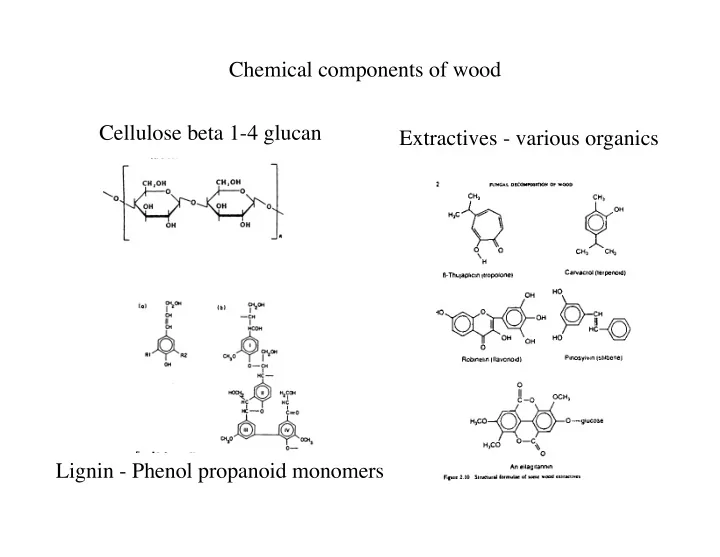

Chemical components of wood Cellulose beta 1-4 glucan Extractives - various organics Lignin - Phenol propanoid monomers
Straight from Wikipedia The three types of reaction catalyzed by cellulases:1. Breakage of the non-covalent interactions present in the crystalline structure of cellulose (endo-cellulase) 2. Hydrolysis of the individual cellulose fibers to break it into smaller sugars (exo-cellulase) 3. Hydrolysis of disaccharides and tetrasaccharides into glucose (beta-glucosidase).
Chemical components of wood Cellulose beta 1-4 glucan Extractives - various organics Lignin - Phenol propanoid monomers
A fuzzy image of lignin from Wikipedia
Wood X-section (hardwood) Wood X-section (conifer)
Distribution of water and nitrogen in wood
Chemical components of wood Cellulose beta 1-4 glucan Extractives - various organics Lignin - Phenol propanoid monomers
Why the CODIT theory is all wet thanks to Rayner and Boddy
Echinodontium tinctorium Indian paint fungus a fungus that enters branch stubs and waits for years to cause heartrot
Hypoxylon an Ascomycete that decays wood and colonizes endophytically
Diagram of Hypoxylon spore germination in response to bark exudates - work by Ignatio Chapella
Access from one individual tree to another Hymenochaete corrugata - the glue or the bondage fungus
Heartrots Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
Phellinus pini gr. red ring rot See this on the street side of Tolman Hall
The genus Phellinus (& Inonotus) has setae, and a brown hymenium
Ganoderma a common heartrot, white rot
Saprobes Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
Zone lines in wood cause by vegetative interactions between different genotypes of decay fungi
Wood endophytes like Hypoxylon get first dibs
Trichaptum
Saprobes & pathogens that can persist as sabrobes Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
edge of root disease center note progressively thinner crowns and shorter heights
Lion’s tailing A crown symptom caused by lack of expansion of shoot and lower needle retention
Tree failure, a symptom of root decay Heterobasidion annosum P-strain in action at Yosemite village
Recommend
More recommend