Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Air pollution - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
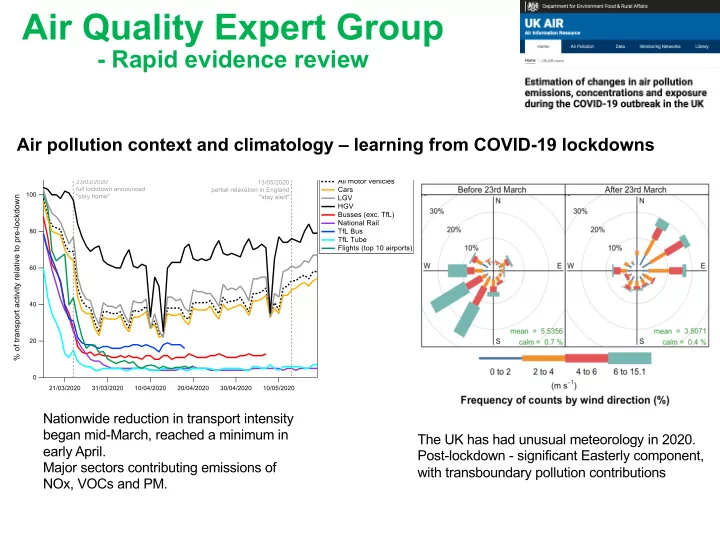
Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Air pollution context and climatology learning from COVID-19 lockdowns Nationwide reduction in transport intensity began mid-March, reached a minimum in The UK has had unusual meteorology in
Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Air pollution context and climatology – learning from COVID-19 lockdowns Nationwide reduction in transport intensity began mid-March, reached a minimum in The UK has had unusual meteorology in 2020. early April. Post-lockdown - significant Easterly component, Major sectors contributing emissions of with transboundary pollution contributions NOx, VOCs and PM.
Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Significant reductions seen UK-wide in NOx and NO 2 Top : Raw data from 225 air quality measurement sites across the UK. Bottom : Same data but corrected to account for meteorological variability Reproduced from Marner, B., Air Quality Consultants , 2020.
Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Changes in PM 2.5 are more complex to quantify Business as usual 2020 actual Compared to 2019, PM 2.5 higher during lockdown - due to Easterly weather o But using computer models, PM 2.5 has been lower in many places compared to a o business-as-usual scenario. Highlights significant AQ influence of wider European emissions. o Reproduced from: Keller C. and Evans, M.J., University of York and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center , 2020.
Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Exposure to pollution depends where you live, work and how you commute Less commuting reduces exposure in London, but could be offset by higher o indoor pollution, for example from additional cooking. Reproduced from: Williams, M., on behalf of the Environmental Research Group, King’s College London , 2020.
Air Quality Expert Group - Rapid evidence review Lower NOx emissions in isolation can lead to local increases in ozone Forecasts of a Springtime ozone case study under COVID-19 emissions Business as usual Lower NOx Lower NOx & VOC Forecasts of a summertime ozone case study under COVID-19 emissions 10% lower NOx 30% lower NOx 50% lower NOx Emphasizes the importance of managing all the key pollutants together with coherent o strategy that recognizes the chemical interconnections Reproduced from: Agnew, P., et al. Met Office , 2020 and Fakes, L. and Evans, M.J., NCAS / University of York , 2020.
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.























