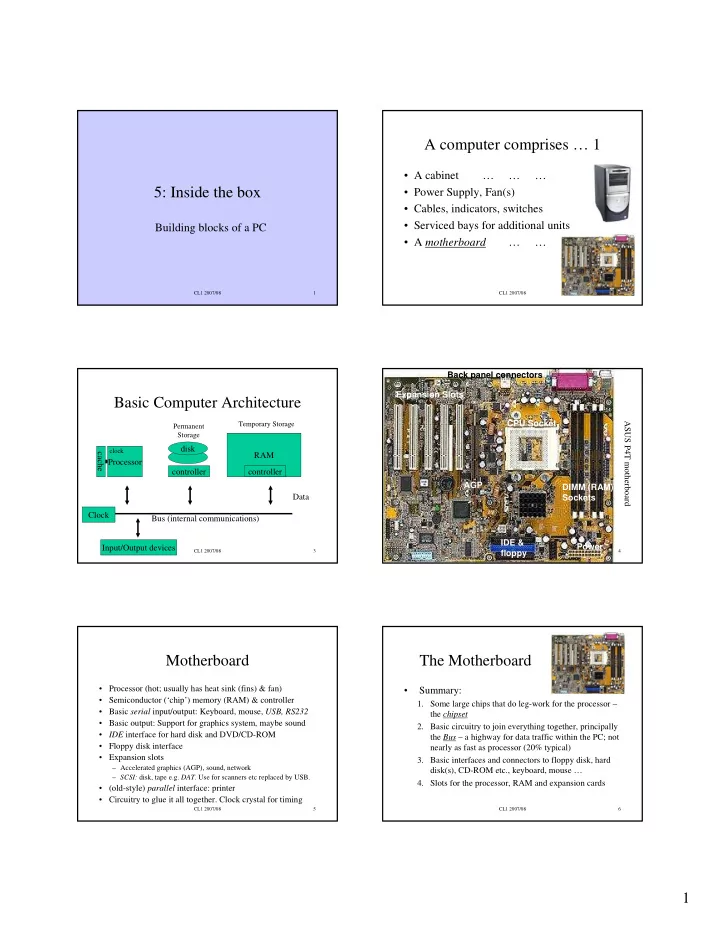

A computer comprises … 1 • A cabinet … … … 5: Inside the box • Power Supply, Fan(s) • Cables, indicators, switches • Serviced bays for additional units Building blocks of a PC • A motherboard … … CL1 2007/08 1 CL1 2007/08 2 Back panel connectors Expansion Slots Basic Computer Architecture CPU Socket Temporary Storage ASUS P4T motherboard Permanent Storage disk clock cache RAM Processor controller controller AGP DIMM (RAM) Data Sockets Clock Bus (internal communications) IDE & Power Input/Output devices CL1 2007/08 3 CL1 2007/08 4 floppy Motherboard The Motherboard • Processor (hot; usually has heat sink (fins) & fan) • Summary: • Semiconductor (‘chip’) memory (RAM) & controller 1. Some large chips that do leg-work for the processor – • Basic serial input/output: Keyboard, mouse, USB, RS232 the chipset • Basic output: Support for graphics system, maybe sound 2. Basic circuitry to join everything together, principally • IDE interface for hard disk and DVD/CD-ROM the Bus – a highway for data traffic within the PC; not • Floppy disk interface nearly as fast as processor (20% typical) • Expansion slots 3. Basic interfaces and connectors to floppy disk, hard – Accelerated graphics (AGP), sound, network disk(s), CD-ROM etc., keyboard, mouse … – SCSI: disk, tape e.g. DAT. Use for scanners etc replaced by USB. 4. Slots for the processor, RAM and expansion cards • (old-style) parallel interface: printer • Circuitry to glue it all together. Clock crystal for timing CL1 2007/08 5 CL1 2007/08 6 1
The Processor RAM memory • Performs most but not all computation and control • “2 Gigabytes of Random Access Memory” (Graphics chips are also complex) • Semiconductor; SIMMs, DIMMs etc. • Much faster than other components • Computer’s ‘notepad’: volatile - contents lost • Clever design needed to achieve speed when switched off – Cache is a small store of ultra-fast memory within the • Unless you are doing heavy number crunching or chip, a sort of scratch-pad serious graphics, adding memory will improve – Parallelism – doing many operations simultaneously performance more than anything else – Pipeline – fetch data or perform calculations that might • Also occurs as video RAM and cache be needed later, discarding them if not. CL1 2007/08 7 CL1 2007/08 8 Cacheing (real world) Cacheing on read Slow storage No cache: Fetch item 1 st time (slow) • You have to phone a list of people from a Processing entity Fetch item 2 nd time (slow) mobile phone • In each case, 1 st time you have to look up With cache: Fetch item 1 st time from storage (slow) number from Directory Enquiries Processing Keep copy • If you need to redial you use ‘recent dialled’ entity number in phone memory (or quickly learn Fetch item 2 nd and subsequent to write numbers down for later use) times from (fast) cache • This is a cache Processors cache instructions and data; Operating system caches disk pages; Web browsers cache bits of Web pages. CL1 2007/08 9 CL1 2007/08 10 (Cacheing on write) The Processor Slow storage No cache: Writes item 1 st time Processing • “Intel Pentium 4, 3.4GHz” Writes item 2nd time entity • Two major PC processor manufacturers left: Intel Reads it back (when required) (Pentium … ) vs AMD (Athlon …) With cache: Writes item 1 st time • Also G3, G4 (IBM, Mac); SPARC (Sun) Processing Writes item 2nd time • The last 20% of clock speed doubles the cost of the entity Keeps copy Writes back to disk processor and gets you 4-5 months future-proofing (i.e. periodically Reads it back from cache before the technology is overtaken) • Processor development and manufacture costs $billions (Disk cacheing) Cache may not be written back to disk immediately. This is why you don’t want to just switch off a PC - disk may not be consistent. CL1 2007/08 11 CL1 2007/08 12 2
