB mode (Ex=200 mm mrad, for orbits with momentum deviations dp/p=±1.4%) Vertical beam envelope in RIB mode (Ey=200 mm mrad) 4 11 July 2012
Beam envelopes in the isochronous mode for half of the ring Horizontal beam envelope in isochronous mode (Ex=100 mm mrad, for orbits with momentum deviations dp/p=±0.4%) Vertical beam envelope in isochronous mode (Ey=100 mm mrad) 5 11 July 2012
2.5.2 Magnets 2.5.2.1. Dipole Magnets (MH01-MH06) Number of magnets 24 Design H-type Type sector magnet Normal or super conducting normal-conducting Min / Max. field T 1.2 / 1.6 Effective length, L m 2.127 Bending angle deg 15 Bending radius m 8.128 Entrance/Exit edge angle deg 0 Pole gap height mm ± 85 Max. ramp rate T/s 0.054 Usable horizontal aperture mm ± 190 Usable vertical aperture mm ± 70 ± 1 × 10 -4 Integrated tolerable field error ∆ BL/BL < ±1 x 10 -4 Tolerable sextupole field, b 2 < ±1 x10 -4 Tolerable octupole field , b 3 < ±1 x 10 -4 Tolerable decapole field, b 4 2 x 10 -4 Magnet to magnet identity Overall length m 2.69 Overall width m 2.21 Overall height m 1.45 Yoke length m 2.026 Iron weight t 46 Copper weight t 3.308 Overall weight t 49.308 Number of turns per pole 10 x 8 Current at max field A 1396 A/mm 2 Average current density 3.1 A/mm 2 Current density in conductor 4.24 Voltage V 88 Inductance per magnet mH 377 Resistance per magnet m Ω 65.55 Power consumption kW 127.7 Temperature drop C 30 Water consumption l/s 0.98 Coil dim. 212 x 170 mm ⋅ mm Conductor insulation mm 0.5 Ground insulation mm 1 Conductor cross section mm.mm 20 x 20 Cooling channel diameter mm 9.5 Fill factor 0.73 Time for polarity change, ramp s 60 The dipole magnet should provide the additional horizontal beam deflection within ±3 mrad by an additional power convertor (see table 2.5.3.6.3) 6 11 July 2012
2.5.2.2 Quadrupoles 2.5.2.2.1. Wide Quadrupole Magnets* , ** (QS01,QS02,QS04-QS11 ) Number of magnets 36 Design symmetric quad Type figure of eight Normal or super conducting nc Max. quadrupole gradient, b 1 T/m 4.9 Min. quadrupole gradient T/m 0.15 Max. octupole field * T/m 2 10 T/m 2 Min. octupole field 0 Effective length, L m 1.0 Aperture radius mm 156 Max. ramp rate T/m/s 0.162 Usable horizontal aperture mm ± 200 Usable vertical aperture mm ± 90 ± 5 × 10 -4 (at r = 156 mm ) Integrated field error ∆ GL/GL < ± 5 x 10 -5 Tolerable octupole harmonic, b 3 < ± 1 x 10 -4 Tolerable decapole harmonic, b 4 < ± 3 x 10 -4 Tolerable dodecapole harmonic, b 5 < ± 1 x 10 -4 Tolerable dodecapole harmonic, b 9 2 x 10 -3 Magnet to magnet identity Overall length m 1.04 Overall width m 1.42 Overall height m 1.42 Iron/copper weight t 9.1 /0.92 Overall weight t 10.02 Number of turns per pole 2 x 8 Current at max field A 3215 A/mm 2 Current density 5.921 Voltage V 23 Inductance per magnet mH 10.06 Resistance per magnet 7 m Ω Power consumption kW 70.21 Coil copper cross section 25 x 25 mm ⋅ mm Cooling channel diameter. mm 8 Cooling water flow rate l/s 0.43 o C Cooling water temp. rise 40 bar Cooling water pressure drop 4.76 Time for polarity change s 60 B. Langenbeck GSI-MT-2008-8.1 design (2D) corrected by Kalimov with 3D design *The octupole field should be provided by an additional coil or winding, which will be powered by a separate power converter (see table 2.5.3.4) **BPM (beam position monitor) should be embedded in quadrupole (table 2.5.6.3) 7 11 July 2012
