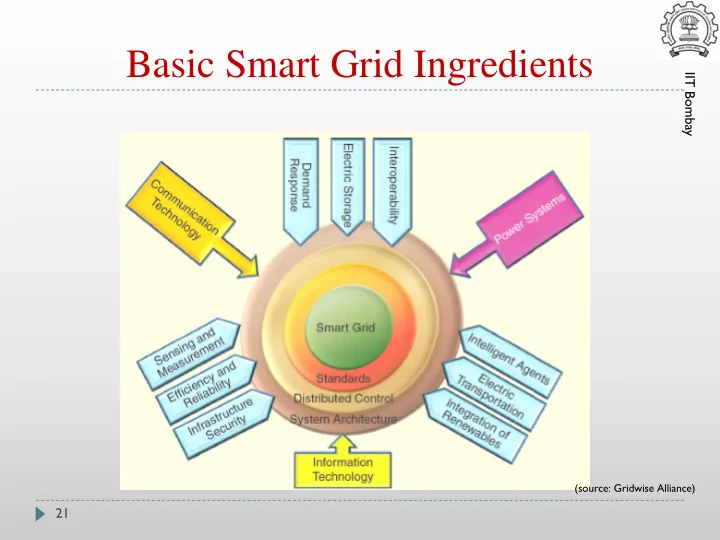

Basic Smart Grid Ingredients IIT Bombay (source: Gridwise Alliance) 21
Smart Grid Pyramid IIT Bombay (source: BC Hydro) 22
IEEE Smart Grid Conceptual Framework IIT Bombay The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Smart Grid Conceptual model provides a high level framework that defines seven important Smart Grid domains: Bulk Generation Transmission Distribution Customers Operations Markets Service Providers 23
Towards SmartGrid IIT Bombay Issues Drivers 2-way Connectivity with end Standardization consumer IT in distribution Customer service orientation Demand Side Management Power quality Outage Management Outlet Issues Distribution Franchises Loss reduction Multi agent Technology Theft control Asset management 24
Smart Grid- Distribution as a Key IIT Bombay 25
Demand Response IIT Bombay Demand response (DR) is form of dynamic demand mechanisms Providing electricity customers in both retail and wholesale electricity markets with a choice whereby they can respond to dynamic or time-based prices or other types of incentives by reducing and/or shifting usage, particularly during peak periods, such that these demand modifications can address issues such as pricing, reliability, emergency response, and infrastructure planning, operation, and deferral. Definition by the United States Demand Response Coordinating Committee (DRCC) In India- at transmission Level ABT based on frequency serves as DR Program 26
Smart Grid activities in India IIT Bombay Union Power Minister Launched India Smart Grid Forum on May 26, 2010 India Smart Grid Forum (ISGF) A non-profit voluntary consortium of public and private stakeholders with the prime objective of accelerating development of Smart Grid technologies in the Indian Power Sector Ten different working groups been constituted for Smart Grid study India Smart Grid Task Force (ISGTF) An inter ministerial group and will serve as Government’s focal point for activities related to “Smart Grid”. Ten different working groups been constituted for Smart Grid study Many Utilities have started their individual activities at different levels web-link: http://173.201.177.176/isgf/ 27
Smart Grid for India – Stakeholder Expectations IIT Bombay Customers: Expand access to electricity – “Power for All” Improve reliability of supply to all customers – no power cuts, no more DG sets and inverters! Improve quality of supply – no more voltage stabilizers! User friendly and transparent interface with utilities Utilities: Reduction of T&D losses in all utilities to 15% or below Peak load management Reduction in power purchase cost Better asset management Increased grid visibility Self healing Renewable integration Government & Regulators: Satisfied customers Financially sound utilities Tariff neutral system upgrade and modernization Reduction in emission intensity
Smart Grid Priorities for India Reduce T&D losses, No more power cuts, improve quality of supply, Prosumer enablement revenue cycle optimization Manage peak power, Integrate renewables / demand response, EV distributed generation proliferation efficiently
National Smart Grid Mission IIT Bombay Quality Power on Demand for All by 2027” Smart Grid Vision for India Transform the Indian power sector into a secure, adaptive, sustainable and digitally enabled ecosystem by 2027 that provides reliable and quality energy for all with active participation of stakeholders. National Smart Grid Mission is a proposal made by ISGF to Ministry of Power (budget- INR 31416 Cr for 2012- 2017) http://173.201.177.176/isgf/Download_files/Roadmap.pdf IIT -Bombay 30 09/11/2016
National Smart Grid Mission IIT Bombay Objectives: In order to achieve this vision, stakeholders will undertake: Smart Customer: • 1. Appropriate policies and programmes to provide access for electricity for all with life line supply (to be defined) by 2015, electrification of 100% households by 2020 and 24x7 quality supply on demand to all citizens by 2027. 2. Smart meter roll out for all customers by 2020 3. Tariff mechanisms, new energy products, energy options and programmes to encourage participation of customers in the energy markets that make them “prosumers” 4. Formulation of effective customer outreach and communication programmes for active involvement of consumers in the smart grid implementation. 31 IIT -Bombay 09/11/2016