Hard disc The big con • PC clock speed (e.g. 3.4 GHz) is always quoted but is an incomplete indication of performance • “300 Gb 7200 RPM SCSI drive” • Performance depends on a chain of factors and on how • 300 Gb (Gigabytes) is the disk capacity the computer is used • 7200 RPM indicates the rotational speed of the disk; • Performance depends on Processor speed + amount of more is better. Seek time is a measure of how fast the Cache + speed of motherboard + Memory speed + Disk disk head can move across the disk; short time is speed + graphics speed better. • Processor spends most of its time idle. • SCSI is the Small Computer Systems Interface used in • Processor activity governed by ticks of a very fast clock many computer disks; alternative is IDE (PCs, Macs) • MHz, GHz: MegaHertz, GigaHertz – measures of (clock) frequency CL1 2007/08 13 CL1 2007/08 14 CD/DVD Graphics • “12x DVD; 40r16w12rw DVD/CD-ROM” • “PCI-Express accelerated graphics card” • Drive can read CDs and DVDs and write CD-R (write • If you’re a gamer the graphics card may be once) and CD-RW (rewritable) disks. Speeds refer. the most important aspect of the PC • DVD is taking over from CD; 12x is an indication of speed; more is better • CD-ROM media have a capacity of around 650 Mb • DVD media capacity depends on no. of layers – 1 layer, 1 side: 4.7 Gb – 2 layer, 2 side: 17 Gb CL1 2007/08 15 CL1 2007/08 16 Monitor Hardware options • “17" FST monitor, 0.28 mm, 1280*1024” • Sound card, microphone • 17” is the diagonal size of the tube; visible part is • Network Card usually rather less. FST = Flatter Squarer Tube • Accelerated graphics • (0.28 mm is the dot pitch; smaller is better) • Video capture card • 1280*1024 is the screen resolution in pixels • High performance disk interface (e.g. SCSI ) – About 4:3 aspect ratio (like a TV) • TV tuner? Etc. etc. • LCD screens: big laptop screens with backlight • Trend is to put intelligence in peripherals attached – Some widescreen; overlap with HD TVs via fast interfaces such as USB CL1 2007/08 17 CL1 2007/08 18 3
Connectors Connectors - diagrams RJ45 PS/2 mouse, (Ethernet) keyboard PS/2 mouse, keyboard USB (General purpose) S-VGA RS-232 S-VGA USB (Monitor) CL1 2007/08 19 CL1 2007/08 20 Systems in a nutshell Unix, Linux • Operating system is the software you need to • First there was Unix (1970s) run your applications (Office, Web browser) … • Solaris, HP-UX, AIX: proprietary versions of Unix • Windows utterly dominates business world • Linux (Linus Torvalds), Richard Stallman: version of Unix – Software ‘Source’ free (distributions at low cost) • Windows (3.1 … 98.. Me) / XP-home: home – Free Software Foundation - GNU • Windows NT / 2000 / XP-Pro, Vista: corporate, – Many thousands of people producing Linux software specialist – Secure, reliable but user interface ‘clunkier’ – Some ‘killer apps’ missing (Office, Photoshop) • Mac – Specialist, especially multimedia, • Windows: for ‘vanilla’ office desktop IT collaboration, art, design, architecture. More • Unix for ‘back office’, infrastructure, anything home-grown user friendly, stylish. Now Unix-based or specialised. • All this IMHO . Beware religious wars CL1 2007/08 21 CL1 2007/08 22 A computer is like a Banana Key Points • It is perishable – write-down 2-3 years • Major units of a small computer and how they work together • So is this kind of information • Design tricks for performance • To keep up to date read PC magazines, manufacturer catalogues & web pages, trade – Cache, pipeline, parallelism papers etc. • PC raw speed is not the whole story • From CL1 point of view, terms here are • Characteristics of the principal operating systems illustrations of principles • A few things to consider when buying a PC CL1 2007/08 23 CL1 2007/08 24 4
Recommend
More recommend