2.5.2.2.2. Narrow Quadrupole Magnets (QS03) Number of magnets 4 Design symmetric quad Type figure of eight Normal or super conducting Nc Max. gradient T/m 8.0 Min. gradient T/m 0.8 Effective length, L m 0.5 Max. ramp rate T/m/s 0.27 Usable horizontal aperture mm ± 90 Usable vertical aperture mm ± 90 Pole radius mm ± 95 ± 5 × 10 -4 at r = 90 mm Integrated field error ∆ GL/GL < ± 5 x 10 -5 Tolerable octupole harmonic, b 3 < ± 1 x 10 -4 Tolerable decapole harmonic, b 4 < ± 3 x 10 -4 Tolerable dodecapole harmonic, b 5 < ± 1 x 10 -4 Tolerable dodecapole harmonic, b 9 2 x 10 -3 Magnet to magnet identity Overall length m 0.55 Overall width m 0.63 Overall height m 0.80 Yoke length m 0.49 Iron/copper weight t 1.1 / 0.26 Overall weight t 1.4 Number of turns per pole 2 x 4 Current at max field A 3790 1×10 -4 Current stability ∆ I/I Voltage V 5.6 Inductance per magnet mH 1.23 Resistance per magnet m Ω 1.5 Power consumption kW 21 Coil copper cross section mm ⋅ mm 24 x 26 Cooling channel diameter. mm 5 Conductor insulation mm 0.5 Ground insulation mm 1 Cooling water flow rate l/s 0.17 o C Cooling water temp. rise 30 bar Cooling water pressure drop 2.3 Time for polarity change s 60 Kalimovs 3D design august 2009 8 11 July 2012
2.5.2.3 Sextupole 2.5.2.3.1 Wide Sextupole Magnets (KS01-KS06) Number of magnets 28 Design symmetric Normal or super conducting nc T/m 2 Max. gradient 10.0 T/m 2 Min. gradient 1.0 Effective length, L m 0.688 Aperture radius mm 210 T/m 2 /s Max. ramp rate 0.34 Usable horizontal aperture mm ± 200 Usable vertical aperture mm ± 90 ± 5 × 10 -3 Integrated field error ∆ GL/GL at r =200 mm Tolerable harmonic b 4 Tolerable harmonic b 6 Tolerable harmonic b 8 Tolerable harmonic a 4 Tolerable harmonic a 6 10 -2 Magnet to magnet identity Overall length m 0.71 Overall width m 0.9 Overall height m 0.9 Yoke length m 0.6 Iron/copper weight t 1.13 / 0.27 Overall weight t 1.4 Number of turns per pole 4 x 8 Current at max field A 385 Voltage V 28 A/mm 2 Average current density 3.2 A/mm 2 Current density in conductor 4.4 10 -3 Field stability ∆ I/I Inductance per magnet mH 11.7 Resistance per magnet Ω 0.073 Power consumption kW 10.8 Coil copper cross section 10 x 10 mm ⋅ mm Cooling channel diameter. mm 4 Conductor insulation mm 0.5 Cooling water flow rate l/s 0.103 o C Cooling water temp. rise 25 bar Cooling water pressure drop 6.7 Time for polarity change s 60 Kalimovs 3D design February 2009 9 11 July 2012
2.5.2.5 Injection/Extraction 2.5.2.5.1. Injection Septum Magnet (CR04MPI) Name of the magnet Septum IS Number of magnets 1 Design pulsed, curved Max. Field T 0.85 Min. Field T 0.425 Bending angle mrad 125 Curvature radius, R m 16 Effective path length, L m 2.0 Useable horizontal aperture mm 160 Horizontal width mm 170 Useable vertical gap mm 140 Vertical pole gap height mm 150 Thickness of vacuum chamber mm 5 (rectangular shape)) Septum thickness (including screen and mm <20 vacuum chamber of 3 mm) 10 -3 Integral field quality relative Overall length m 2.3 Overall width m 0.381 Overall height m 0.463 Overall weight t 1.96 Current at max. field kA 6.4 Inductance mH 0.95 Resistance mOhm 9.8 Rise/fall time ms 100 Ramp rate T/s 8.5 High field flat top ms 5 Low field flat top ms 5 Cycle length s 1.5 Average power consumption kW 30 -100 ? Number of power supplies 1 Number of magnet in series 1 Maximum current rate kA/s 64 Driving voltage V Maximum voltage to ground V 62.2 Maximum active power kW 398.2 Water pressure bar 2.2 Water flow l/min 25.2 Water flow m/s Water temperature rise deg C 40 Time for polarity change s 60 10 11 July 2012
Recommend
More recommend