National Smart Grid Mission IIT Bombay Smart Utilities: • 1. Enabling programmes and projects in distribution utilities to reduce AT&C losses to below 15% by 2017, below 12% by 2022, and below 10% by 2027; and in transmission utilities to reduce transmission losses to below 3% by 2017 and below 2% by 2022. 2. Development of reliable, secure and resilient grid supported by a strong communication infrastructure that enables greater visibility and control of efficient power flow between all sources of production and consumption by 2027. 3. Development of utility specific strategic roadmap for implementation of smart grid technologies across the utility by 2013. Required business process reengineering, change management and capacity building programmes to be initiated by 2014. 4. Integrated technology trials through a set of smart grid pilot projects by 2015; and rollout of smart grids in all urban areas (to be defined) by 2020 and nationwide by 2027. 5. Create an effective information exchange platform that can be shared by all market participants, including prosumers, in real time which will lead to the development of energy markets. 32 IIT -Bombay 09/11/2016
National Smart Grid Mission IIT Bombay Smart Policies: • 1. Formulation of policies and programmes by 2013, for mandatory demand response (DR) infrastructure for all customers with load above 1 MW by 2013, above 500 kW by 2015, above 100 kW by 2017 and above 20 kW by 2022. 2. Policies for DR ready appliances and public infrastructure including EV charging facilities by 2014. 3. Investment in research and development, training and capacity building programmes for creation of adequate resource pools for developing and implementing smart grid technologies in India as well as export of smart grid know- how, products and services. 4. Development of appropriate standards for smart grid development in India; and active involvement of Indian experts in international bodies engaged in smart grid standards development. 33 IIT -Bombay 09/11/2016
Pilot Projects IIT Bombay National smart grid mission Smart grid pilot project implementation aspects Pilot project at Bangalore, BESCOM Conclusion 34 09/11/2016
Smart Grid Pilot Implementation IIT Bombay Identify desired functionalities AMI Install intelligent smart meters Configure and Maintain the Metering System Obtain Meter Reading Data Manage Power Quality Data Manage Interference to Metering System Manage Tariff Settings on the Metering System Theft detection & control Home Display Unit Enable and Disable the Metering System IIT -Bombay 35 09/11/2016
Smart Grid Pilot Implementation IIT Bombay Smart Distribution Peak management Outage management AT & C loss Load Research Network Monitoring • Self healing IIT -Bombay 36 09/11/2016
Smart Grid Pilot Implementation IIT Bombay Demand Control Facilitate DSM measures Facilitate Demand Response Remote Connect / Disconnect Building / Home automation Interact with Appliances at the Premise Facilitate Demand Response Facilitate Energy Efficiency Measures IIT -Bombay 37 09/11/2016
Smart Grid Pilot Implementation IIT Bombay Renewable Integration Roof T op Solar – Grid tied Solar PV farm – Grid tie PEV Bay – Demo Charging Stations Grid Connectivity Two-way communication System for Smart Meters Power apparatus Distributed Resources HAN IIT -Bombay 38 09/11/2016
Smart Grid Pilot Implementation IIT Bombay Condition Based Maintenance Mobile Workforce Management Enterprise Application Integration Distribution Automation System R-APDRP Business Intelligence Analytics Decision Support Key Performance Indicator/Metrics Calculation Energy Accounting / Audit IIT -Bombay 39 09/11/2016
Pilot Projects for Distribution Smart Grid IIT Bombay 14 Pilots with following Smart Grid functionalities sanctioned: Automated Metering Infrastructure for residential and industrial consumers Outage Management System Peak Load Management System Power Quality Management System Micro Grid Integration Distributed Generation Integration for Roof Top Solar Panels Investment shall be around Rs 4 billion (US $ 80 million) with 50% funding from Govt. of India. These pilots will aim at integrating the consumer, operations and asset management domains of Distribution Sector to bring in efficiency and enhance reliability. Build business cases, policy and regulatory recommendations IIT -Bombay 40 09/11/2016
Recommend
More recommend