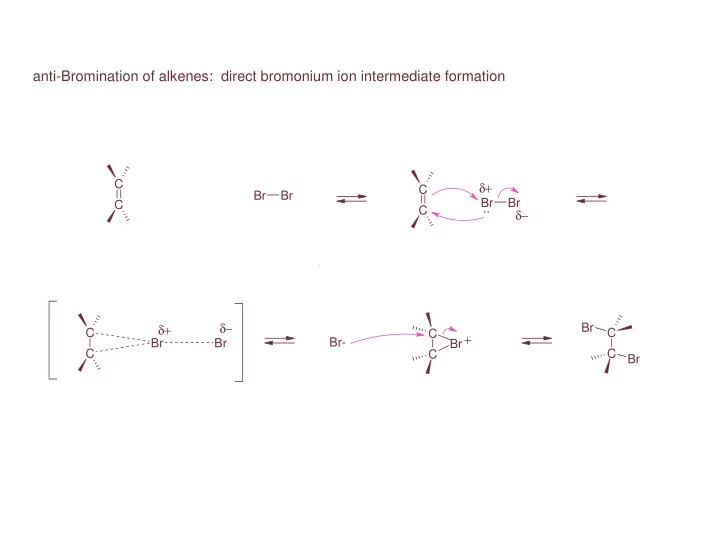

anti-Bromination of alkenes: direct bromonium ion intermediate formation C δ+ C Br Br Br Br C .. C δ− δ− δ+ Br C C C + Br Br Br- Br C C C Br
Orbital interactions in the anti-Bromination of alkenes: direct bromonium ion intermediate formation C C Br Br Br Br C C δ− δ+ Br C C C + Br- Br Br Br C C C Br
Alkyl substituents on the bromomium ion desymmetrize it: the more substitued carbon can bear more of the burden of the bromine’s positive charge: C δ+ C Br Br Br Br C .. C δ− H H H H δ+ δ− δ+ Br C C C Br- Br Br C C C Br H Br H δ+ H H H H So, the electrophilic Br ends up on the less substituted carbon and the nucleophilic Br ends up on the more substituted carbon.
This is a Markovnikov-like addition: when adding HCl, the electrophile (H) ends up on the less substituted carbon and the nucleophile (Cl) ends up on the more substituted carbon. Although the mechanism is different, the regiochemistry is not: Cl δ+ C C C + Cl- H Cl C C C δ− H H H H H H H H
Anti-addition of Cl 2 to trans -3-hexene Cl H Cl H H Cl Cl H H H Cl Cl H Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 H Cl H H Cl Cl H Cl H Cl Cl H H meso Anti-addition of Cl 2 to cis -3-hexene H Cl Cl Cl H H H Cl Cl 2 H CH 2 Cl 2 H Cl H H H Cl Cl Cl H enantiomers
Ozonolysis of alkenes aldehyde H H R O 1. O 3 H + R O H 2. Zn, H 2 O H ketone H 1 R mono 1 R formaldehyde R O 1. O 3 H + R O H 2. Zn, H 2 O 2 R ketone 2 R 1 tri R 1 aldehyde R R O 1. O 3 H + R O H 2. Zn, H 2 O H terminal di H 1 formaldehyde ketone R 1 R O 3 1. O 3 R R + R 3 R 2. Zn, H 2 O O aldehyde 2 R H 2 tetra H R R O 1. O 3 ketone H + R O H 2. Zn, H 2 O 2 R 2 internal di R ( E ) or ( Z ) aldehyde
It doesn’t matter if the alkene is a cycloalkene: O 1. O 3 2. Zn, H 2 O O H H H
Addition reactions of carbon-carbon double bonds Reaction Adds Regiochemistry Diastereoselective? Rearrangement observed? Hydrohalogenation H–X Markovnikov No Yes H–Br AntiMarkovnikov No No Hydration Acid-catalyzed Hydration H–OH Markonikov No Yes Oxymercuration- demercuration H–OH Markovnikov No No Borohydration- oxidation H–OH AntiMarkovnikov Yes - syn No Hydrogenation H–H -- Yes - syn No * Halogenation X–X -- Yes - anti No Halohydroxylation X–OH Markovnikov Yes - anti No Dihydroxylation Epoxidation- acid hydroylsis HO–OH -- Yes - anti No * OsO 4 HO–OH -- Yes - syn No Oxidative cleavage O + O -- No No
Recommend
More recommend