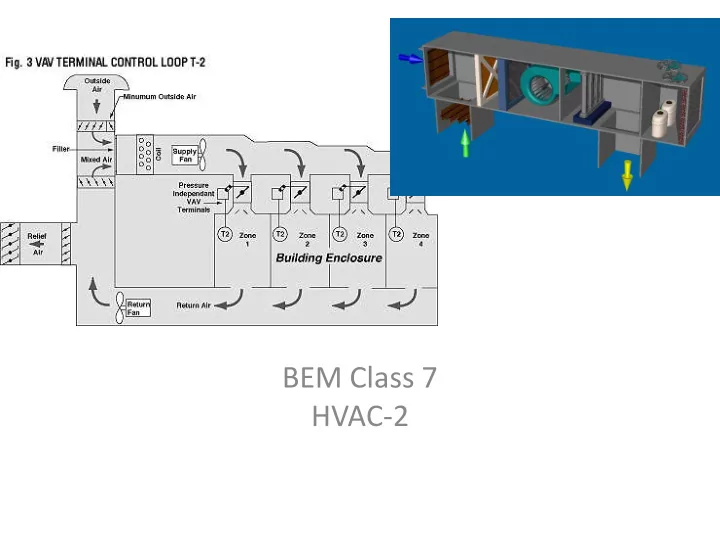

BEM Class 7 HVAC-2
Course adjustment • EnergyPlus (E+) - SIMERGY – http://simulationresearch.lbl.gov/projects/gui – http://simergy-beta.lbl.gov/ – Download please for use in class demo sessions (April classes)
Review from class 6 • Discussion: Principles for Zoning Exposures Usage types Schedule Tenancy & Metering On shared HVAC equipment
Review from class 6 • EQuest tutorial: what do you need to know to set up HVAC system in EQuest ? • How do you obtain this data? • How do you know if it’s right?
Review from class 6 HVAC systems and components Packaged assemblies – air-handling units, rooftop units
HVAC Equations Solving from Load to Flows Air Q BTUH = CFM x dT x .018 x 60 (.018 x 60 = 1.08) CFM = Q BTUH / (dT x 1.08) typ dT = 20 dF Water Q BTUH = GPM x dT x 8.33 x 60 (8.33 x 60 = 500) GPM = Q BTUH / (dT x 500) typ dT = 10 dF
HVAC Equations Solving from Flows to Power Fan HP = CFM x dP / (6356 x FE) dP is total pressure in inches of water column, Typ dP = 3 in w.c. FE (fan efficiency) typical value = .65 Pump (closed loop) HP = GPM x dP / (1715 x PE) dP is dynamic pressure created by pump in psi (for an open loop pump, dP is “lift” in feet of head and the conversion constant is 3956; 2.31 ft of head = 1 psi) PE (Pump Efficiency) typical value = .65 Convert Brake Horsepower to Electrical Power HP x .746 = KW
HVAC Component Characterization Pump & Fan Curves • Component performance model based on mfr (test) data • Plots output (flow) vs pressure • Dampers and valves also have curves – flow vs position
HVAC Component Characterization Part Load Factors – Boilers & Chillers • Efficiency vs Load • Boilers & Chillers lose efficiency at part-loads (with exception of most current generation of hi- efficiency equipment) • Most operation is at part- loads
HVAC Equipment Variables Constant vs Variable Volume – In CV systems, part-loads typically met by some form of simultaneous heating & cooling (eg – dual duct, re-heat) – Significant electrical savings in slowing down pumps or fans when possible • Dampers for variable air volumes delivered to rooms • Variable frequency drive controls on fans
HVAC Equipment Variables Outside Air control and Economizer • Minimum OA for ventilation when heating or cooling • Match OA to occupancy (DCV) • Maximize OA when cooler than RA (cooling)
New Construction vs Existing • ASHRAE “Appendix G” (90.1) – Models for comparison only to other models, not for projection of actual energy use • Why?
Model “Calibration” • Matching model results to metered data – How close a match? – What granularity? • How is model calibration done? – Tune individual parameters, such as….. – But which ones and how much? Multiple solutions….but only one actually matches conditions – Use of building data to inform
Recommend
More recommend